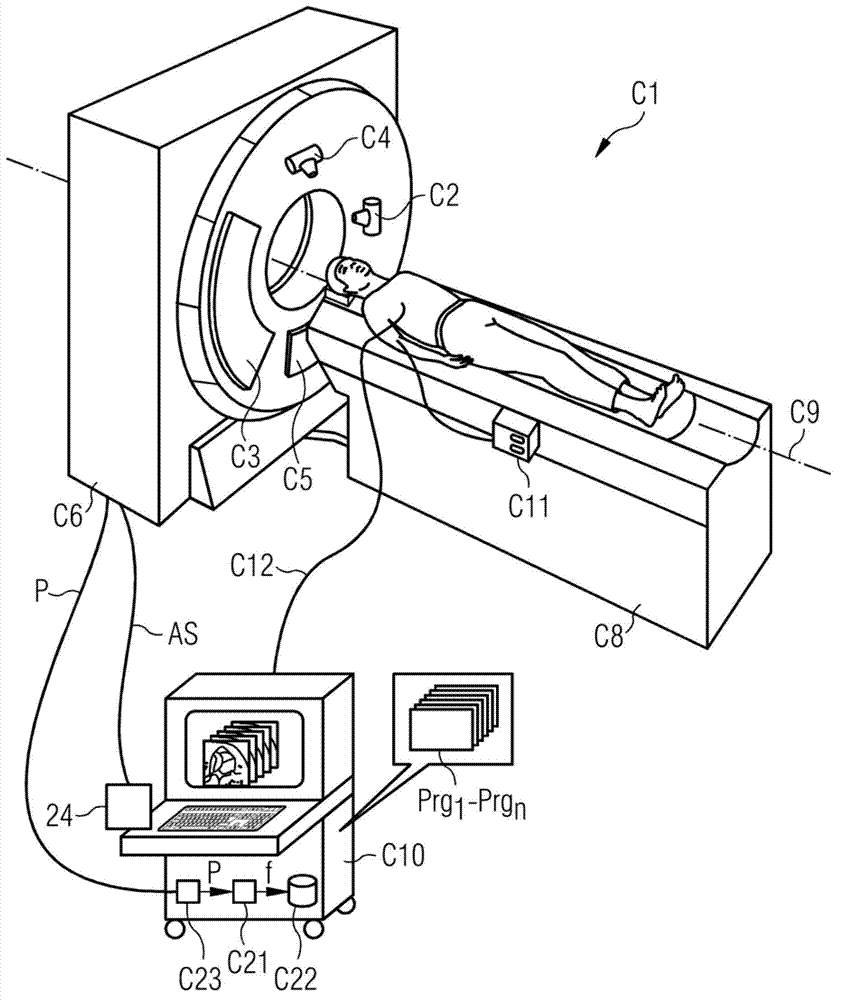
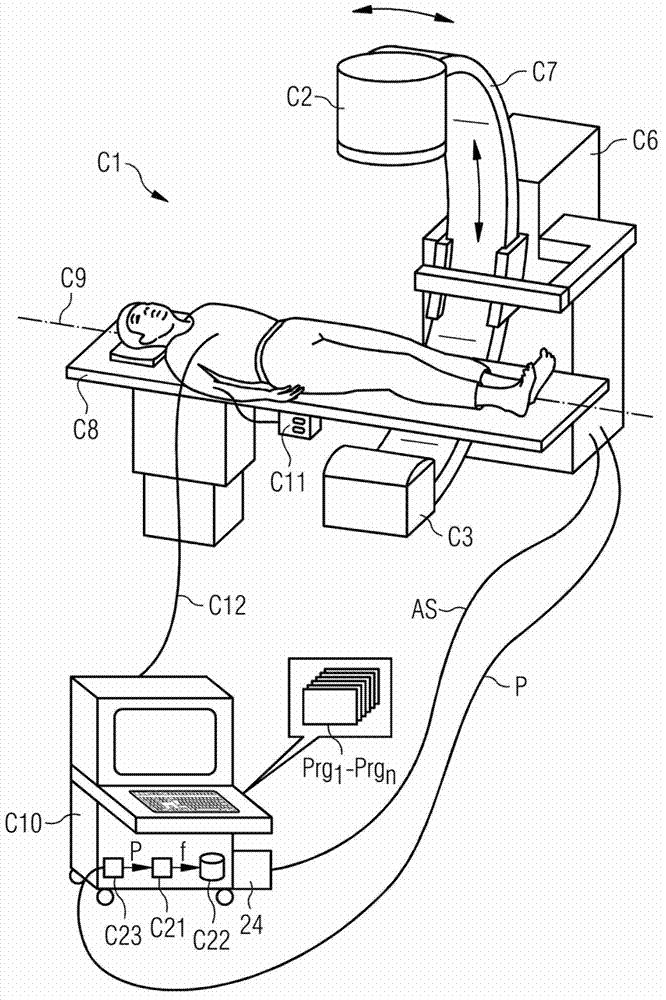
Method for iterative image reconstruction for bi-modal CT data
An iterative algorithm, image data technology, applied in 2D image generation, image analysis, image generation and other directions, can solve the problem of not being adopted
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0088] Example 1: Dual Energy Measurement
[0089] The purpose of dual energy measurements is usually to enable material partitioning. For example, iodine and bone can be distinguished in this way. Small noise simplifies the calculation of material decomposition. For this reason, CT images are usually reconstructed with soft convolution kernels, which result in low-noise images. However these smooth images have extremely limited spatial resolution. This leads to an incorrect assignment of image points to substances in some image regions. It is therefore desirable to improve the contrast-to-noise ratio of the image in order to enable error-free substance segmentation.
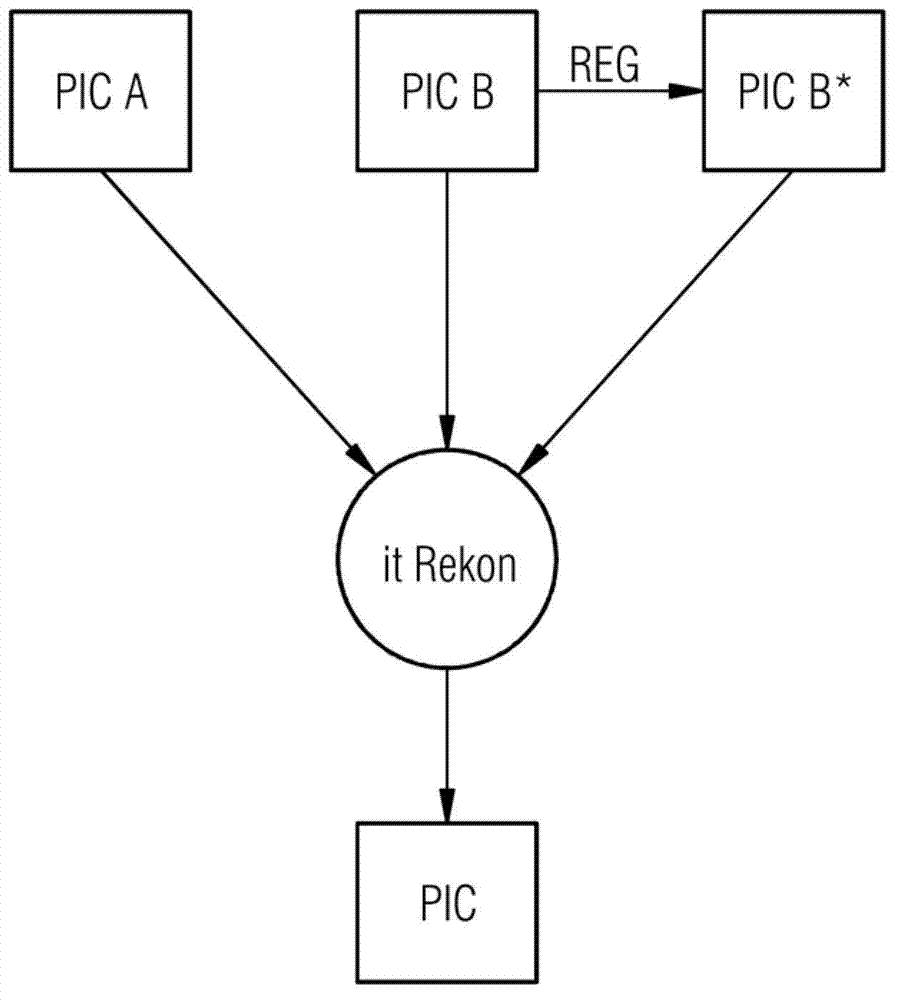
[0090] Two CT images are presented after the dual source CT measurement and the first image reconstruction, the first with respect to the first tube voltage (eg 80 kV) and the second with respect to the second tube voltage (eg 140 kV). For image PIC A, only the image of the first tube voltage is considered ...
example 2
[0093] Example 2: High-resolution-CT measurement
[0094] CT measurements of standard bores with detector channels are performed, as well as measurements and high-resolution measurements with reduced bores. Such a reduction of the detector aperture makes it possible to obtain spatially high-resolution images. CT images are reconstructed from the two measurements. In contrast to high-resolution measurements in standard measurements, limited positional resolution is present, but a better signal-to-noise ratio because quanta are lost through the reduced aperture.
[0095] Use high resolution measurements for image PIC A and standard measurements for image PIC B. The iterative image reconstruction according to formula (1) results in a high-resolution image with reduced noise.
example 3
[0096] Example 3: Perfusion measurements, especially cardiac perfusion measurements
[0097] After administration of the contrast agent, CT measurement data are acquired at successive times, and a series of temporally successive images, ie images in a plurality of so-called time frames, are reconstructed accordingly. In order to save dose, the measurement is performed with a not too high X-ray intensity. The image thus has noise.
[0098] One of this single image is used as image PIC A; it is temporally high resolution, but has a poor signal-to-noise ratio due to the aforementioned dose savings. As image PIC B, a (possibly weighted) sum is formed from several or all images of the series; this sum image has a high signal-to-noise ratio due to the statistical independence of the individual images. The iterative image reconstruction according to formula (1) results in a temporally high-resolution image with a good signal-to-noise ratio.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com