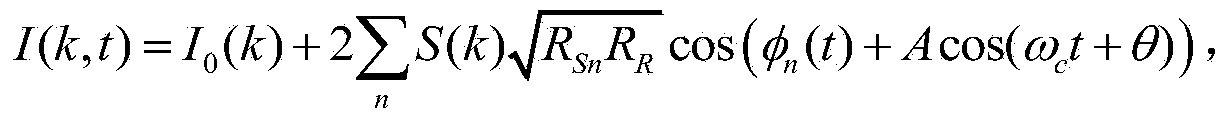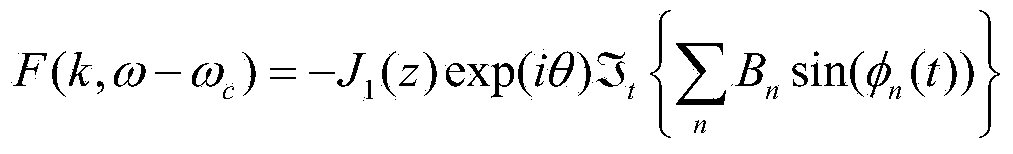Full-range Fourier-domain Doppler optical coherence tomography method
An optical coherence tomography and Doppler optics technology, which is applied in the field of full-depth frequency-domain Doppler optical coherence tomography, can solve the problems of increasing the acquisition time of interference signals, increasing the complexity of experimental devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the embodiments and accompanying drawings, but the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited thereby.
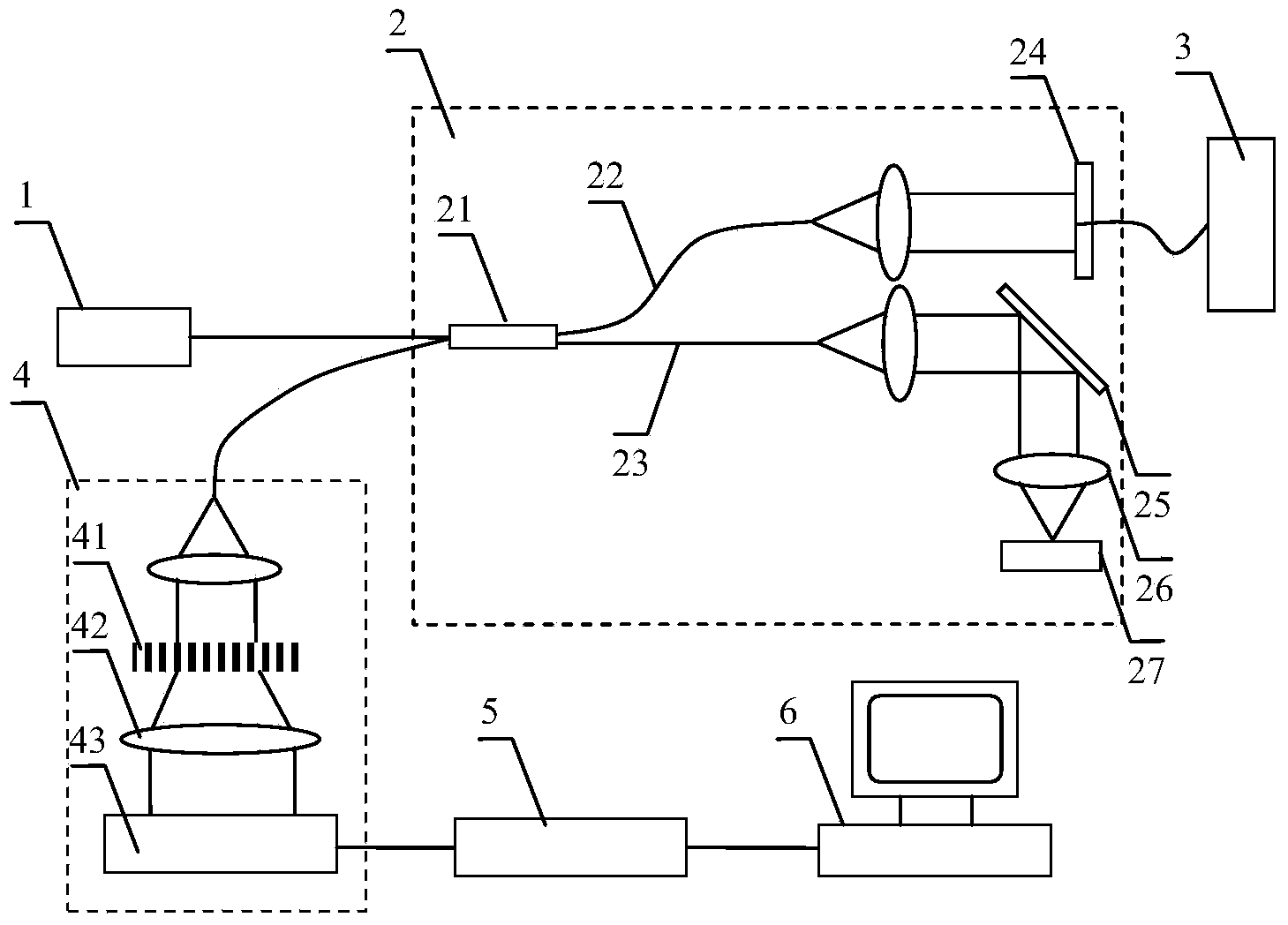
[0049] see figure 1 , figure 1 Schematic diagram of the structure of the optical fiber complex frequency domain optical coherence tomography system used in the method of the present invention. The optical fiber complex frequency domain optical coherence tomography system includes a low-coherence light source 1, a Michelson interferometer 2 is placed in the direction of the output beam of the low-coherence light source, and the beam splitter 21 of the Michelson interferometer divides the incident light into a reference arm optical path 22 and the sample arm optical path 23, the end of the reference arm optical path is a reference mirror 24, and in the sample arm optical path along the direction of light beam incidence, there are two-dimensional scanning galvanometer 25, foc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com