Method of producing low-sulfur low freezing point diesel by full-range shale oil
A technology for shale oil and full distillate, which is applied in the production of low-sulfur and low-concentration diesel oil, can solve problems such as high investment and operating costs, complex process flow, etc., achieve high product yield, solve insufficient processing depth, and solve quality and Effects of Diesel Yield Problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
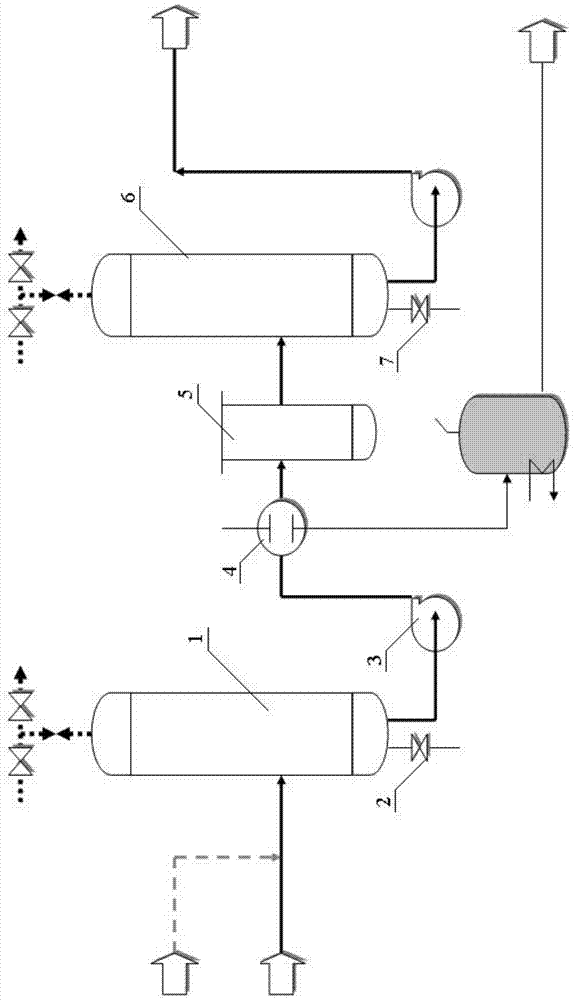
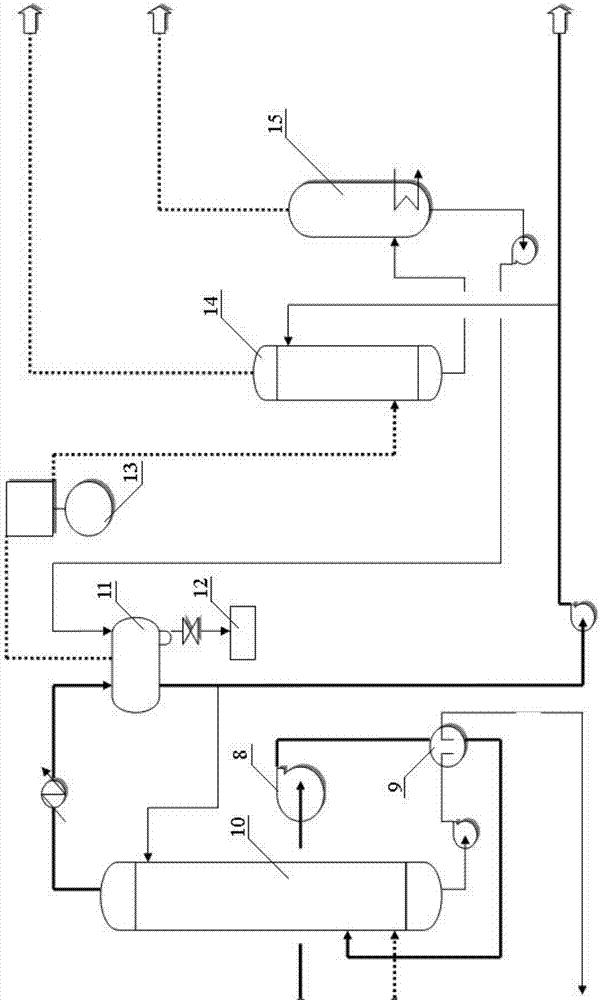
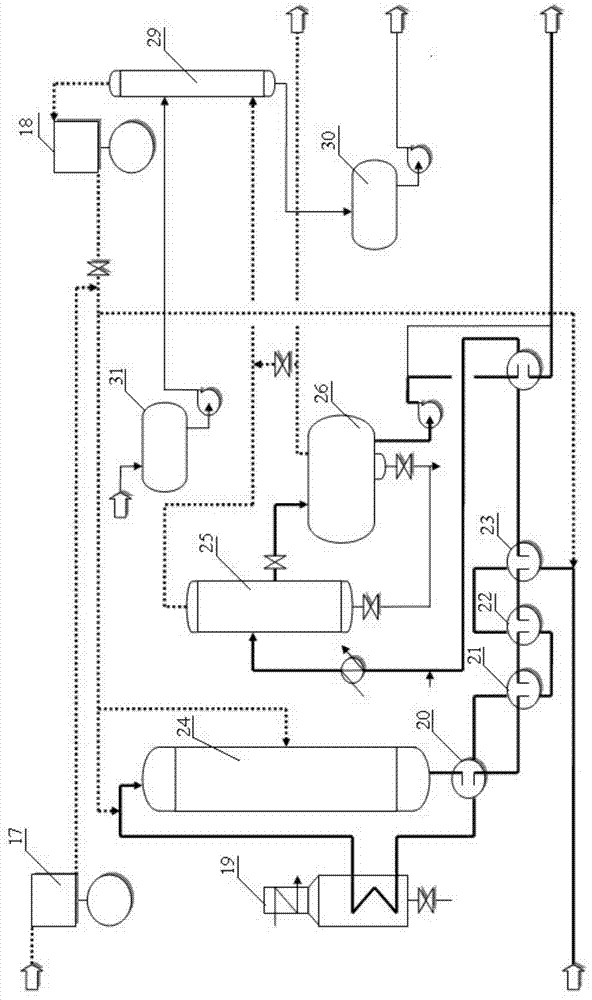
[0046] Specific implementation mode 1: In this implementation mode, the method for producing low-sulfur and low-point-point diesel oil using full-fraction shale oil is as follows:
[0047] 1. Raw material pre-fractionation unit:
[0048] The full-fraction shale oil enters the atmospheric fractionation tower for pre-fractionation under the conditions of tower top temperature 165-175°C, tower bottom temperature 295-310°C, tower top pressure 0.30-0.35MPaG, and the product is light shale Rock oil, heavy shale oil and non-condensable gas;
[0049] 2. Reaction unit:
[0050] The non-condensable gas is compressed to 0.5MPa in the first stage and enters the liquid separation tank for liquid separation, and then compressed to 3.5MPa in the second stage and enters the absorption tower. It is absorbed by light shale oil to obtain absorbed oil and fuel gas, and the absorbed oil is sent to the flash tank Flash evaporation to obtain desorption gas and desorption oil. The desorption oil re...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0064] Specific embodiment two: What this embodiment differs from specific embodiment one is that the diameter of the atmospheric fractionation tower described in step one is 3.5m, high 25.0m, adopts 20 layers of single-flow composite float valve trays, and the fractionation tower adopts normal pressure The operation does not draw the side line, the light shale oil is discharged from the top of the tower, and the heavy shale oil is pumped out from the bottom of the tower. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0065] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the dehydrogen sulfide stripping tower described in step 3 has a diameter of 3 m and a height of 20 m, and adopts 15 layers of single-flow composite valve trays. Others are different from the first or second specific embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com