Processing method for producing aerated concrete building block from fly ash
A technology of aerated concrete and processing methods, which can be applied in applications, household appliances, climate sustainability, etc., and can solve problems such as unreasonable production formula design, high production costs, and exhaust gas pollution, and improve the level of comprehensive utilization and utilization rate, the effect of increasing state taxation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] (1) Selection and ingredients of raw materials:
[0064] Select raw materials and batch according to the following mass percentages:
[0065] 70% fly ash, 25% quicklime, 4.5% gypsum, 0.1% aluminum powder paste, and the rest is saponin powder
[0066] (2) Ball milling and feeding and stirring:
[0067] The ingredients in step (1) were ball milled and pulverized, and mixed and stirred evenly to obtain a mixed material. The stirring temperature during feeding and stirring was 45°C;
[0068] (3) Pouring:
[0069] Casting the mixed material in step (2);
[0070] (4) Static stop for initial maintenance, steam recovery and waste heat utilization:
[0071] The temperature during the static stop and initial curing is 42.5°C, and the static stop and initial curing time is 1.75h, and the waste steam generated in the autoclaving curing process is recycled as a heat source, which is used as an energy source for maintaining the temperature during the static stop and initial curin...
Embodiment 2
[0078] (1) Selection and ingredients of raw materials:
[0079] Select raw materials and batch according to the following mass percentages:
[0080] 65% fly ash, 20% quicklime, 3% gypsum, 0.05% aluminum powder paste, and the rest is saponin powder;
[0081] (2) Ball milling and feeding and stirring:
[0082] The ingredients in step (1) were ball milled and pulverized, and mixed and stirred evenly to obtain a mixed material. The stirring temperature during feeding and stirring was 40°C;
[0083] (3) Pouring:
[0084] Casting the mixed material in step (2);
[0085] (4) Static stop for initial maintenance, steam recovery and waste heat utilization:
[0086] The temperature during static stop and initial maintenance is 40°C, and the time for static stop and initial maintenance is 1.25 hours. The waste steam generated in the autoclaving maintenance process is recycled as a heat source, which is used as energy for maintaining the temperature during static stop and initial maint...
Embodiment 3
[0093] (1) Selection and ingredients of raw materials:
[0094] Select raw materials and batch according to the following mass percentages:
[0095] 75% fly ash, 30% quicklime, 6% gypsum, 0.15% aluminum powder paste, and the rest is saponin powder;
[0096] (2) Ball milling and feeding and stirring:
[0097] The ingredients in step (1) were ball milled and pulverized, and mixed and stirred evenly to obtain a mixed material. The stirring temperature during feeding and stirring was 50°C;
[0098] (3) Pouring:
[0099] Casting the mixed material in step (2);
[0100] (4) Static stop for initial maintenance, steam recovery and waste heat utilization:
[0101] The temperature during static stop and initial maintenance is 45°C, and the time for static stop and initial maintenance is 2.25 hours. The waste steam generated in the autoclave curing process is recycled and used as a heat source, which is used as energy for maintaining the temperature during static stop and initial mai...
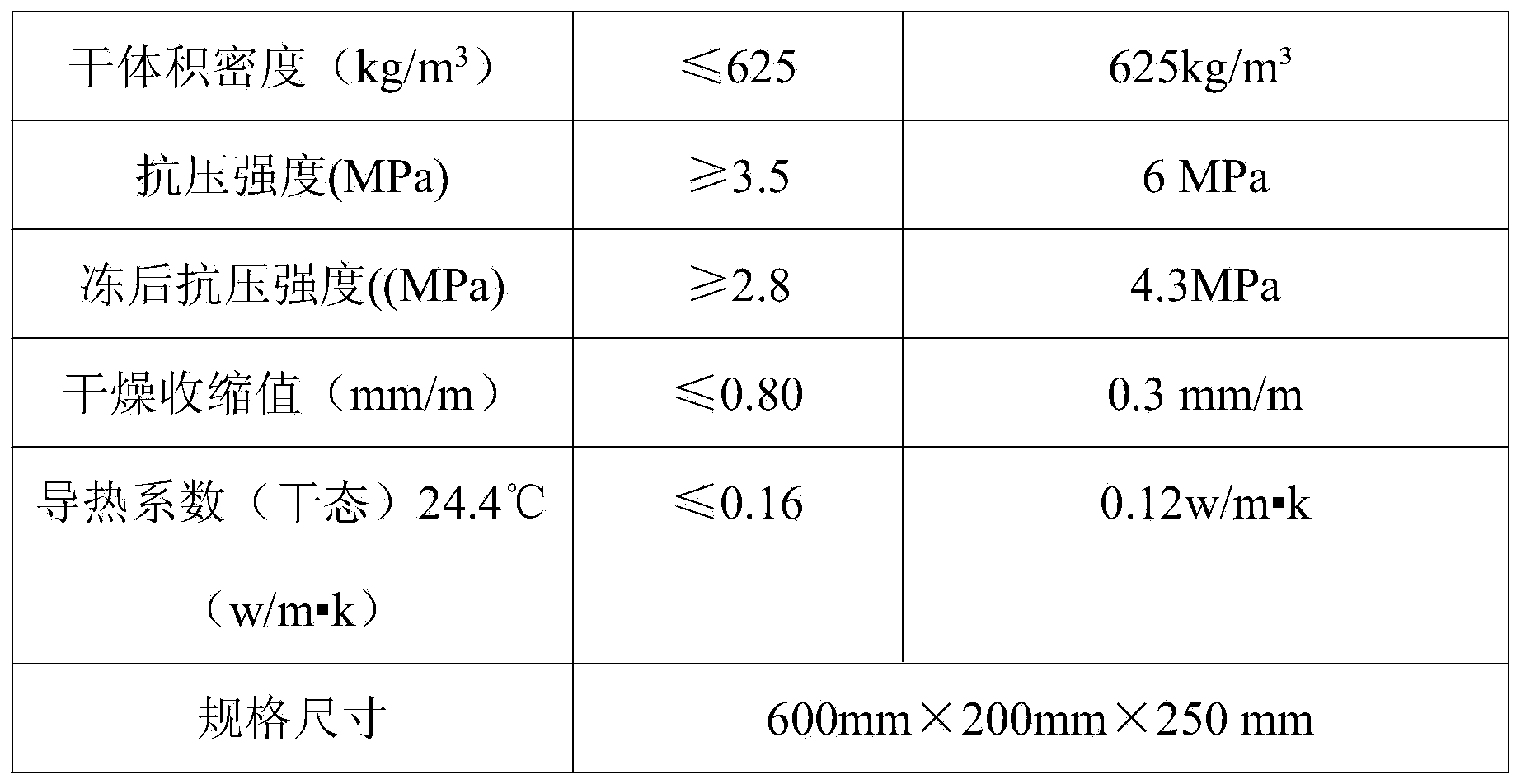
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com