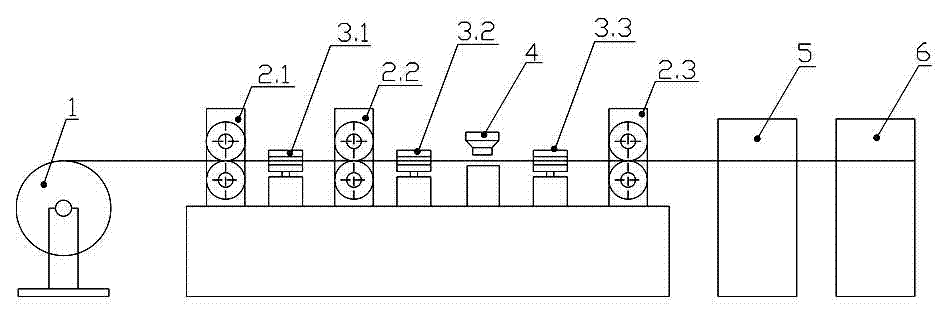
A kind of high-tin silver-based welding rod
A welding rod and silver-based technology, applied in the direction of welding medium, welding equipment, welding/cutting medium/material, etc., can solve the problems of deterioration of solder processing performance, unsatisfactory, high-tin-silver solder cannot be made into welding rods, etc., to meet the welding requirements Production process requirements, easy operation, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment 1: Preparation of Ag29Cu35Zn30Sn6 electrode
[0020] The first step is to atomize tin (Sn) and copper (Cu) with a lower melting point into alloy powder according to the weight ratio of Cu20 and Sn80;
[0021] The second step is to melt the alloy ingot according to the percentage ratio of silver (Ag): 31.5%, copper (Cu): 35.9%, zinc (Zn): 32.6%:
[0022] 1. Melt copper in an intermediate frequency furnace, add silver when the temperature reaches 1150~1200°C, and cover it with a compound salt prepared with dehydrated borax and boric anhydride in a weight ratio of 7:3 after fully melting; reduce the temperature of the molten metal to 950~1000°C ℃, add zinc;
[0023] 2. After the zinc is fully fused, the metal solution is allowed to stand still for 30-60 minutes and then poured into an ingot with an outer diameter of 90mm;
[0024] The third step is to remove the outer skin of the cast ingot and perform homogenization annealing in a box-type resistance furnac...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: Preparation of Ag44Cu26Zn23Sn7 electrode
[0029] The first step, with embodiment 1;
[0030] The second step is to melt the alloy ingot according to the percentage ratio of silver (Ag): 48.2%, copper (Cu): 26.6%, zinc (Zn): 25.2%:
[0031] 1. Melt copper in an intermediate frequency furnace, add silver when the temperature reaches 1150~1200°C, and cover it with a compound salt prepared with dehydrated borax and boric anhydride in a weight ratio of 7:3 after fully melting; reduce the temperature of the molten metal to 950~1000°C ℃, add zinc;
[0032] 2. After the zinc is fully fused, the metal solution is allowed to stand still for 30-60 minutes and then poured into an ingot with an outer diameter of 90mm;
[0033] The third step to the fifth step are the same as in Embodiment 1.
example 3
[0034] Example 3: Preparation of Ag55Cu21Zn16Sn8 electrode:
[0035] The first step, with embodiment 1;
[0036] The second step is to melt the alloy ingot according to the percentage ratio of silver (Ag): 61.1%, copper (Cu): 21.2%, zinc (Zn): 17.8%:
[0037] 1. Melt copper in an intermediate frequency furnace, add silver when the temperature reaches 1150~1200°C, and cover it with a compound salt prepared with dehydrated borax and boric anhydride in a weight ratio of 7:3 after fully melting; reduce the temperature of the molten metal to 950~1000°C ℃, add zinc;
[0038] 2. After the zinc is fully fused, the metal solution is allowed to stand still for 30-60 minutes and then poured into an ingot with an outer diameter of 90 mm;
[0039] The third step to the fifth step are the same as in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com