A high-efficiency identification method for salt tolerance of cotton germplasm
An identification method and technology of salt tolerance, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of time-consuming and laborious identification of salt ponds, unfavorable identification of germplasm resources, and failure to consider the difference in the weight of different types of indicators.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1: build the material of standard equation
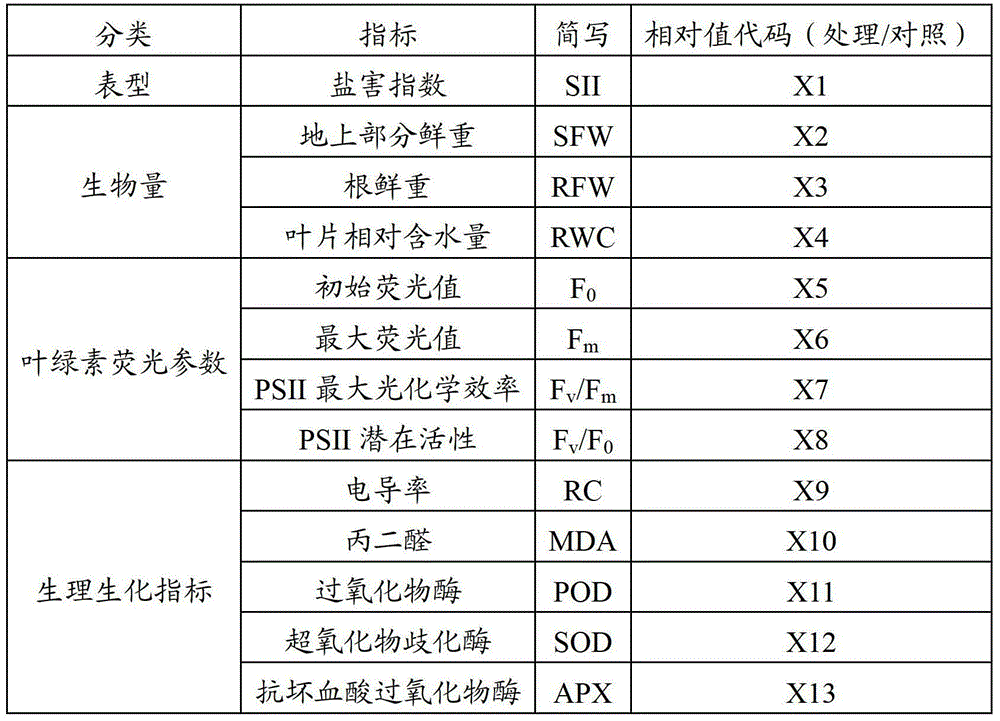
[0021] We selected two salt-tolerant germplasm resources and two salt-sensitive germplasm resources identified by us over the years, see Table 1 for details. The seedling raising method is to cultivate cotton seedlings to the three-leaf and one-heart stage by using the pot soil seedling cultivation method, and select materials with normal and consistent growth for salt stress treatment. The mass concentration of NaCl solution used for the treatment is 0.04g / mL, and the treatment time is 72h. The whole plant was used to calculate the salt damage index, and then the second true leaf was selected to measure the other 12 indexes related to the salt tolerance of the plant except the salt damage index. Another same amount of control material was planted and treated with 150mL of water.
[0022] Table 1 Materials used to construct the standard equation
[0023] Germplasm name
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: construct the index that standard equation needs to measure
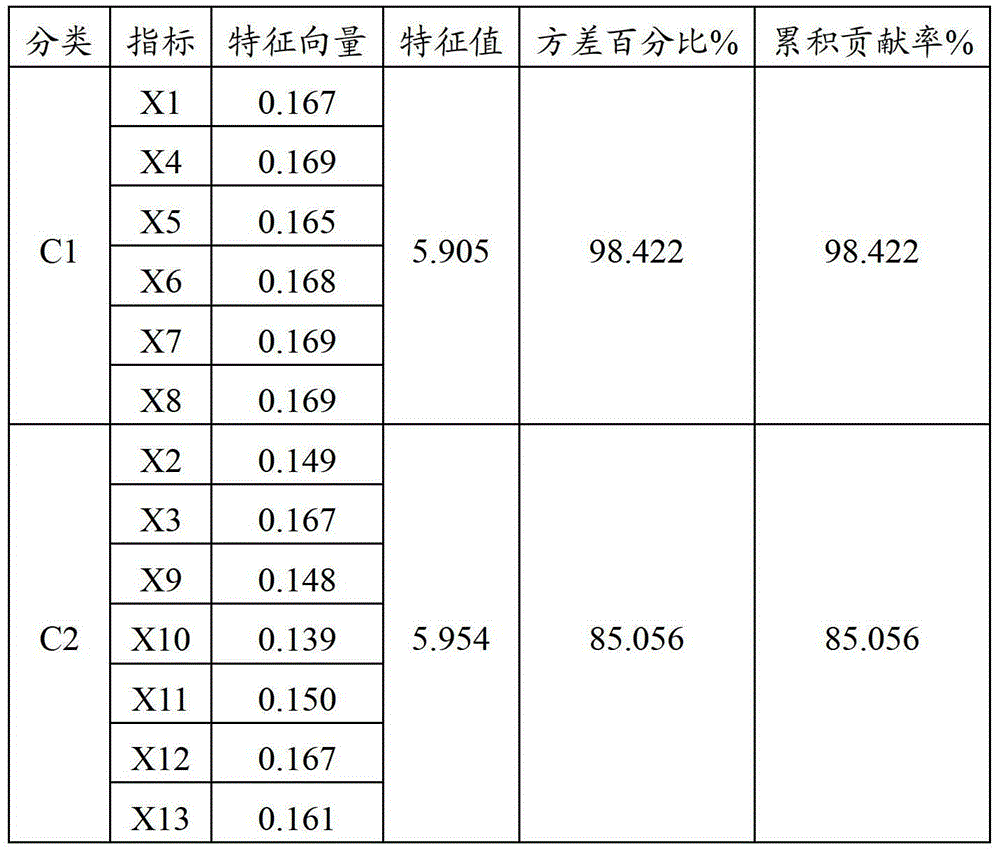
[0025] The 13 indicators related to plant salt tolerance were identified as the raw data for constructing the standard equation of salt tolerance index, see Table 2 for details. These include the salt damage index, 3 biomass indicators, 4 chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, and 5 physiological and biochemical indicators.
[0026]Table 2 The indicators used to construct the standard equation
[0027]
[0028] Note: Since the control was not subjected to salt damage, the salt damage index only counts the plants treated with salt; F V is the variable fluorescence value, F V =F m -F 0
Embodiment 3
[0029] Embodiment 3: membership function conversion
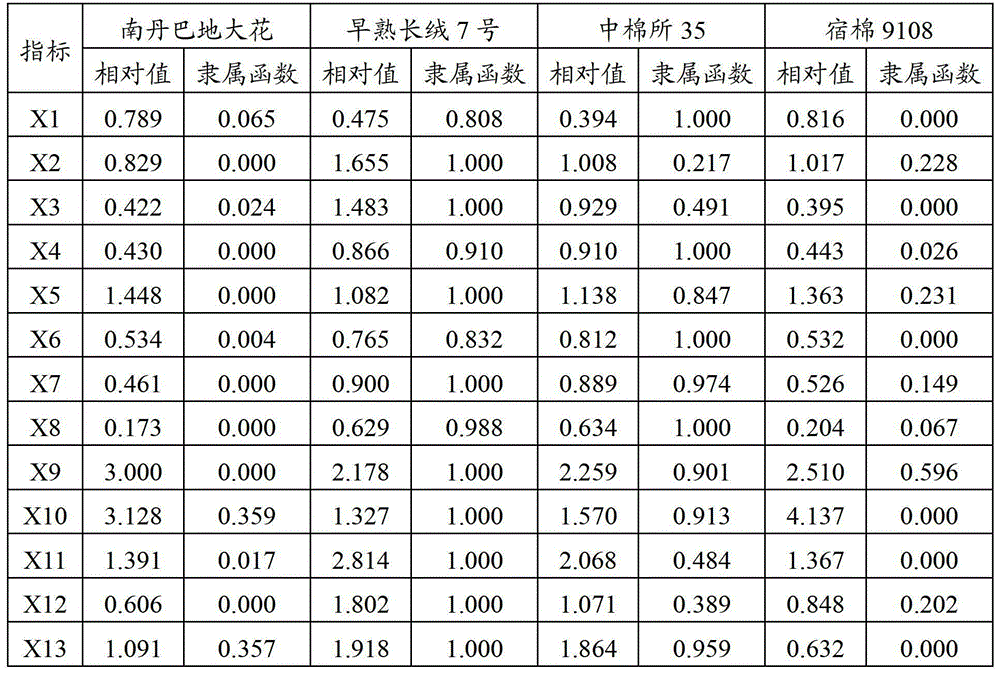
[0030] The relative values of all the above indicators were obtained through the relative value formula of the indicators. In order to realize the non-dimensionalization of all data, the membership function values were calculated. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0031] Wherein, the index relative value formula is: relative value=the average value of the salt treatment value / the average value of the control;
[0032] If a certain index is negatively correlated with salt tolerance, the membership function value X is calculated using the method of fuzzy mathematics membership function value (ij) , the formula is: X (ij) =(X ij -X jmin ) / (X jmax -X jmin ),
[0033] where X (ij) Indicates the membership value of i germplasm j index; X ij Indicates the measured value of j index of germplasm i; X jmax 、X jmin are the maximum and minimum values of j index of germplasm i, respectively.
[0034] If an index is po...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com