Quantization method of light space distribution of crop population
A technology of spatial distribution and quantitative method, which is applied in the field of agricultural planting, can solve problems such as large deviations, errors, and inability to accurately describe the characteristics of spatial distribution, and achieve the effect of convenient moving distance and convenient testing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] The test was carried out in Anyang City, Henan Province (36°06′N, 114°21′E) in 2011 and 2012 at the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. The test cotton variety was Lumianyan 28, and six different planting Density of cotton population, respectively 15000, 33000, 51000, 69000, 87000, 105000 plants / hm 2 ;The experiment adopts random block design, repeats 4 times, and the area of each plot is 66.6m 2 , row spacing is 0.80m, 20 rows for each plot. The 2011 planting time is April 20, and the 2012 planting time is April 22.
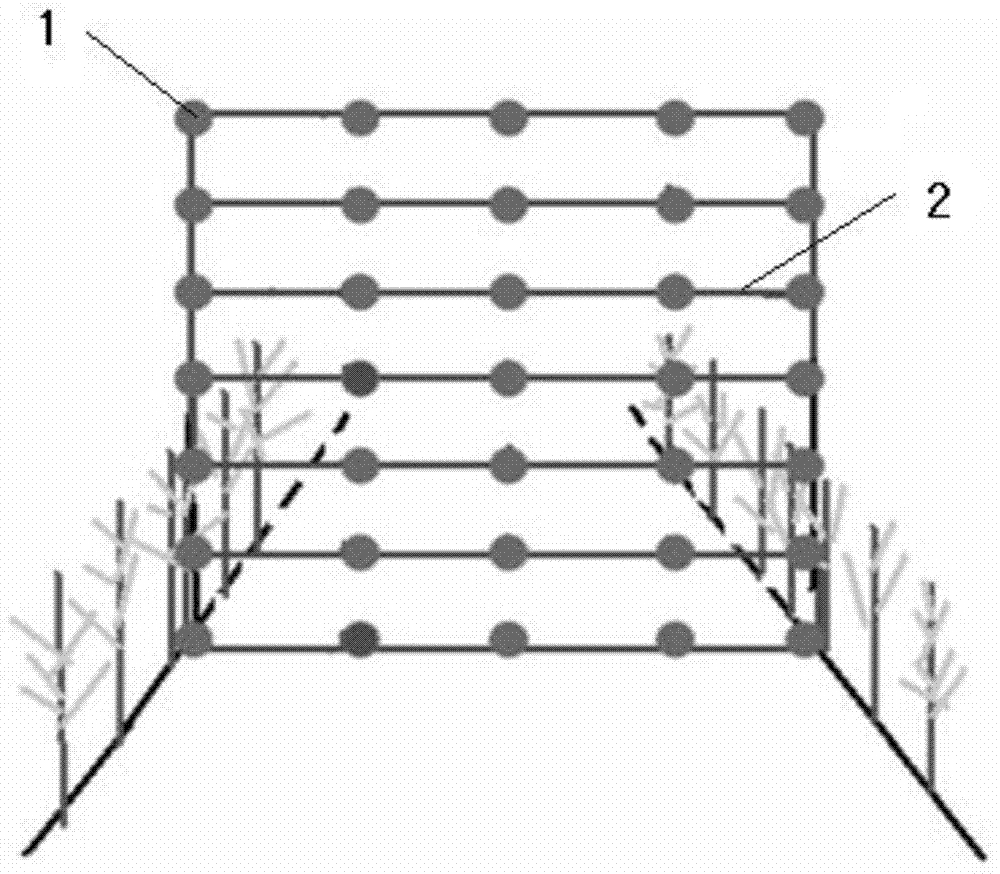
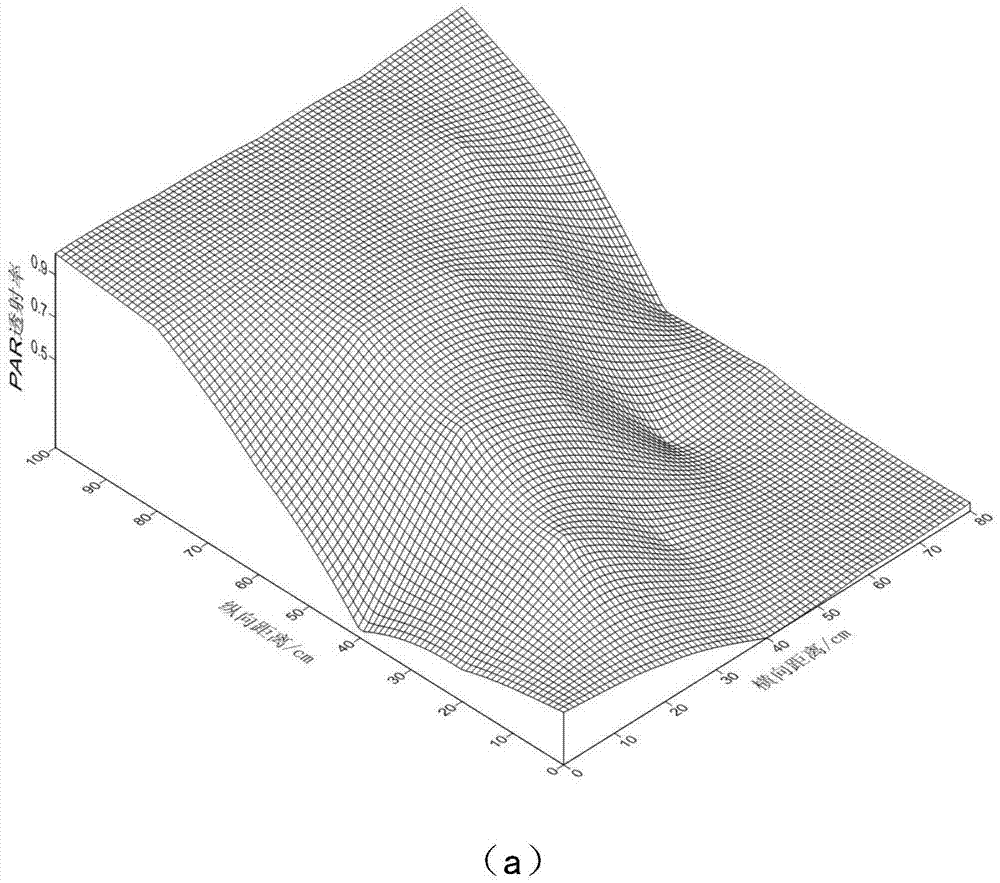
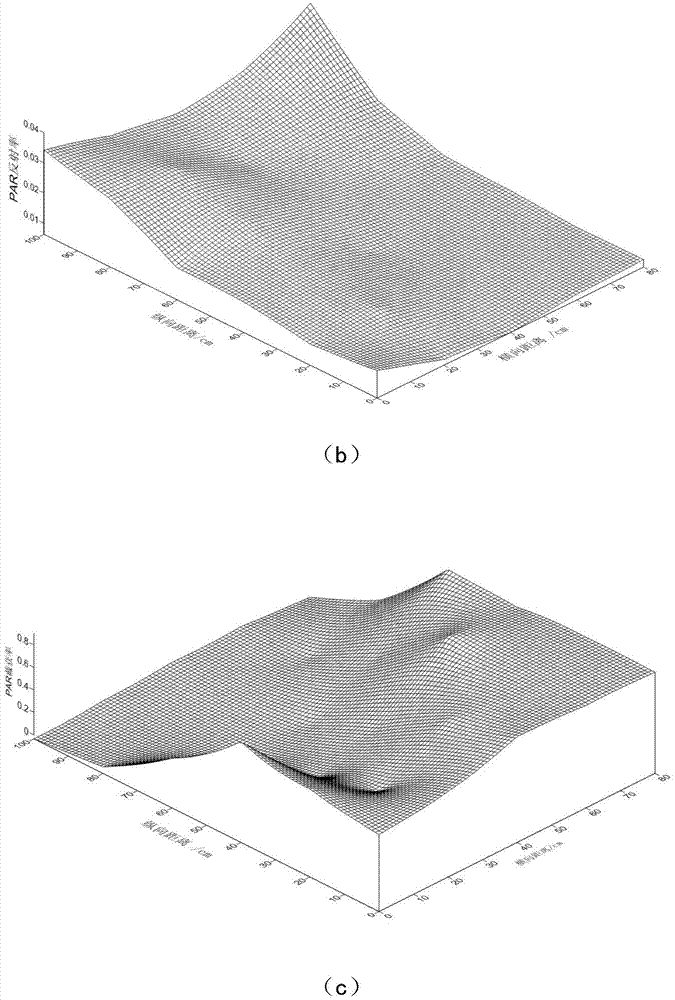
[0046] Photosynthetically active radiation PAR data collection uses the principle of spatial statistics. Firstly, the sampling method of spatial grid method is used to select 2 representative cotton rows in each density group, and a test frame is placed in the longitudinal section area between the cotton rows to measure each The PAR value of the test point: the probe is horizontally upward to measure the transmis...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Cotton group photosynthetically active radiation PAR data collection method and group PAR transmittance, PAR reflectance calculation method are the same as embodiment 1; the difference is that the present embodiment 2 selects 9 cotton varieties and new lines with different plant types, which are respectively cotton Institute 79, China Cotton Institute 60, Lumian 28, Ji 228, Ji 958, ZM3799, ZM120, ZM113, DG002 constructed 9 different types of cotton populations by using 9 different cotton varieties. The test was carried out in Anyang City, Henan Province (36°06′N, 114°21′E) in 2012 at the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and the design test planting density was 90,000 plants / hm 2 , the row spacing is 0.8m and other row settings, the sowing period is April 22, the plot is 10 rows, the row length is 8m, the width is 0.8m, and the plot area is 64.0㎡. For different cotton populations constructed with different plant types (lines), qu...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Cotton population photosynthetically active radiation PAR data collection method and population PAR transmittance, PAR reflectance calculation method are the same as in Example 1, the difference is that this embodiment 3 selects a cotton variety Zhongmian Institute 79, adopts different row spacing configurations, Constructed 6 different cotton populations, 6 different row spacing configurations are: 80cm equal row spacing planting and 90cm+20cm, 90cm+10cm, 80cm+20cm, 80cm+10cm, 70cm+20cm and other 5 wide and narrow row double row configuration mode. The experiment was carried out in 2012 in Anyang City, Henan Province (36°06′N, 114°21′E) at the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. The field sowing period is April 22, the plot is 8m long, 8m wide, and the planting density is 90,000 plants / hm 2 . Quantify the light energy distribution of six cotton populations constructed with different plant row spacing configurations, and provide ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com