Preparation method of homoporous biological ceramic implant material having gradient calcium and phosphor content
A technology of bioceramics and implants, applied in the direction of electrolytic coatings, coatings, surface reaction electrolytic coatings, etc., can solve the problem that the oxidation voltage and frequency should not be too high, the ceramic layer lacks a gradient of calcium and phosphorus content, and it is difficult to adjust the calcium and phosphorus content. Pore structure and other issues, to achieve good osteoinduction and osseointegration performance, uniform micropores, and good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
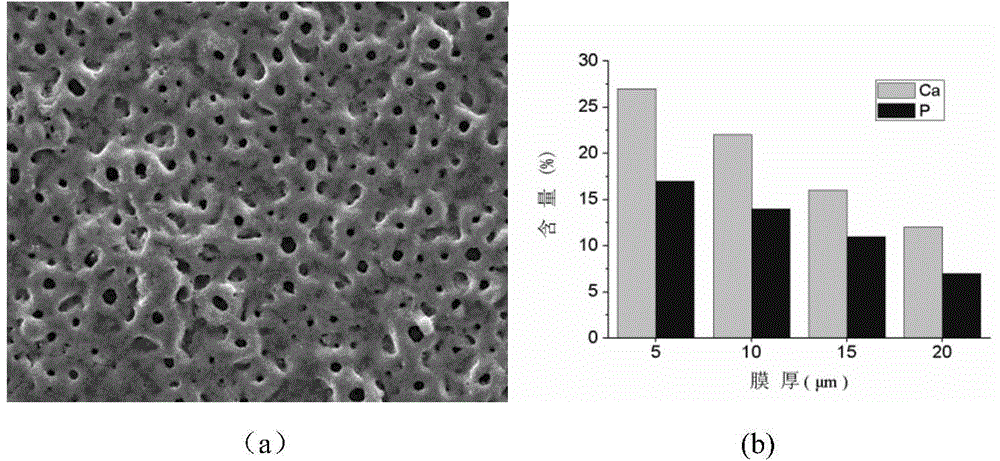
[0019] Perform micro-arc oxidation treatment on titanium or titanium alloy in 1L of ice-water mixed low-temperature electrolyte containing calcium and phosphorus, freeze deionized water (or distilled water) into 1L of ice and place it in the electrolyte. The process parameters are: constant voltage micro-arc oxidation process, electrode voltage U=650V, electrode frequency f=800Hz, duty cycle d=15%, micro-arc oxidation treatment time t=20min; electrolyte contains calcium ion concentration C( Ca)=15mmol / L, phosphorus ion concentration C(P)=3mmol / L. The surface micropores of the oxide film obtained by treating the titanium surface with this process are uniform and uniform, and the phase composition is anatase TiO 2 + rutile phase TiO 2 +CaTiO 3 +PO 4 3- group, the thickness of the oxide film is 22.8 μm, the Ca / P in the oxide film is 1.608, the critical load value is 29.7N, and the maturation period of the bone interface is shortened from 3 to 6 months for titanium implants to...
Embodiment 2
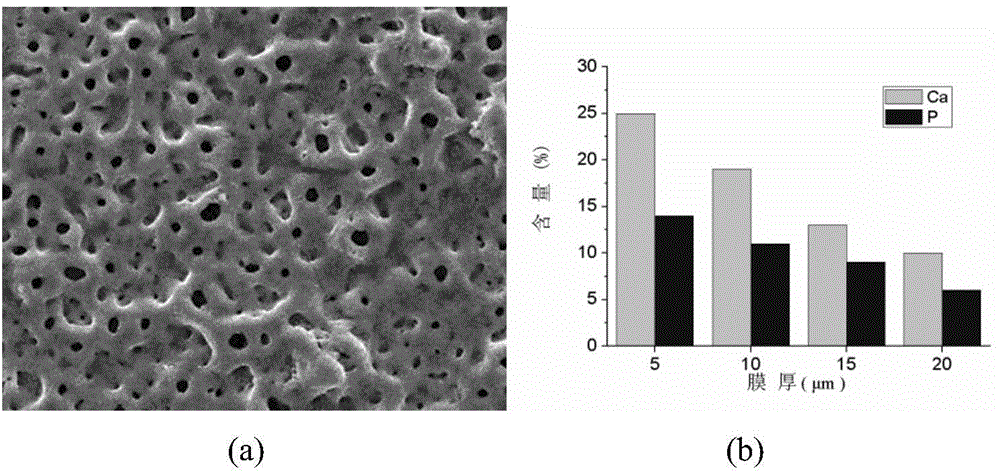
[0021] Perform micro-arc oxidation treatment on titanium or titanium alloy in 1L of ice-water mixed low-temperature electrolyte containing calcium and phosphorus, freeze deionized water (or distilled water) into 1L of ice and place it in the electrolyte. The process parameters are: constant voltage micro-arc oxidation process, electrode voltage U=600V, electrode frequency f=700Hz, duty cycle d=15%, micro-arc oxidation treatment time t=25min; electrolyte contains calcium ion concentration C( Ca)=20mmol / L, phosphorus ion concentration C(P)=4mmol / L. The micropores on the surface of the oxide film obtained by treating the titanium surface with this process are uniform and uniform.
Embodiment 3
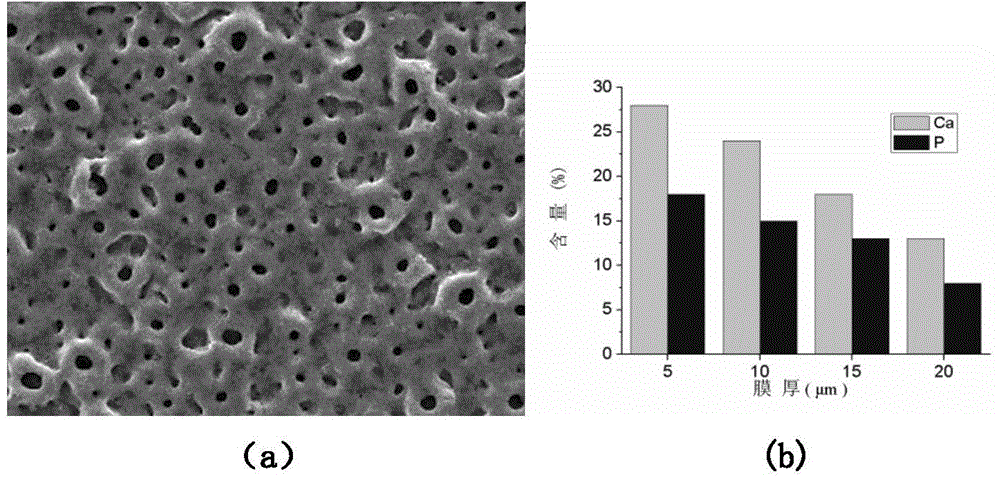
[0023] Perform micro-arc oxidation treatment on titanium or titanium alloy in 1L of ice-water mixed low-temperature electrolyte containing calcium and phosphorus, freeze deionized water (or distilled water) into 1L of ice and place it in the electrolyte. The process parameters are: constant voltage micro-arc oxidation process, electrode voltage U=700V, electrode frequency f=900Hz, duty cycle d=20%, micro-arc oxidation treatment time t=15min; electrolyte contains calcium ion concentration C( Ca)=10mmol / L, phosphorus ion concentration C(P)=2mmol / L. The micropores on the surface of the oxide film obtained by treating the titanium surface with this process are uniform and consistent.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com