Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Improve osseointegration performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
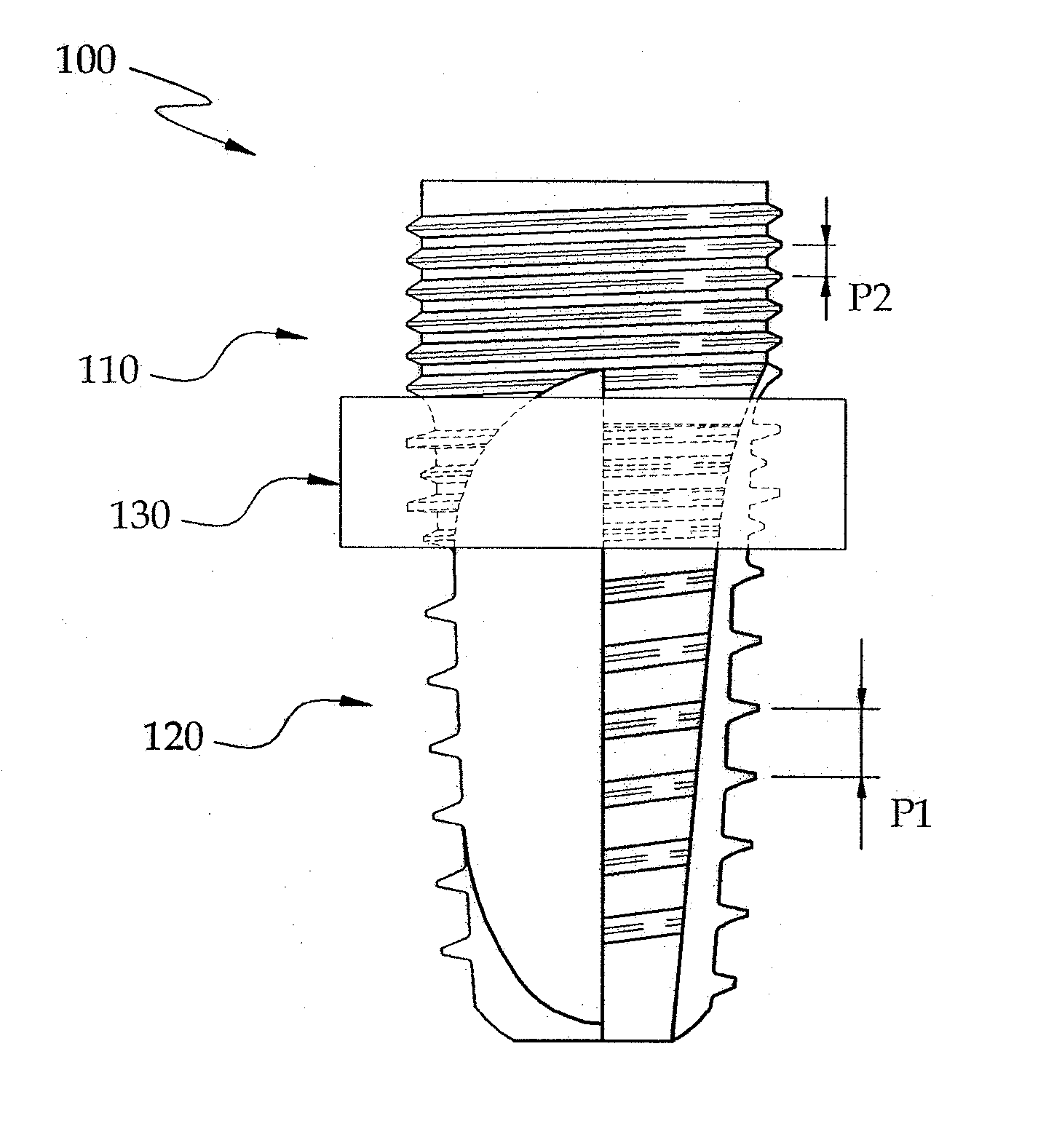
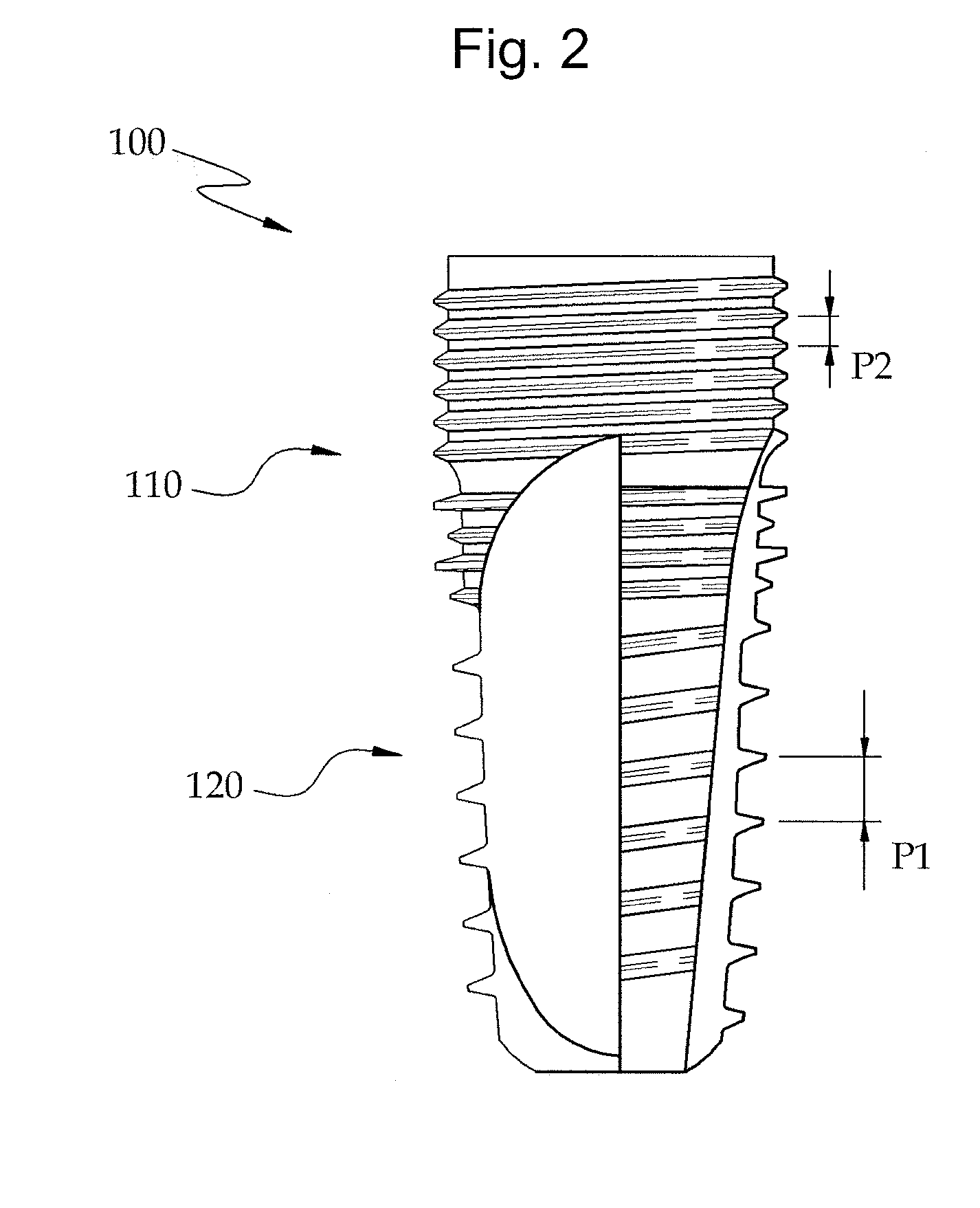
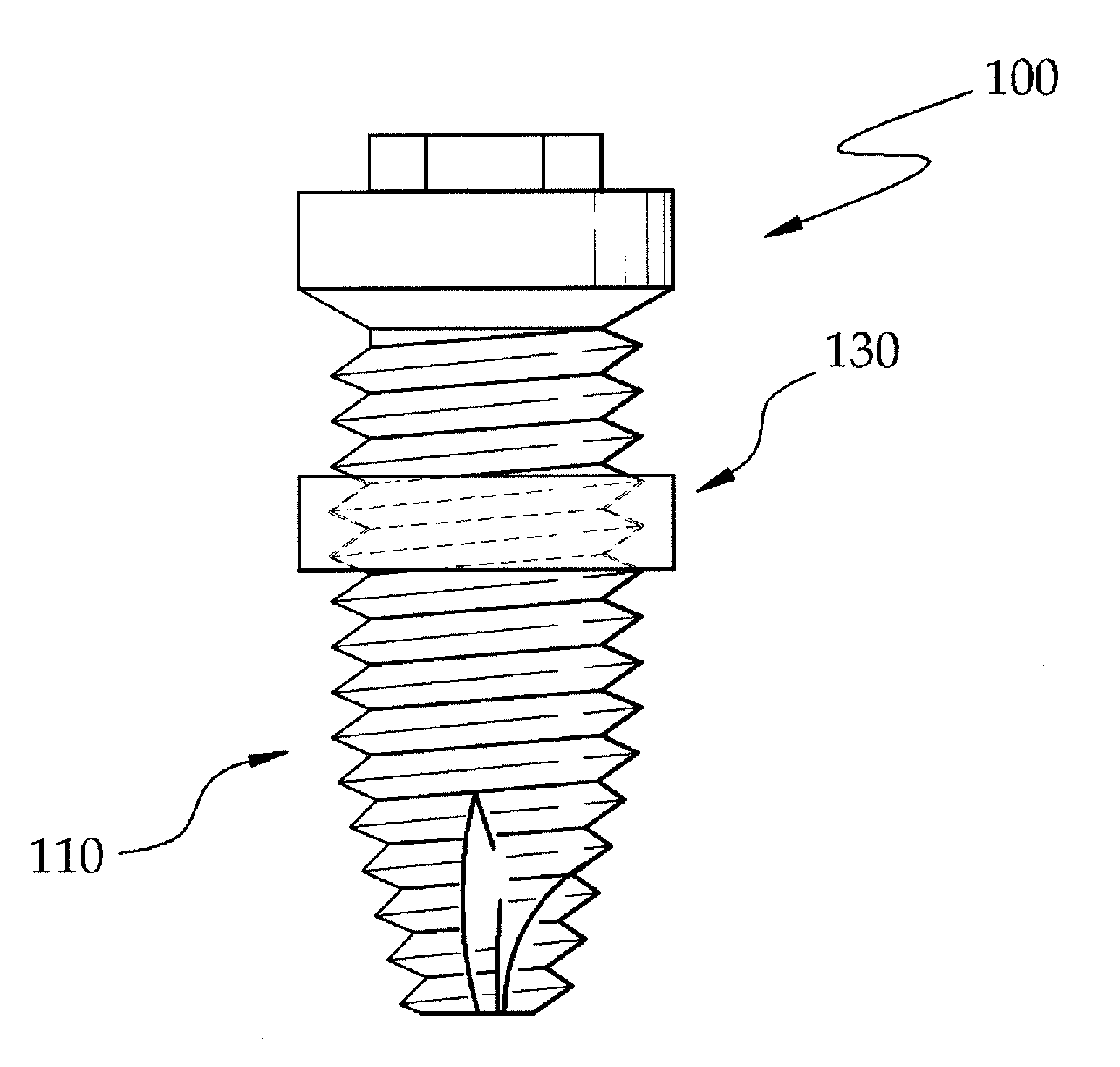
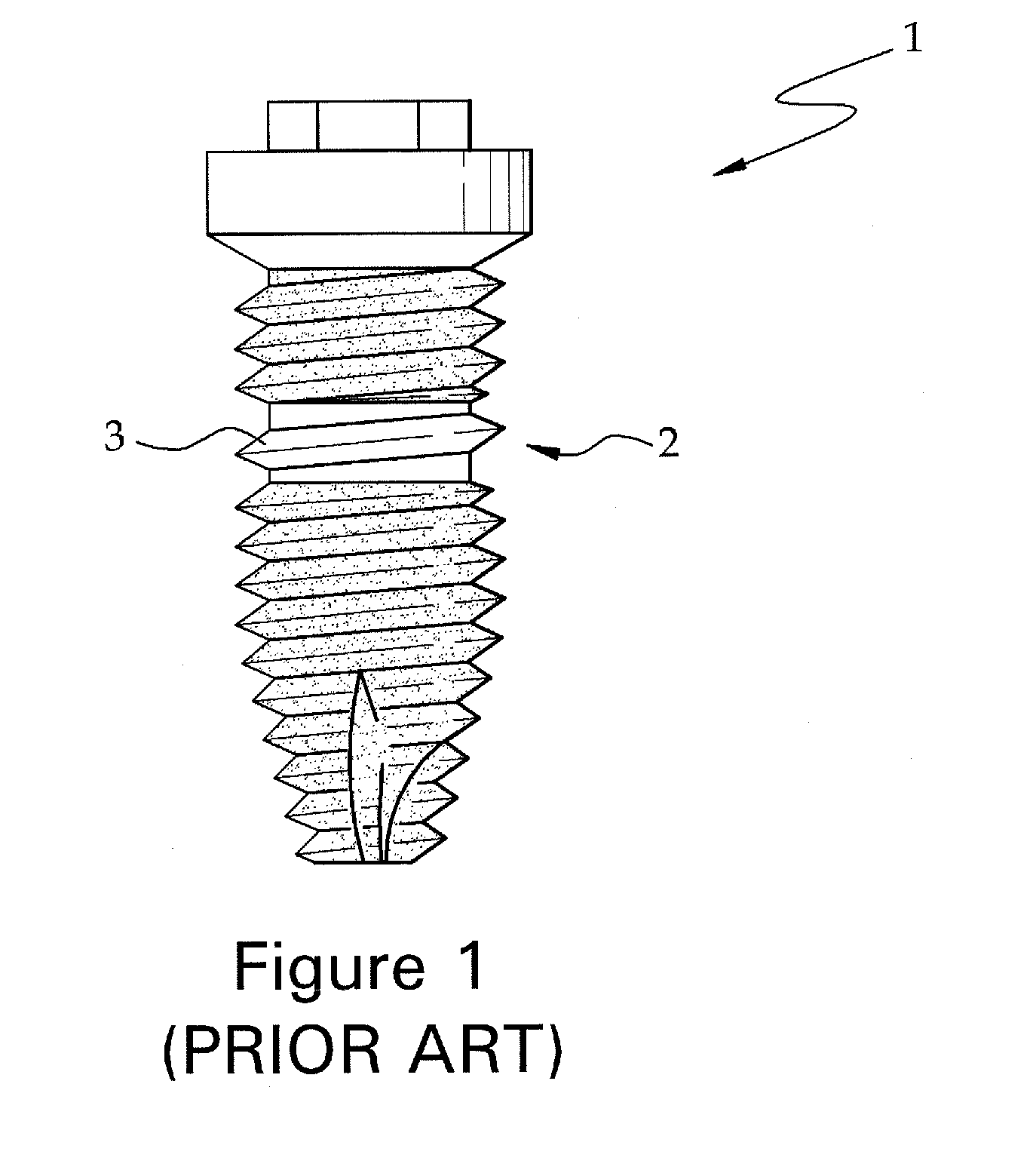
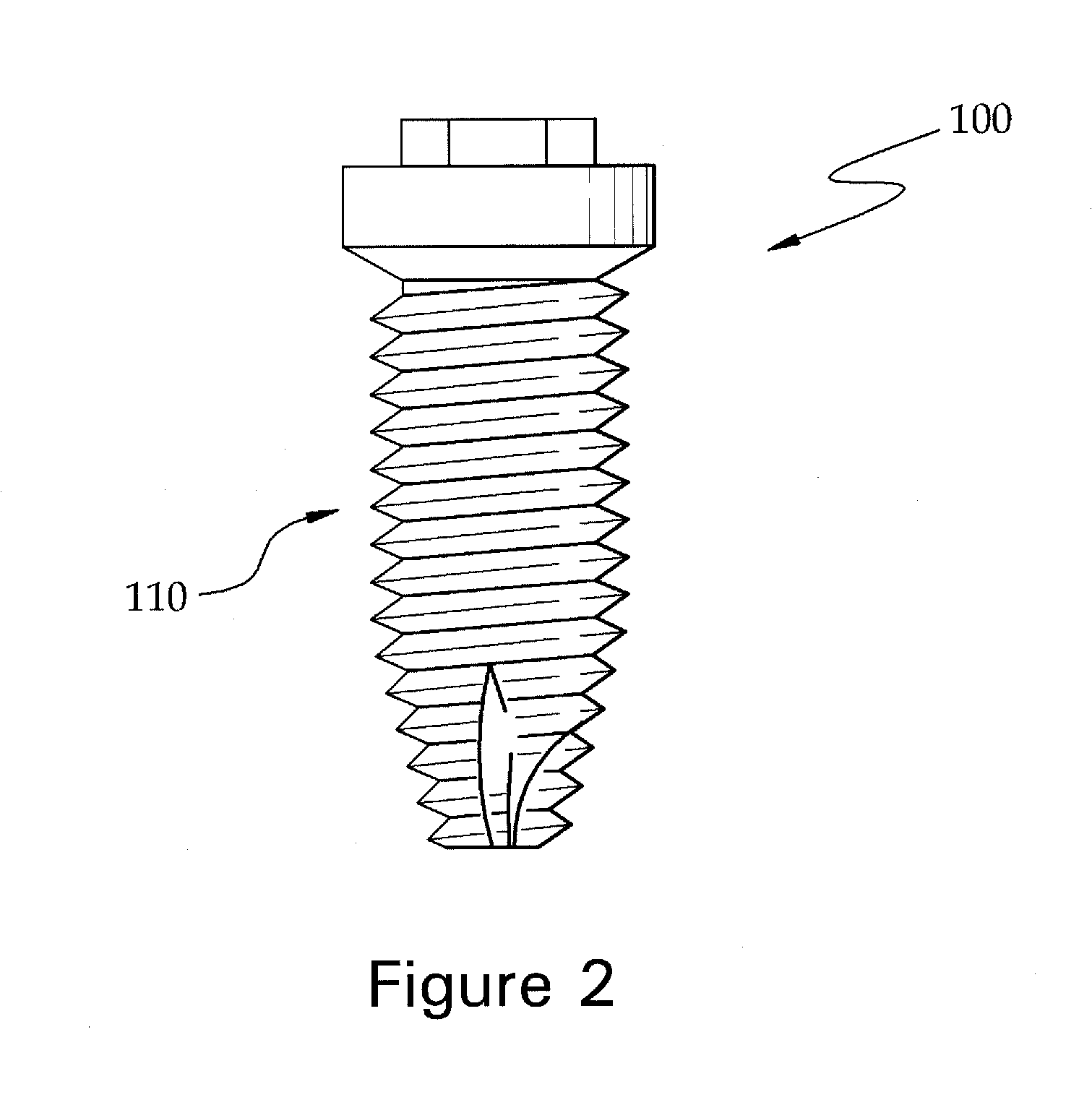
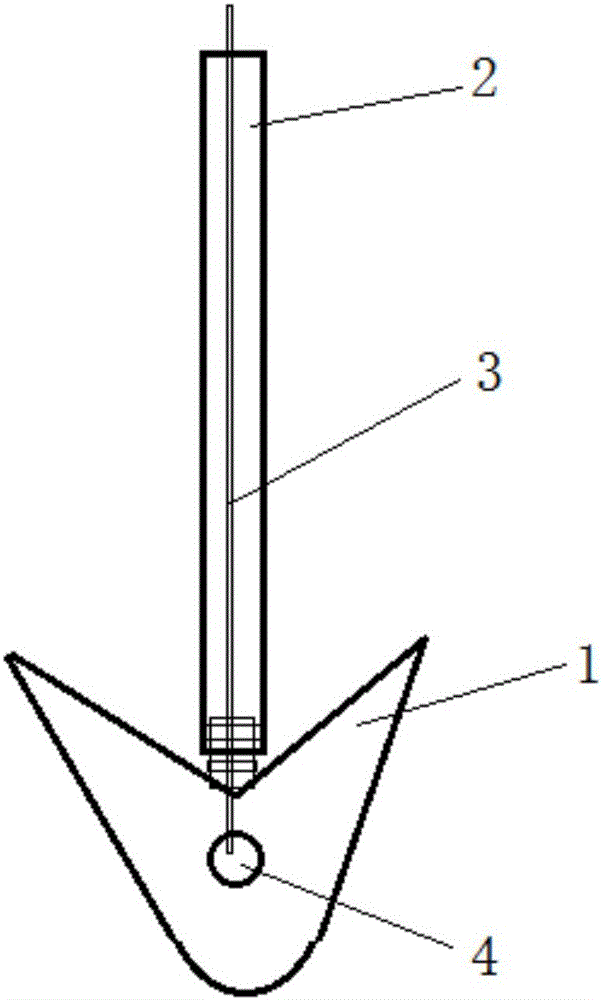
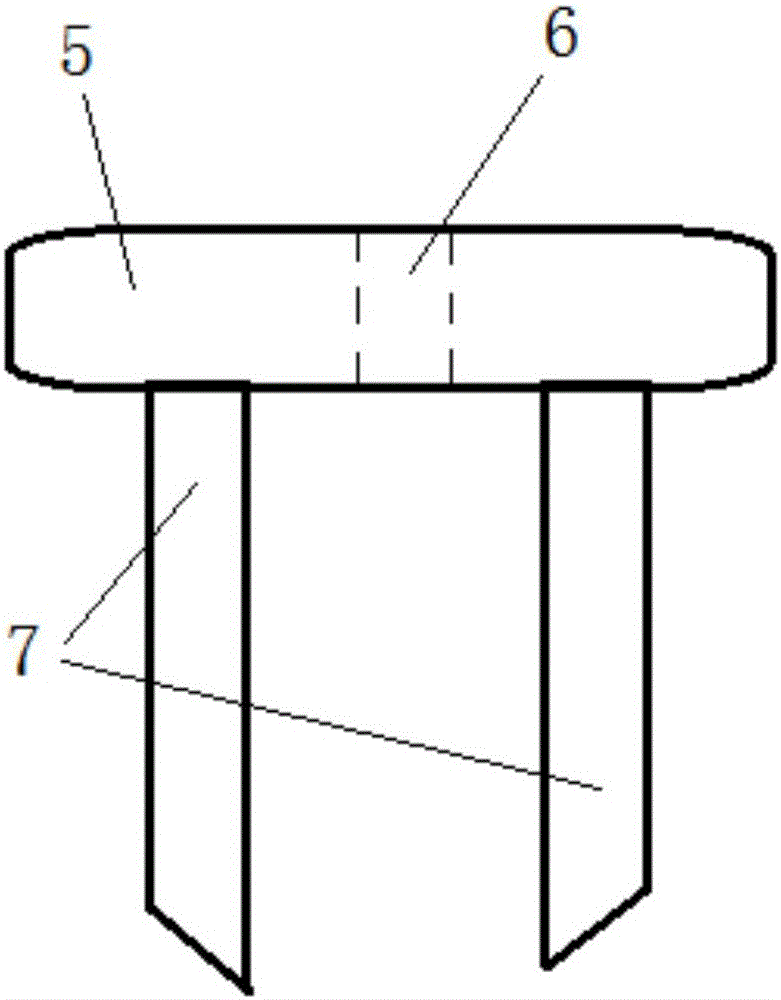
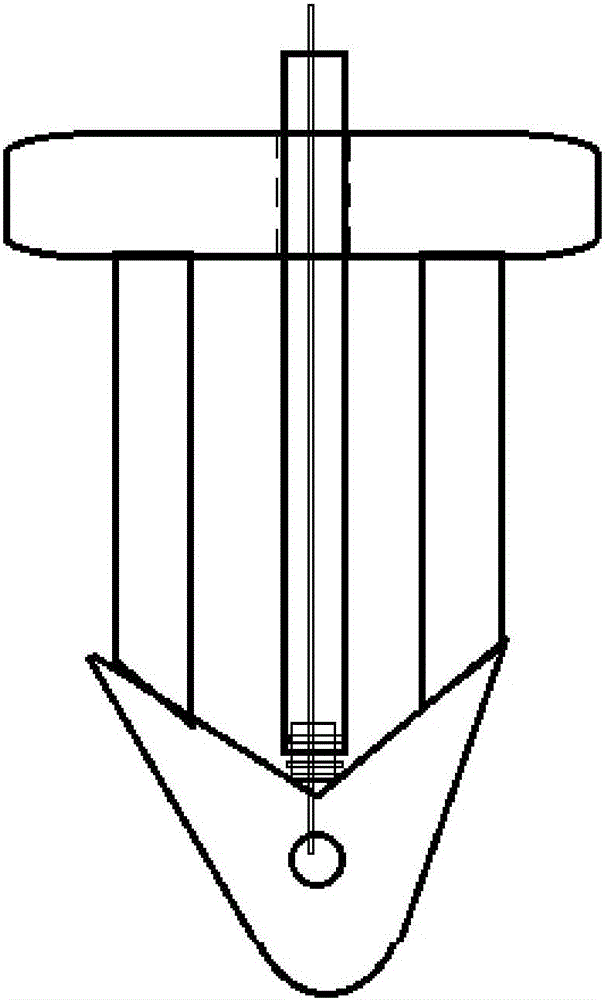
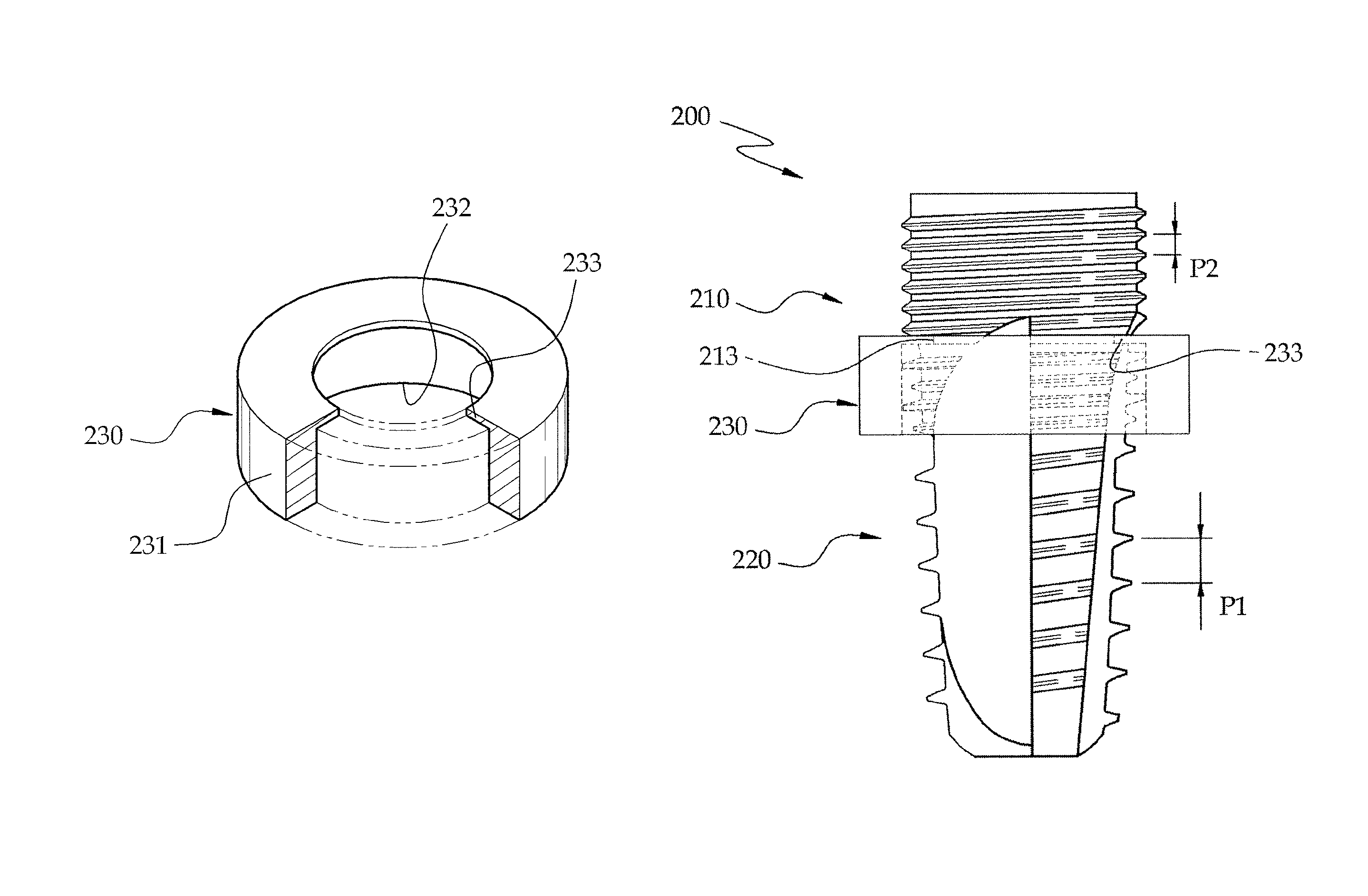
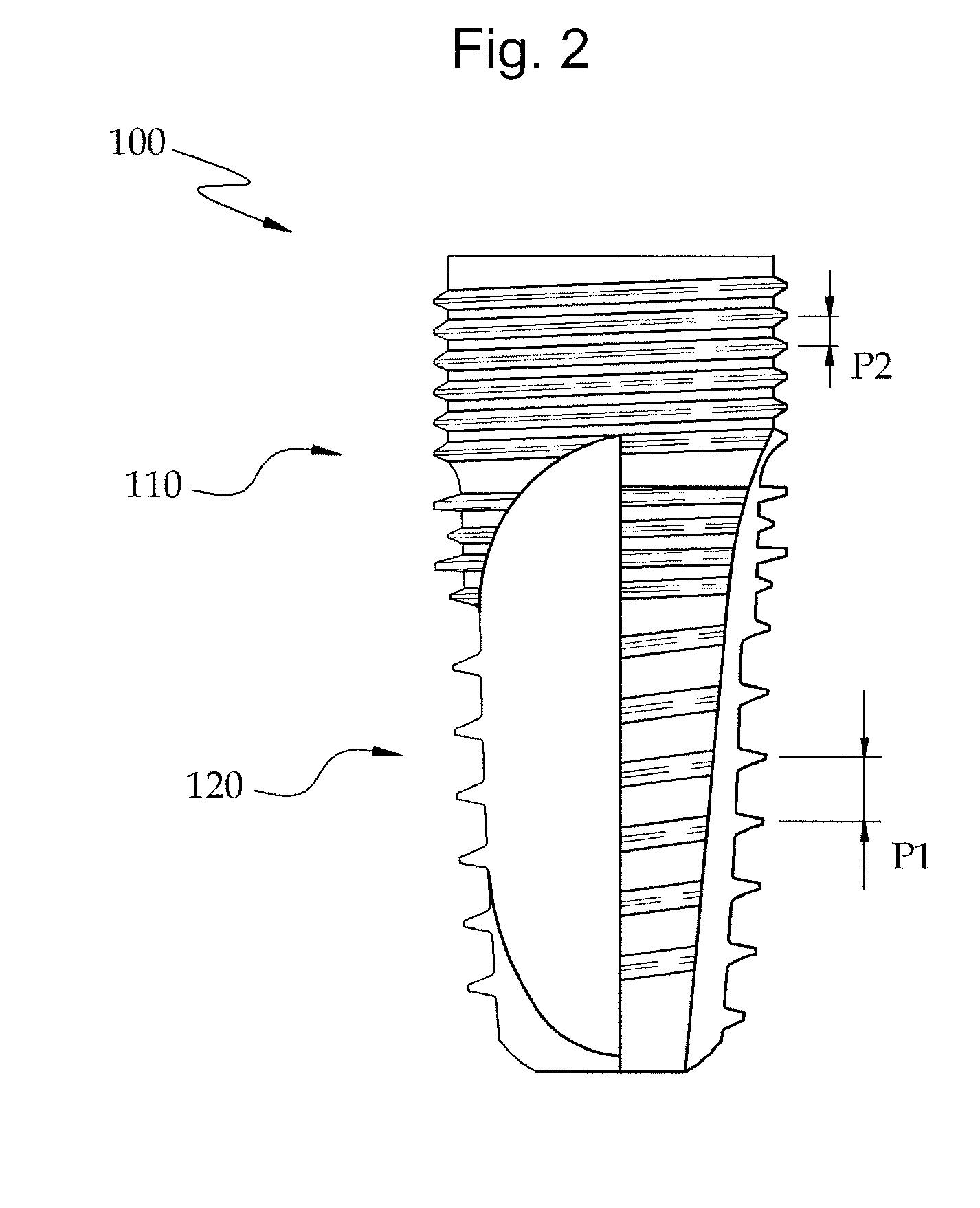
Fixture of dental implant and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100330534A1Simple structureImprove osseointegration performanceDental implantsWristbandsOsseointegrationDental implant
Provided are a method of manufacturing a fixture of a dental implant with an improved structure in which the performance of osseointegration is excellent, spread of inflammation is reduced and a combination force between the fixture and an alveolar bone is remarkably increased, and a fixture of a dental implant manufactured by the method. The performance of osseointegration is excellent, and spread of inflammation can be reduced, and a combination between the fixture and an alveolar bone can be remarkably improved. Furthermore, the fixture of the dental implant having the above structure can be easily manufactured.
Owner:HYUN
A bioactive porous titanium alloy human cervical intervertebral fusion device and its preparation method
ActiveCN102293693AEven by forceSolve the interface binding problemInternal osteosythesisMedical devicesMetallurgyDrug biological activity
The invention provides a porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage with bioactivity and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, inputting model data into electron beam melting equipment according to a design requirement to prepare a porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage; secondly, preparing gelatin microspheres; and immersing gelatin microsphere dry powder in an rhBMP-2 solution for gelatin coating modification, preparing a gelatin solution A in double distilled water, immersing the porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage in the gelatin solution A, mixing the rhBMP-2 gelatin microspheres and absolute ethanol to obtain suspension B, and immersing the gelatin-coating-modified porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage in the suspension B to prepare the porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage internally containing an rhBMP-2 sustained-release system. The cervical interbody fusion cage prepared with the method has modulus of elasticity close to that of natural bone tissues, and the porous structure and the bioactivity factor sustained-release system inside the cervical interbody fusion cage can induce growth of new bone tissues, so that the binding problem of bone-material interfaces is solved. Therefore, the cervical interbody fusion cage has bettermechanical compatibility and bone integration capability than those of a compact material.
Owner:维度(西安)生物医疗科技有限公司
Preparation method of hydroxyapatite/polylactic acid composite coating on surface of medical magnesium alloy
InactiveCN103933611AHigh strengthReduce corrosion ratePretreated surfacesMetallic material coating processesAcid etchingCalcium nitrate tetrahydrate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hydroxyapatite / polylactic acid composite coating on the surface of medical magnesium alloy, which comprises the following steps of polishing a magnesium alloy basal body to remove an oxidation layer on the surface; carrying out acid etching pretreatment and neutralizing treatment on the magnesium alloy basal body; preparing transfer solution from sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate and calcium nitrate terahydrate; preparing a biomimetic calcium-phosphate coating; dissolving polylactic acid in a chloroform solvent to prepare polylactic acid solution; immersing the prepared magnesium alloy / hydroxyapatite composite material in the polylactic acid solution, and coating the polylactic acid coating on the surface of the magnesium alloy / hydroxyapatite composite material by adopting the solution dip-coating method; and putting the magnesium alloy material for 2-3 days till chloroform in the polylactic acid solution is completely volatilized, thereby obtaining the composite material of which the surface of magnesium alloy is wrapped with the hydroxyapatite / polylactic acid composite coating. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method of the hydroxyapatite / polylactic acid composite coating on the surface of medical magnesium alloy overcomes the disadvantages of the single coating, and therefore, the corrosion resistance and the biocompatibility of magnesium alloy are obviously increased.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Medical titanium alloy with antibacterial and osteocyte-facilitating functions and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104005016AImprove antibacterial propertiesImprove osseointegrationMetallic material coating processesProsthesisBone cellAdsorption method
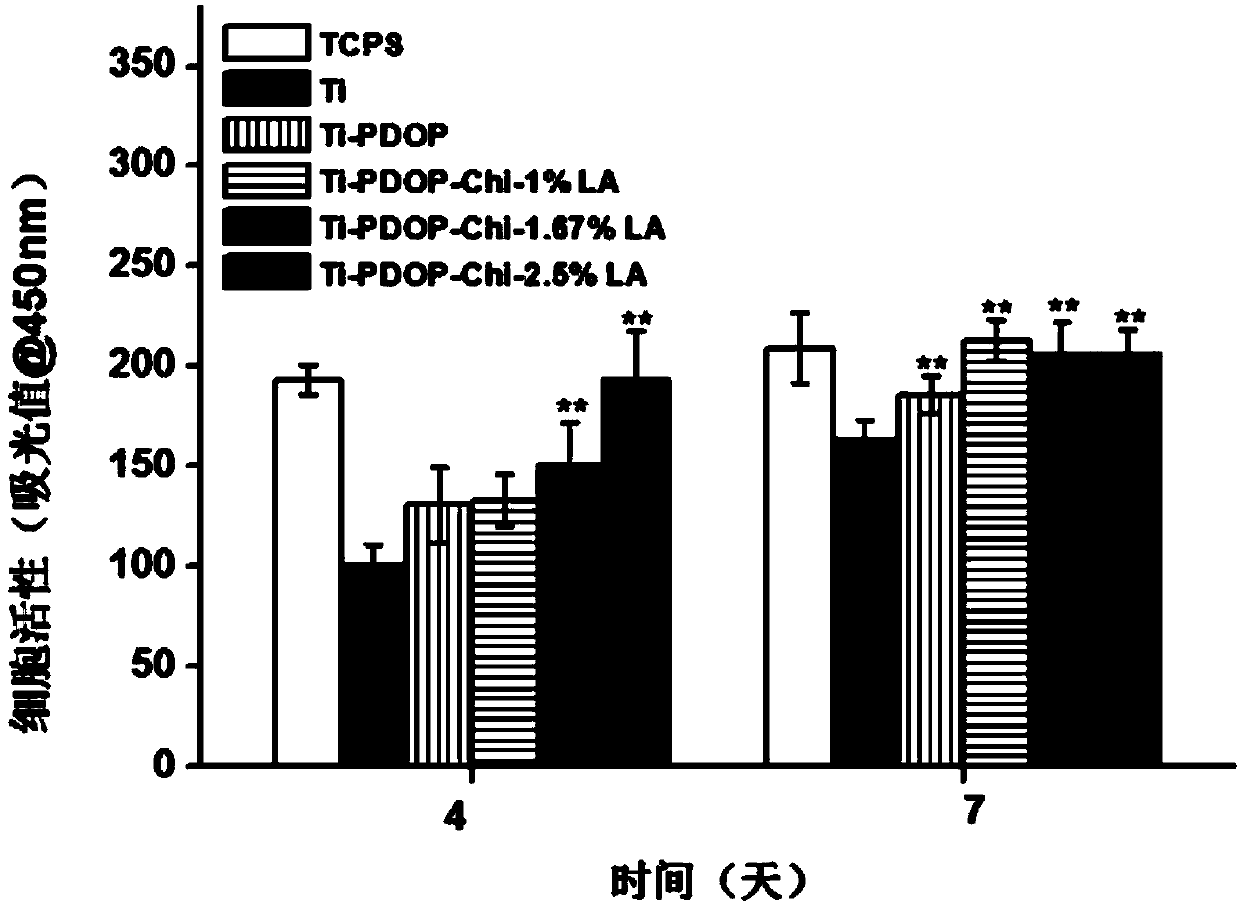
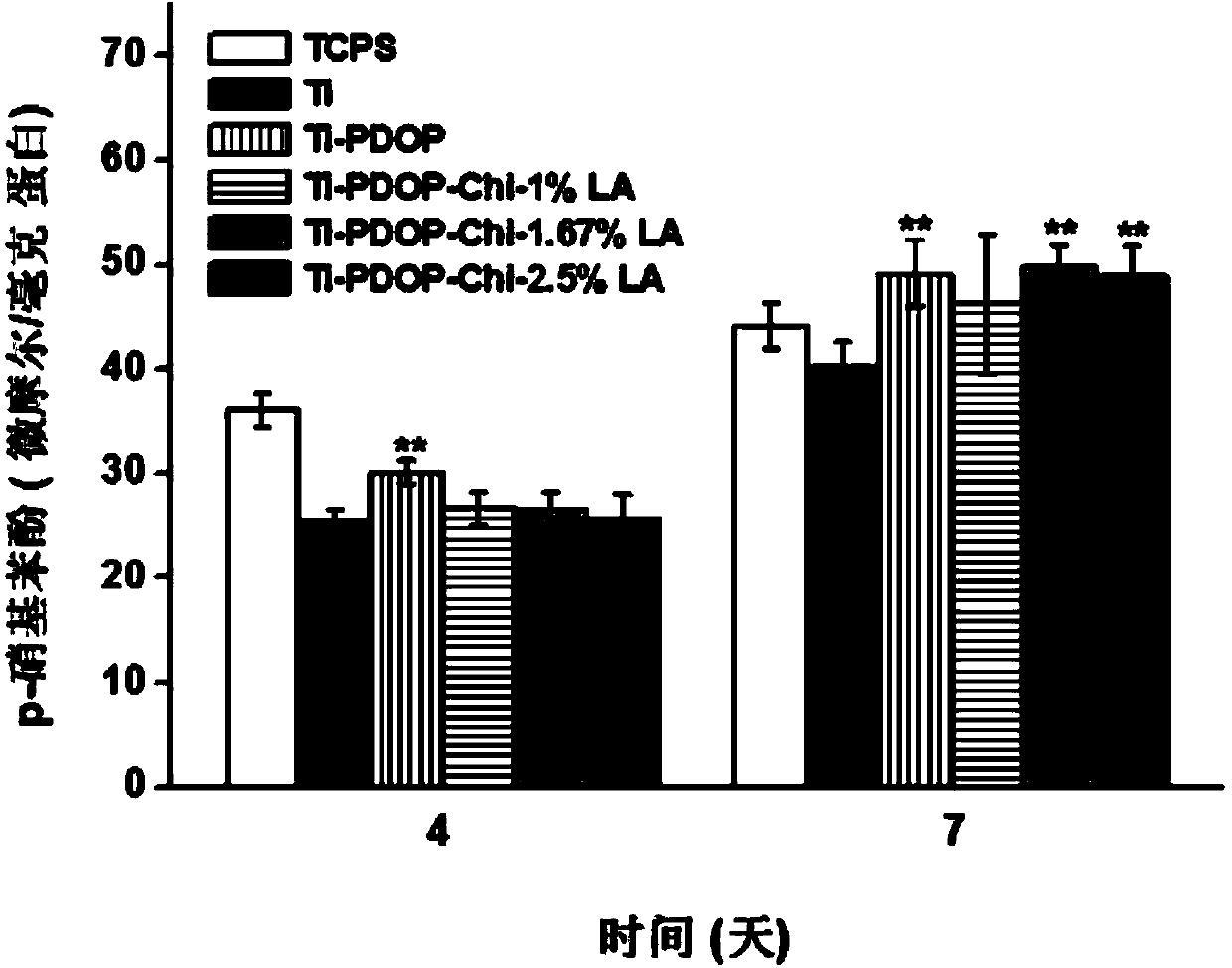
The invention provides a preparation method of nanolayer medical titanium alloy with antibacterial and osteocyte-facilitating functions. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing different concentrations of chitosan-lauric acid (1%, 1.67% and 2.5%) conjugates by esterification reaction; secondly, utilizing a physical adsorption method and a chemical fixation method, adopting poly-dopamine as an intermediate layer, fixing the chitosan-lauric acid conjugates on the surface of a titanium implant, so as to build a nano structure layer with dual antibacterial and osteocyte proliferation facilitating properties on the titanium material surface, so as to regulate and control the biological function of the osteocyte, and improve the short-term antimicrobial capability of the titanium implant.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Biological functionalized nano titanium material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102058904AGood biocompatibilityImprove osseointegration performanceSurface reaction electrolytic coatingProsthesisGrowth cellNanotube array
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical materials, and relates to a biological functionalized nano titanium material. The surface of the titanium material is provided with a TiO2 nano tube array with tube diameter of 30-100nm, and the surface of the TiO2 nano tube array is also fixed with a bone morphogenetic protein 2(BMP2). A preparation method of the biological functionalized nano titanium material comprises the steps of: preparing the TiO2 nano tube array with the tube diameter of 30-100nm on the surface of the titanium material by adopting an anode oxidizing method, and fixing the BMP2 on the surface of the TiO2 nano tube array through polydopamine to obtain the biological functionalized nano titanium material. The biological functionalized nano titanium material has better biocompatibility; on one hand, the TiO2 nano tube array with proper tube diameter can provide a proper topological structure for the cell growth, on the other hand, the BMP2 is used as a growth factor capable of promoting the cell differentiation, and the proliferation and differentiation capacity of the cells on the surface of the titanium material can be improved through the synergistic effect of the topological structure and the chemical components, thus the osseointegration of the titanium material is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
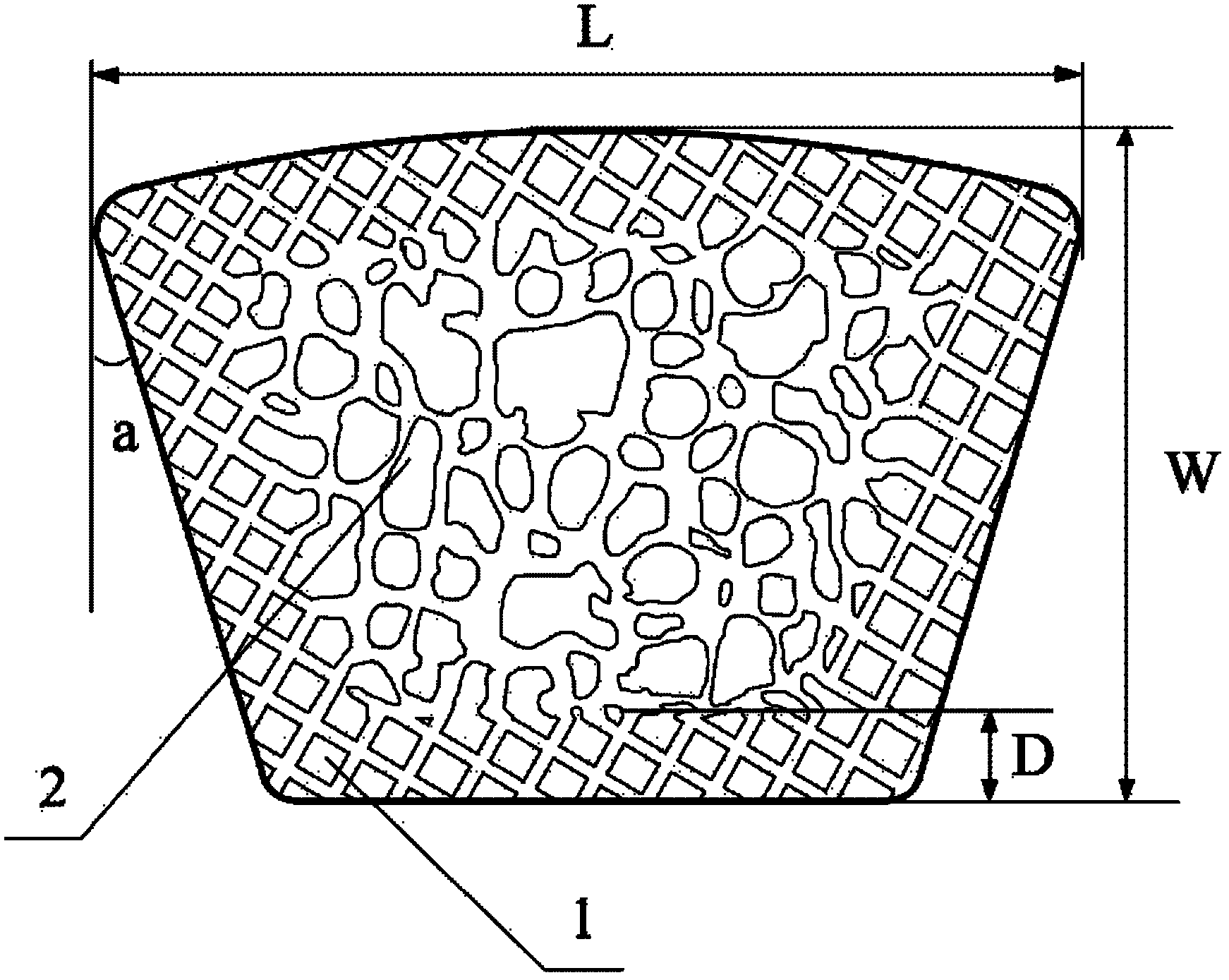
Preparation method for reticulate structural part provided with component and pore double gradient transition layers
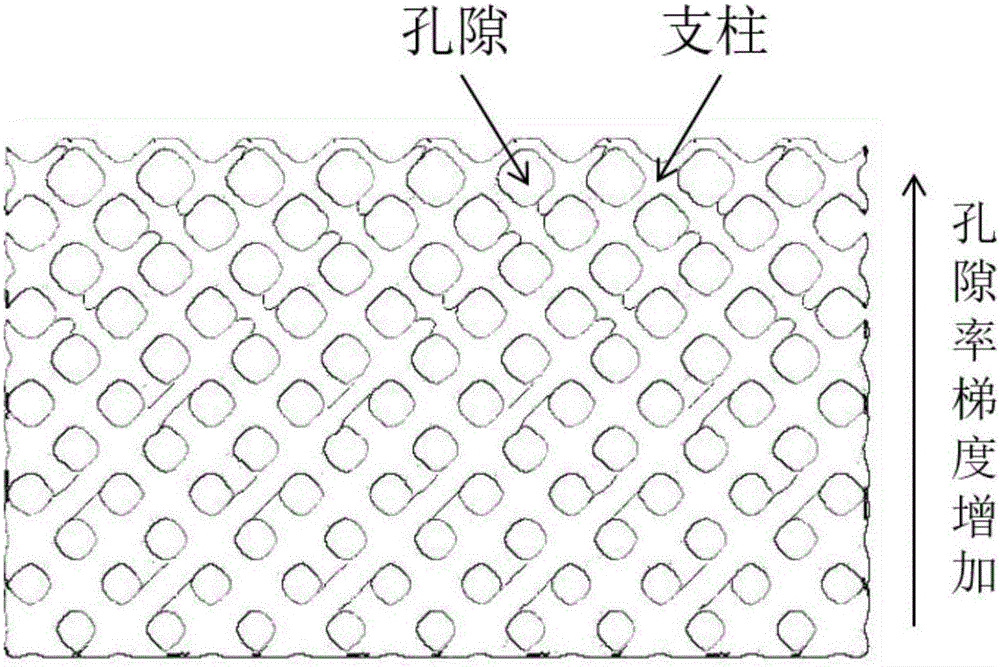
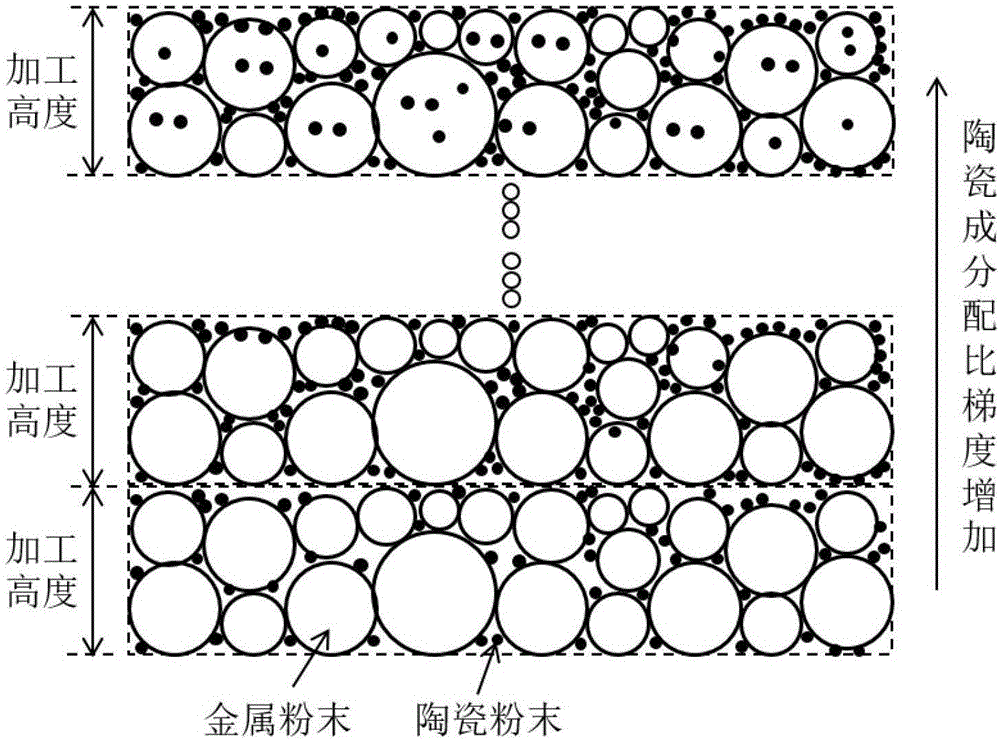
ActiveCN106270517AUniform mechanical propertiesImprove osseointegration performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusLaser scanningTransition layer
The invention discloses a preparation method for a reticulate structural part provided with component and pore double gradient transition layers. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a three-dimensional model of a reticulate structure with bionic unit topology and gap dimension gradient changes is design, the three-dimensional model is subjected to slicing treatment and then converted into an STL document, and the STL document is input into SLM forming equipment; (2) various powders are evenly mixed according to a preset ratio, and a mixed powder is fed and laid; (3) a current slice layer of the reticulate structural part is subjected to laser scanning forming and is descended by the thickness of a laid power layer after forming is finished, and then the mixed powder in the current ratio is adopted for forming the next slice layer; (4) the step (3) is repeated until forming of the layers with the set height is completed through the powder in the current ratio, mixing of powder in another ratio is completed, and powder feeding and laying are conducted; and (5) the step (3) and (4) are repeated until forming of the whole reticulate structure with various components being in gradient transition is completed. The preparation method has the advantages of being high in preparation efficiency, simple in preparation technological process, low in cost and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Composition capable of forming composite bone cement and bone cement formed by same
ActiveCN106139253AImprove utilizationReduce pollutionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationMicrospherePolymethyl methacrylate
The invention provides a composition capable of forming composite bone cement and the bone cement formed by the same. The composition contains a composition forming polymethyl methacrylate bone cement and tuna fish bone meal / hyaluronic acid microspheres. The composition contains, by 100% total weight, the tuna fish bone meal / hyaluronic acid microspheres accounting for the mass fraction of 8%-60%. The microspheres are prepared from tuna fish bone meal and hyaluronic acid as raw materials, and by the 100% total weight of the tuna fish bone meal and hyaluronic acid, the mass fraction of the tuna fish bone meal accounts for 30%-70%, and the mass fraction of the hyaluronic acid accounts for 30%-70%. The tuna fish bone meal / hyaluronic acid microspheres promoting bone growth are added in the composition on the basis that the composition can form a PMMA bone cement composition, and the obtained bone cement has the advantages of excellent biological activity, biocompatibility, bone integration performance and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH +2
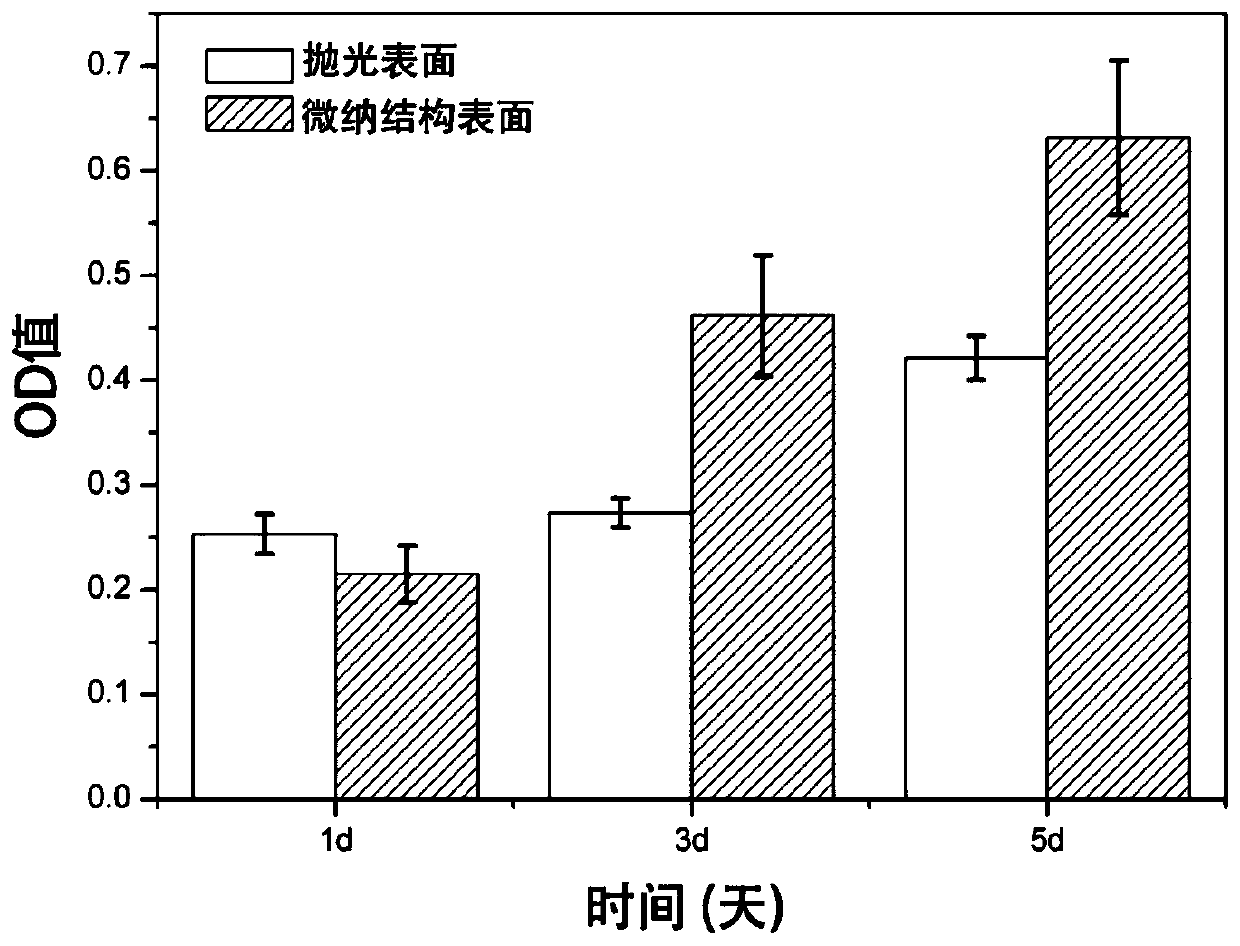
Titanium and titanium alloy surface micro-nano structure modification method
ActiveCN109848546AImprove antibacterial abilityImprove osseointegrationSurface reaction electrolytic coatingLaser beam welding apparatusAnodic oxidationPlastic surgery
Metal titanium and titanium alloy are widely applied to implants of oral prosthodontics, orthopedic surgery and plastic surgery at present, but have the problems of having poor osseous integration capability and being prone to have bacterial infection after implantation. The invention discloses a titanium and titanium alloy surface micro-nano structure modification method, and aims to improve theosseous integration capability and antibacterial capability of titanium and titanium alloy surfaces. The micro-nano structure modification method is characterized in that a femtosecond laser processing technology is adopted, the polished titanium alloy surface is ablated to form a micropost periodic structure with the spacing and the depth not greater than 200 microns, nanotubes with the diameterssmaller than 200 nm are prepared on the micropost periodic structure in an anodic oxidation mode after further acid pickling, and then annealing heat treatment is carried out to obtain a final sample. According to the method, the surface with a micro-nano structure can be prepared on the titanium and titanium alloy surfaces, and the titanium and the titanium alloy with such surfaces have good biocompatibility and antibacterial capability.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
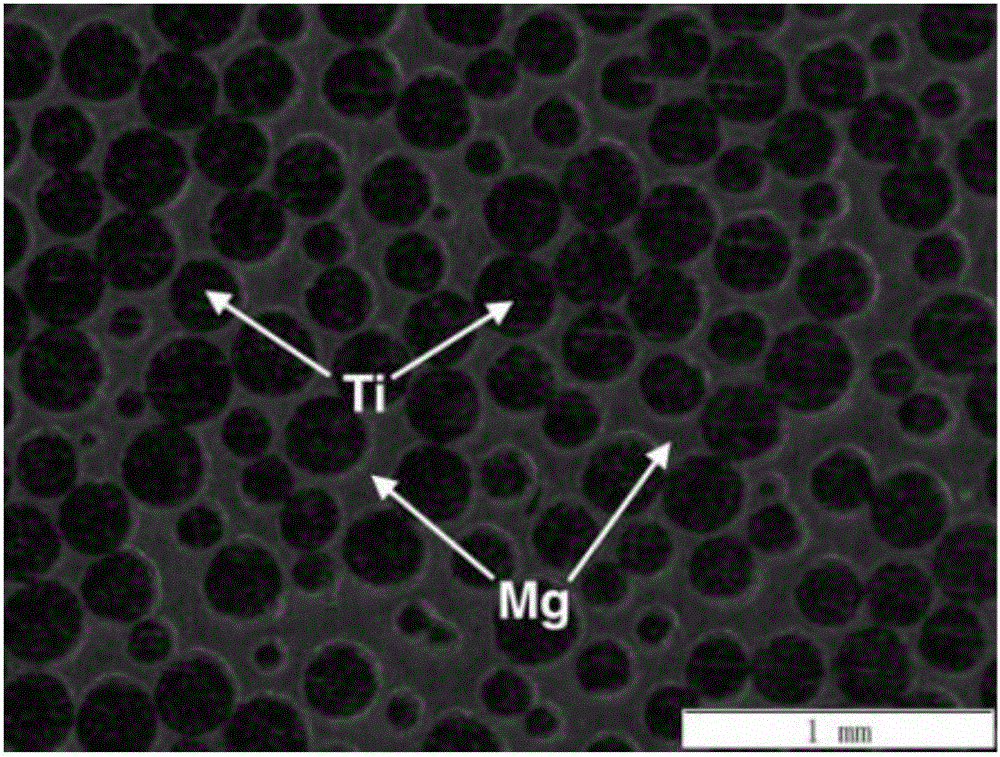
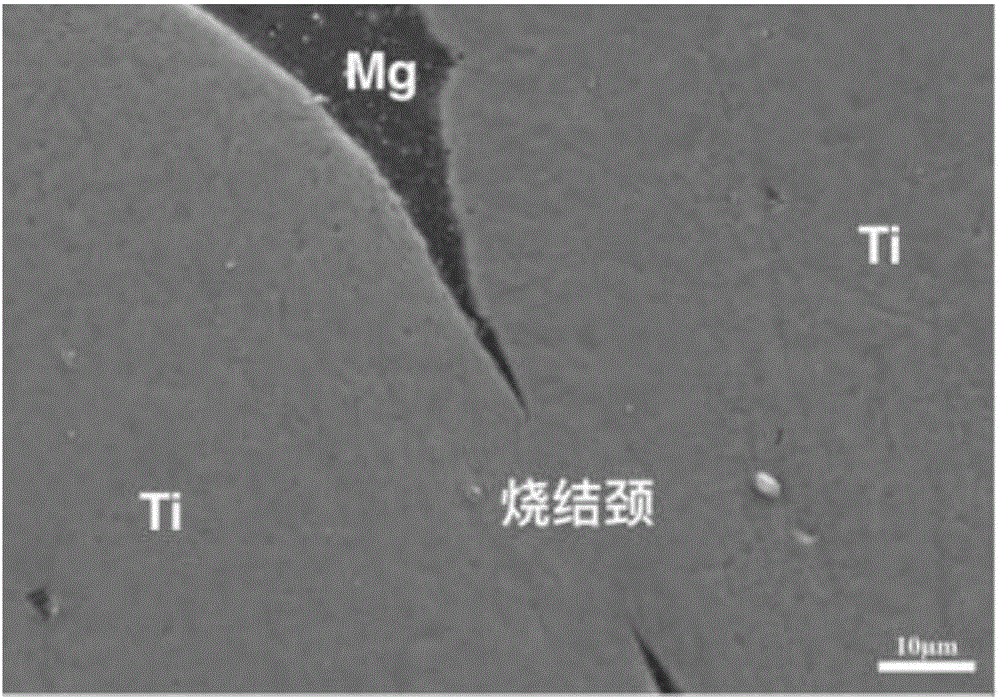
Preparation method for titanium-magnesium double-metal composite of double-communication netted structure
ActiveCN106670464APromote bone growthExcellent osteoinductive propertiesLow elastic modulusStress shielding
The invention relates to a preparation method for a titanium-magnesium double-metal composite of a double-communication netted structure to solve the problems of stress shielding and poor bioactivity caused by a high elasticity modulus of traditional biochemical metal materials such as stainless steel and a titanium alloy. The preparation method comprises the steps that a magnesium alloy with a low elasticity modulus and good osteogenic induction performance is permeated into porous titanium with a low elasticity modulus through a permeation method after being melted; and the titanium-magnesium double-metal composite of the double-communication netted structure is prepared through cooling. The preparation method is used for preparing the titanium-magnesium double-metal composite of the double-communication netted structure.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Polyetheretherketone composite material and bone repairing body as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102643514ARandom combinationSimple processProsthesisBarium titanateBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a fluorapatite / barium titanate / polyetheretherketone composite material as well as a preparation method and application of the composite material. The preparation method comprises the following step of: carrying out melt blending and extrusion granulating on fluorapatite, barium titanate and polyetheretherketone, wherein the use amount of fluorapatite is 10-30wt%, the use amount of barium titanate is 10-40wt%, and the use amount of polyetheretherketone is 50-60wt%. The invention also discloses a bone repairing body and a preparation method of the bone repairing body. The composite material has excellent biological activity and biocompatibility, and better mechanical compatibility with bone tissue, and can stimulate bone growth, accelerate bone healing and reduce the healing time of the material is implanted to the bone. The preparation method is simple and feasible in process. The bone repairing body has excellent biocompatibility, biological activity, bone mechanical compatibility and microorganism resistance, thereby shortening the bone healing time, and is high in strength, good in fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance and long in service life, thereby meeting the clinical bone repairing requirements.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
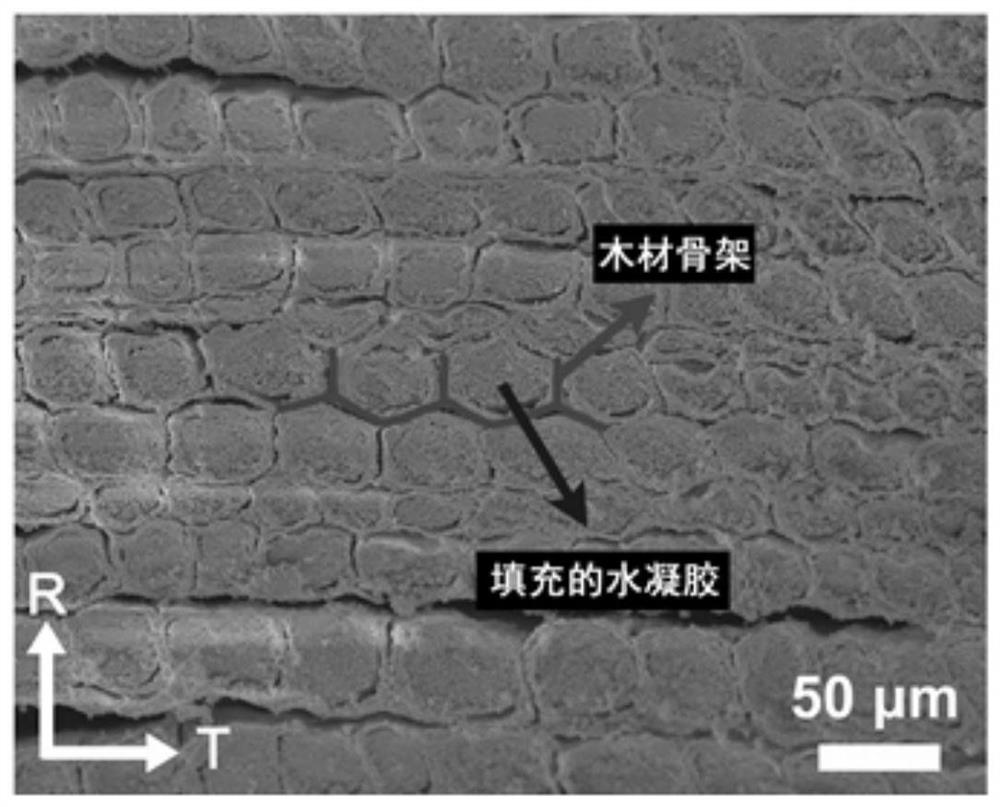
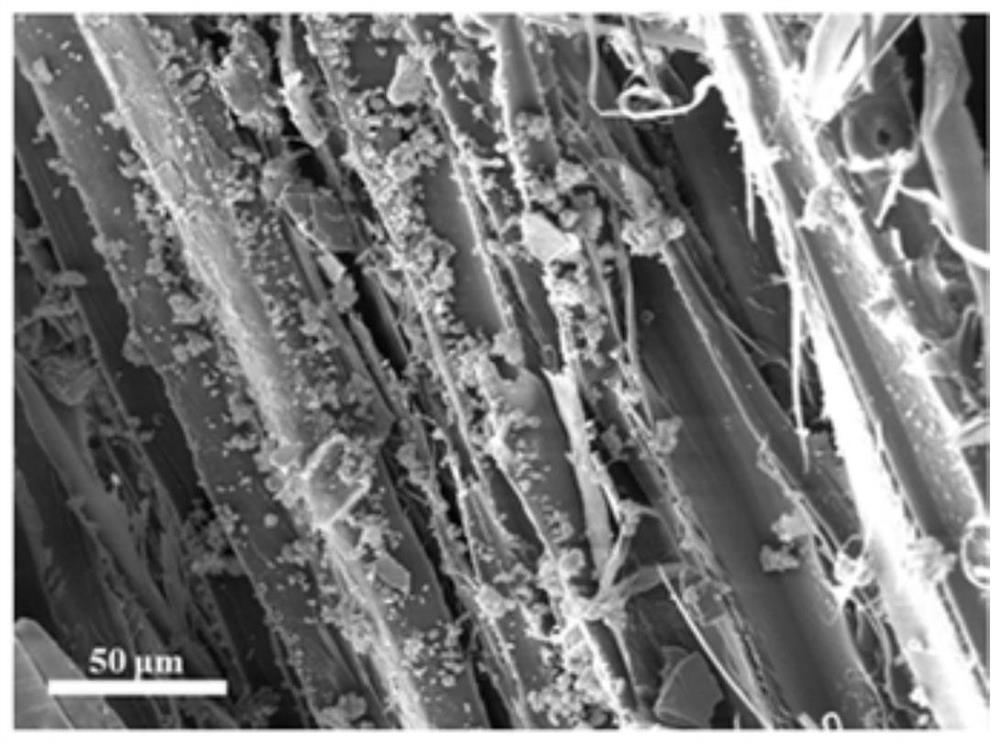
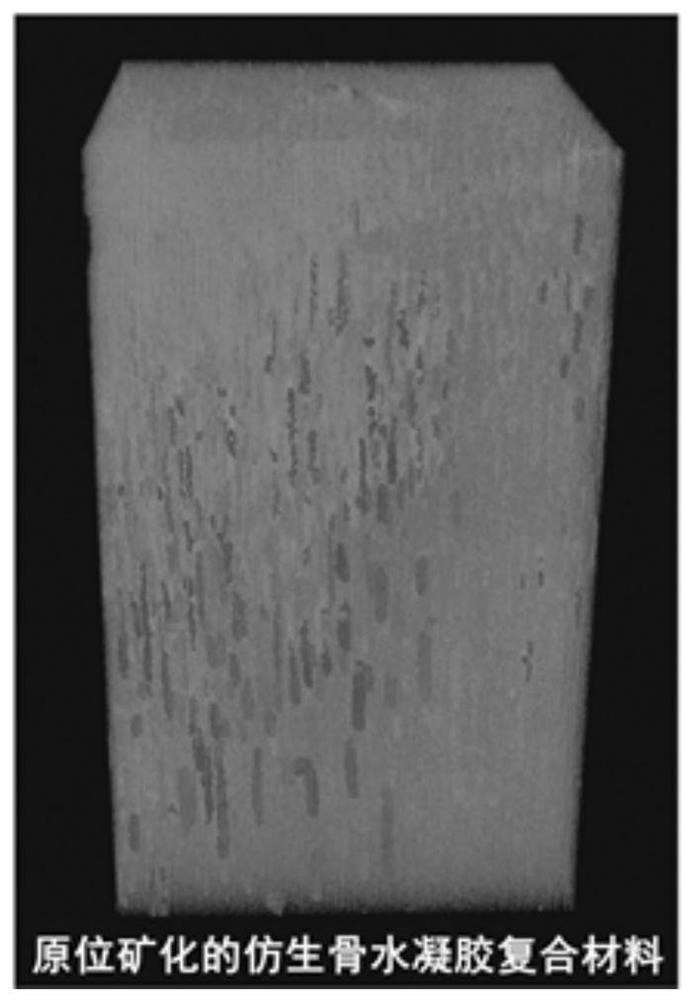
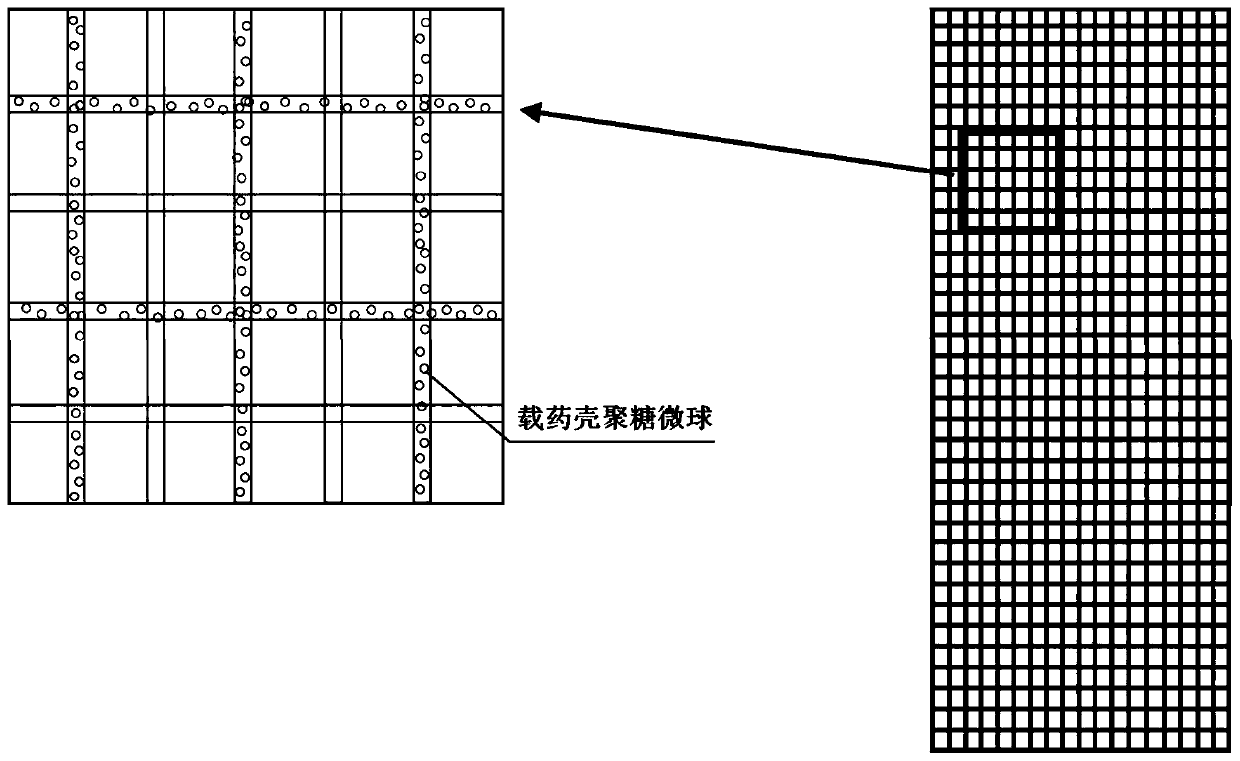
In-situ mineralized bionic bone hydrogel composite material with oriented structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112402695APromote new bone growthGood osseointegration and mechanical stabilityTissue regenerationProsthesisOsteoblast adhesionMacromolecule
The invention relates to an in-situ mineralized bionic bone hydrogel composite material with an oriented structure as well as a preparation method and application thereof, which comprises a natural plant fiber template, natural polymer hydrogel directionally filled in the natural plant fiber template and hydroxyapatite directionally deposited in the natural plant fiber template. The hydrogel composite material has a three-dimensional porous structure and is anisotropic, which overcomes the problem of uneven distribution of hydroxyapatite particles in the hydrogel matrix; the material has super-strong tensile strength, compression strength, bending strength and toughness, and the mechanical properties are matched with those of hard bone tissues. The material is beneficial to induce pre-osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic differentiation, promote new bone growth, has good osseointegration and mechanical stability, and is suitable for large-area hard bone tissue repair; in addition, the material has adjustable surface activity, and fine adjustment and control of the structure and the surface can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Porous PCL-TCP (polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate) artificial bone scaffold with drug sustained release function and preparation method of porous PCL-TCP artificial bone scaffold
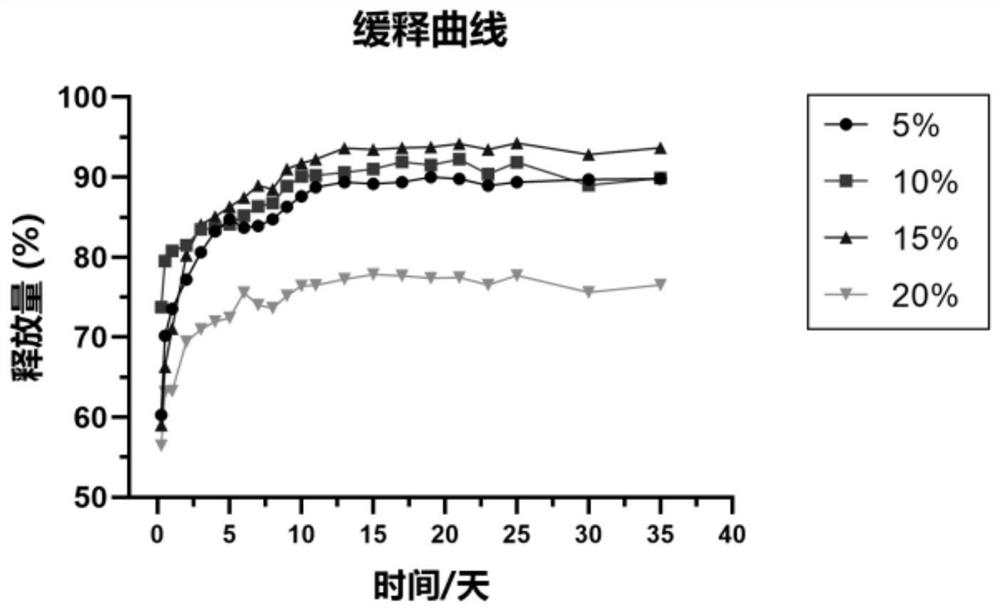
ActiveCN110279896AGood mechanical support and degradable propertiesHigh activityTissue regenerationMicrocapsulesPhosphateNatural bone
The invention provides a preparation method of a porous PCL-TCP (polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate) artificial bone scaffold with a drug sustained release function. The PCL-TCP artificial bone scaffold prepared with the method has biological activity and regular pore diameter, the porosity is higher than or equal to 60%, the pore diameter is in a range of 300-500 mu m, the compressive strength is higher than or equal to 20 MPa, the compression modulus is 0.5-1 GPa, the degradation time of the PCL-TCP artificial bone scaffold is gradually prolonged from the edge layer to the middle layer, the degradation time of the middle layer of the scaffold is 1-3 years, the degradation time of the edge layer is 2-6 months, besides, composite printing with chitosan microspheres / collagen wires is performed, chitosan microspheres wrap a drug for promoting bone formation, and the sustained release function of the drug is played. The prepared PCL-TCP artificial bone scaffold has elasticity modulus and mechanical strength which are close to those of natural bone tissue, a porous structure and the chitosan microspheres in the porous structure can realize sustained release of the drug for promoting bone formation, new bone tissue is induced to grow, the problem about bone-material interface bonding is solved, a good osseointegration effect is realized, the PCL-TCP artificial bone scaffold has better mechanical compatibility and osseointegration capacity than a metal material, and the ideal material and preparation method are provided for overcoming poor bone healing of a patient with bone defects.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Outer-layer porous orthopedic hard implant material with integrated radial structure and function and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109666820AImprove corrosion resistanceGood modulus of elasticityTissue regenerationProsthesisImplant materialNiobium
The invention discloses an outer-layer porous orthopedic hard implant material with integrated radial structure and function and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of mechanical ball milling titanium, niobium and zirconium powder according to the proportion to obtain the Ti-Nb-Zr composite powder, mechanical ball milling titanium, niobium, zirconium and HA powder to obtain the Ti-Nb-Zr -HA powder, then mixing with the pore-forming agent ammonium bicarbonate powder to obtain the composite powder B, pre-compression molding the Ti-Nb-Zr composite powder and the composite powder B to obtain the cylinder pressed blank of the radial grading structure, and finally sintering by utilizing a pulse plasma activated sintering furnace to obtain the orthopedic hard implant material. The orthopedic hard implant material not only has a porous structure due to the outer layer, the bioactive ceramic HA is added, so that the composite material has good bone bonding, the bone integration performance and the low elastic modulus suitable for matching with bone, the orthopedic hard implant material also has excellent compression resistance due to the compact structure of the core part, can be used as a good artificial bone tissue replacement material.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Fixture of dental implant and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110223561A1Simple structureImprove osseointegration performanceDental implantsWristbandsOsseointegrationBone formation
Provided are a fixture of a dental implant and a method of manufacturing the same, and more particularly, a method of manufacturing a fixture of a dental implant easily that allows fast bone formation at an early stage and prevents infection and inflammation, and a fixture of a dental implant having an improved structure that can be manufactured by using the method of manufacturing the same. The fixture of a dental implant with an improved structure in which the performance of osseointegration is excellent and spread of inflammation is reduced, and the method of manufacturing the fixture of a dental implant easily are provided. In the method of manufacturing a fixture of a dental implant, the fixture of the dental implant in which the performance of osseointegration is excellent and spread of inflammation can be reduced, can be easily manufactured. Furthermore, in the fixture of the dental implant, the performance of osseointegration is excellent and spread of inflammation can be reduced.
Owner:HYUN YOUNG KEUN
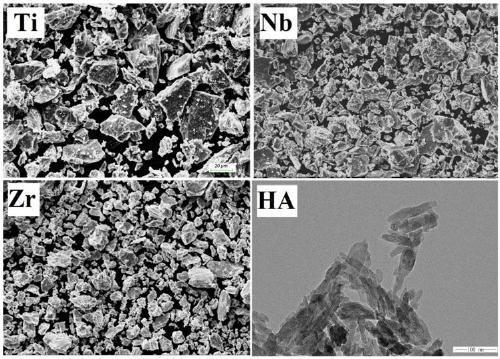
Porous titanium-tantalum-niobium-zirconium stent for bone defect repair
InactiveCN109621000AImproved lattice structureHigh strengthTissue regenerationProsthesisOsseointegrationNiobium
The invention discloses a porous titanium-tantalum-niobium-zirconium stent for bone defect repair. The porous titanium-tantalum-niobium-zirconium stent contains, by weight, 55%-65% of titanium, 1%-5%of tantalum, 30%-35% of niobium and 2%-6% of zirconium; the porous titanium-tantalum-niobium-zirconium stent has a regular porous structure, pores are completely communicated, the pores are 300-500 microns, and the porosity is 78.3 + / - 1.6%. The elastic modulus of the porous titanium-tantalum-niobium-zirconium stent is 2.27-18.96 GPa. The porous titanium-tantalum-niobium-zirconium stent has the effect of promoting bone defect repair. The regular porous structure and the completely communicated pores facilitate the growth of a new bone into a material, and a better osseointegration effect is obtained. The pores of 300-500 microns and the porosity of 78.3 + / - 1.6% promote cell adhesion, promote the healing of bone defects and the growth of bone tissues.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Artificial prosthesis of long bone diaphysis tenon and mortise structure
PendingCN107349032AImprove medium and long-term stabilityExtend your lifeFemurSkullNormal boneSurgical Manipulation
The invention relates to an artificial prosthesis of a long bone diaphysis tenon and mortise structure. A protruding face I and a rectangular protrusion I of a prosthesis proximal handle connecting part I are inserted into a strip-shaped groove II and a rectangular notch II of a prosthesis far-end handle connecting part II respectively, a protruding face II and a rectangular protrusion II of the prosthesis far-end handle connecting part are inserted into a strip-shaped groove I and a rectangular notch I of the prosthesis proximal handle connecting part I respectively, after a semicircular groove I of the prosthesis proximal handle connecting part I is in butt joint with a semicircular groove II of the prosthesis far-end handle connecting part II, a cylindrical counter bore is formed, tenon is inserted into the cylindrical counter bore formed in one end of the cylinder, and the tenon locks the connecting part I and the connecting part II together. Prosthesis fixation is firm and reliable, the operation is simple and convenient, the operation time is shortened, the operation effect and efficiency are improved, and operative complications are reduced. The artificial prosthesis can be widely applied to different defects of long bone diaphysis, the minimum osteotomy amount can reach 3.0 cm, and the maximum opportunity is provided for reserving normal bone tissue and joints as much as possible.
Owner:胡永成
3D printing Ti-hydrogel-osteoblast bone tissue engineering support and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108853578AThe overall structure is simple and reliableReliable mechanical propertiesTissue regenerationProsthesisBone tissue engineeringOsteoblast
The invention discloses a 3D printing Ti-hydrogel-osteoblast bone tissue engineering support and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of enabling Ti6Al4V powder to beprocessed into a 3D printing Ti support with a porous structure by utilizing SLM technology; then filling a hydrogel-osteoblast mixture in the pores of the 3D printing Ti support under a certain condition so as to prepare a 3D printing Ti-hydrogel-osteoblast bone defect repair support. The support has the advantages that the structure is simple and reliable, the shape and microstructure are controllable, the mechanical property is reliable, the implantation is convenient, the trauma is small, and the cost is low.
Owner:南京冬尚生物科技有限公司
Pure titanium dental implant/micro-implant and preparation method thereof
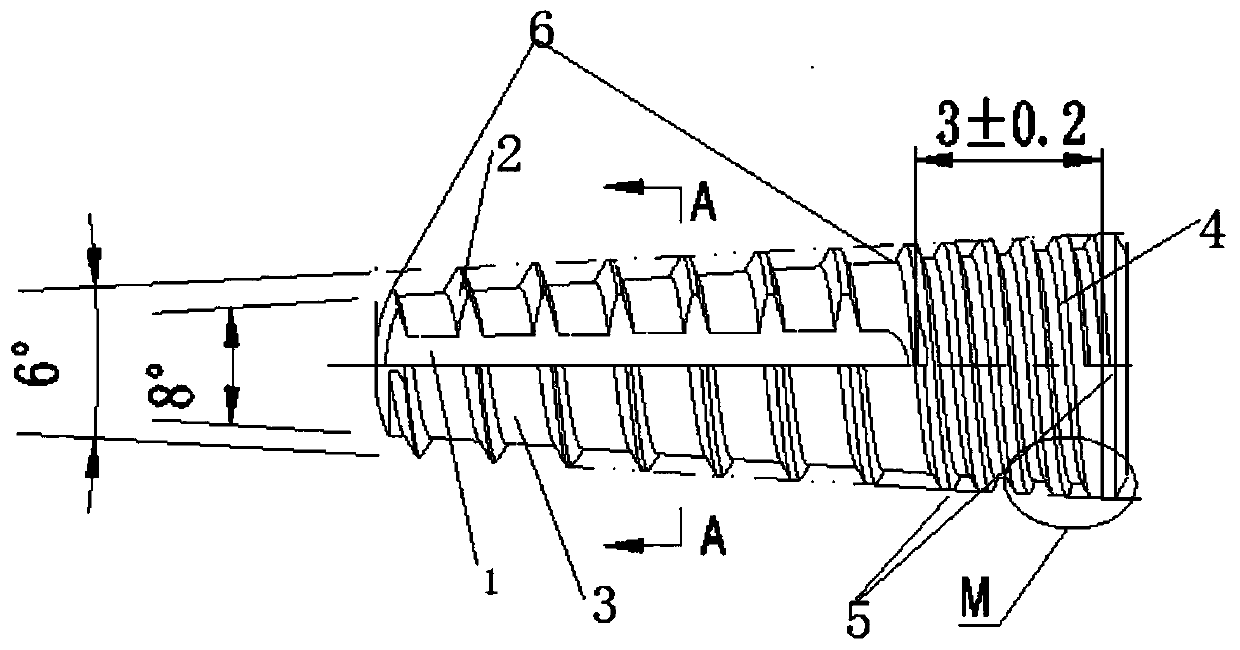
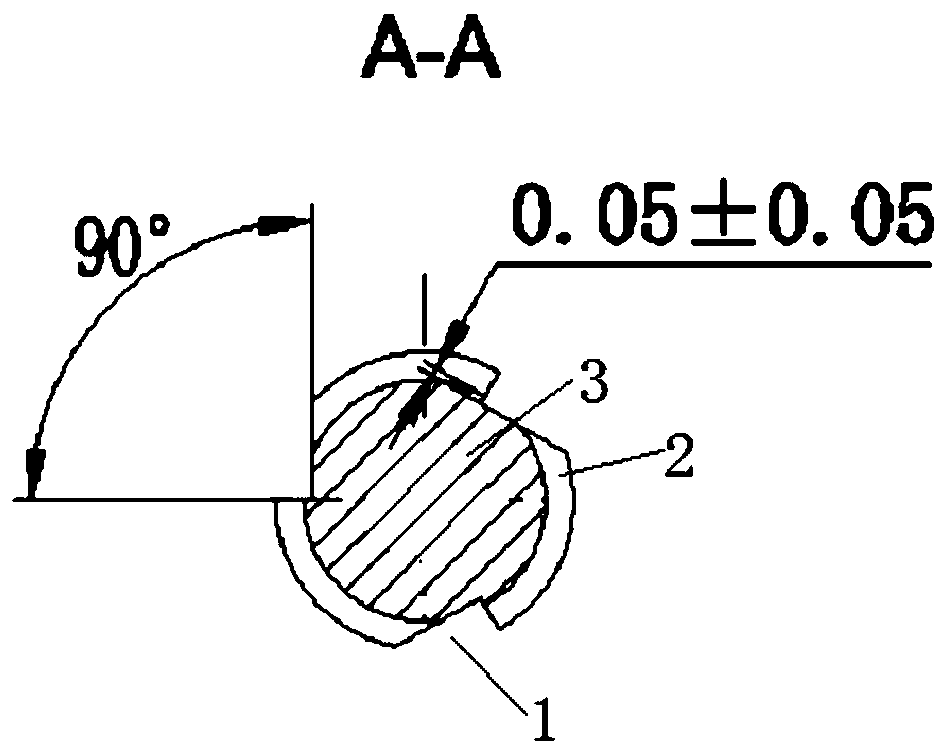
ActiveCN110063805AImprove osseointegration performanceImprove biological activityDental implantsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTitaniumDental implant
The invention belongs to the technical field of titanium dental implants, and particularly relates to a pure titanium dental implant / micro-implant and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that after a bracket is processed into a certain shape, cleaning, sandblasting, acid etching, re-cleaning and drying are carried out, wherein an acid etching mixed solution iscomposed of, by volume, 5.5%-6.5% of nitric acid, 3%-4% of hydrofluoric acid and 89.5-91.5% of purified water. The pure titanium dental implant / micro-implant and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that the biological surface activity of the titanium dental implant is high, the process is simple, low in cost and convenient and fast, and a better osseointegration effect can be obtained.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Titanium implant with bionic electro-active coating and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112791231AAvoid under-bondingImprove long-term stabilitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingTissue regenerationFerroelectric polymersTitanium surface
The invention relates to a titanium implant with a bionic electro-active coating and a preparation method, and solves the technical problem that an existing titanium implant coating is insufficient in biological activity or harmful to a human body, the titanium implant with the bionic electro-active coating is provided with the coating, the coating contains a filler and a polymer matrix, the filler is piezoelectric ceramic nano-particles, the matrix is a ferroelectric high-molecular polymer, the piezoelectric ceramic particles are uniformly dispersed in the ferroelectric polymer, and the invention also provides a preparation method of the titanium implant, so that the bionic electro-active coating can be firmly combined with the titanium surface. The method can be applied to the field of surface functional design and preparation of titanium implant materials.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY +1
Magnesium-based metal suture anchor and implanting device thereof
ActiveCN106137288AUnderstand the purposeLearn about featuresSuture equipmentsStaplesOsseointegrationSuture anchors
The invention discloses a magnesium-based metal suture anchor and an implanting device thereof, and relates to the field of medical devices. The magnesium-based metal suture anchor comprises an anchor body, an implanting rod and a draft line, wherein the anchor body is in a dovetail shape, an anchor hole is formed in the anchor body, the implanting rod is tubular, the draft line is connected with the anchor hole after passing through the implanting rod, and the implanting rod is fixedly connected with the anchor body. The invention further provides an implanting device, wherein the implanting device is a hollow sleeve, a near end is provided with a holding part, a remote end is provided with a trapezoid inclined surface, and the suture anchor and the implanting rod are inserted into the hollow part; and when drawing and pulling the draft line, the trapezoid inclined surface is used for expanding the dovetail part of the dovetail-shaped anchor body. The magnesium-based metal suture anchor provided by the invention has strong pullout resistance, can be degraded and absorbed in the organism body at a controllable degradation speed, and has excellent biocompatibility and excellent osseointegration ability.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage with bioactivity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102293693BEven by forceSolve the interface binding problemInternal osteosythesisMedical devicesMetallurgyDrug biological activity
The invention provides a porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage with bioactivity and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, inputting model data into electron beam melting equipment according to a design requirement to prepare a porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage; secondly, preparing gelatin microspheres; and immersing gelatin microsphere dry powder in an rhBMP-2 solution for gelatin coating modification, preparing a gelatin solution A in double distilled water, immersing the porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage in the gelatin solution A, mixing the rhBMP-2 gelatin microspheres and absolute ethanol to obtain suspension B, and immersing the gelatin-coating-modified porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage in the suspension B to prepare the porous titanium alloy human cervical interbody fusion cage internally containing an rhBMP-2 sustained-release system. The cervical interbody fusion cage prepared with the method has modulus of elasticity close to that of natural bone tissues, and the porous structure and the bioactivity factor sustained-release system inside the cervical interbody fusion cage can induce growth of new bone tissues, so that the binding problem of bone-material interfaces is solved. Therefore, the cervical interbody fusion cage has bettermechanical compatibility and bone integration capability than those of a compact material.
Owner:维度(西安)生物医疗科技有限公司
Anti-bacterial modified nano composite material promoting osteogenesis growth and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107469142AImprove solubilityHigh mechanical strengthTissue regenerationProsthesisNano compositesApatite
The invention discloses an anti-bacterial modified nano composite material promoting osteogenesis growth. The material is prepared from the components of 52-85% of silver carried titanium nano material, 24-56% of graphene oxide, 1-15% of nano ceramic material and 1-10% of nano apatite; PEG modification is performed and osteoblast growth contributing factors are loaded. The method is easy to operate, and the modified nano composite material has good biocompatibility and bone integrity, has a good anti-bacterial effect and strong mechanical property, makes bone cells proliferate and differentiate rapidly, and has low cell toxicity, thereby being a desired bone implant material and being capable of being applied to filling and repairing of various bone losses and bone injuries.
Owner:杨蕾
A kind of preparation method of double connected network structure titanium-magnesium bimetallic composite material
ActiveCN106670464BLow elastic modulusExcellent osteoinductive propertiesNetwork structureStress shielding
The invention relates to a preparation method for a titanium-magnesium double-metal composite of a double-communication netted structure to solve the problems of stress shielding and poor bioactivity caused by a high elasticity modulus of traditional biochemical metal materials such as stainless steel and a titanium alloy. The preparation method comprises the steps that a magnesium alloy with a low elasticity modulus and good osteogenic induction performance is permeated into porous titanium with a low elasticity modulus through a permeation method after being melted; and the titanium-magnesium double-metal composite of the double-communication netted structure is prepared through cooling. The preparation method is used for preparing the titanium-magnesium double-metal composite of the double-communication netted structure.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Medical titanium implant, preparation method thereof and application of medical titanium implant
InactiveCN113648457AGood biocompatibilityGood tensile elongation propertiesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationPharmacologyImplant
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and particularly relates to a medical titanium implant, a preparation method of the medical titanium implant and application of the medical titanium implant. The preparation method of the medical titanium implant comprises the following steps: producing a pretreated titanium matrix; dispersing the titanium matrix in a dopamine solution for polymerization reaction to obtain a composite titanium matrix of which the surface is combined with a polydopamine layer; and preparing a precursor solution containing a polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer and melatonin, and spinning the precursor solution on the surface of the composite titanium substrate to obtain the medical titanium implant. The medical titanium implant prepared by the invention has antioxidant activity, can promote the formation of new bones, and also has a proper in-vivo degradation rate, so that melatonin has a continuous and long-acting drug slow release rate, and therefore, the medical titanium implant plays a long-acting role in promoting the formation of the bones.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Surface treatment method and device for dental implant
ActiveCN107447216AImprove osseointegration performanceReduce the difficulty of positioningDental implantsSurface reaction electrolytic coatingTreatment effectBone tissue
The invention discloses a surface treatment method and device for a dental implant. According to the surface treatment method for the dental implant, the acid etching treatment process and the acid pickling treatment process are combined, a nano-scale rough surface is formed on the surface of the titanium alloy dental implant, and therefore after the titanium alloy dental implant is implanted into a human body, the rough surface can improve the osseointegration performance of the dental implant and bone tissue. Meanwhile, according to the surface treatment device for the dental implant, an automatic centering oxidation tool is arranged, and therefore the positioning difficulty of the oxidation tool can be reduced, the displacement of the oxidation tool in the moving process among stations can be avoided, the surface treatment method for the dental implant can be automatically completed, and the surface treatment effect of the dental implant can be guaranteed.
Owner:JIANGSU TRAUSIM MEDICAL INSTR
Method of manufacturing a fixture of a dental implant
InactiveUS8296951B2Simple structureImprove osseointegration performanceDental implantsWristbandsOsseointegrationDental implant
Provided are a method of manufacturing a fixture of a dental implant with an improved structure in which the performance of osseointegration is excellent, spread of inflammation is reduced and a combination force between the fixture and an alveolar bone is remarkably increased, and a fixture of a dental implant manufactured by the method. The performance of osseointegration is excellent, and spread of inflammation can be reduced, and a combination between the fixture and an alveolar bone can be remarkably improved. Furthermore, the fixture of the dental implant having the above structure can be easily manufactured.
Owner:HYUN
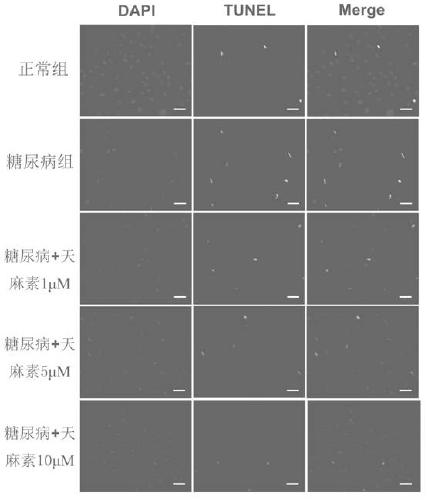
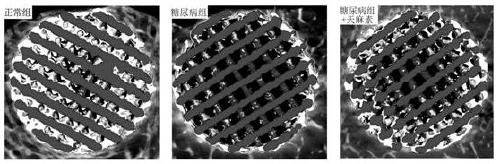
Application of gastrodin to medical titanium metal usage in diabetes environment
ActiveCN111388761AImprove osseointegration performanceReduce looseness and instabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsDiabetes mellitusOsseointegration
The invention relates to an application of gastrodin to medical titanium metal usage in diabetes environment. After a medical material is implanted into a human body, tissue repair of a 'material-bone' interface mainly relates to integration of new bone tissue and materials, wherein the osseointegration effect of the materials is determined by bioactivity and function of osteoblast responsible forosteogenic differentiation on the materials. According to the application disclosed by the invention, through osteoblast adhesive culture on the surface of medical titanium metal, an in vitro 'titanium-bone' interface model is constructed; and the gastrodin of therapeutic dose is used for performing addition culture, so that the improvement effect of the gastrodin on the biological functions of the osteoblast in the 'titanium-bone' interface is proved. The clinical problems that in the prior art, oxidative stress damage is caused to the osteoblast in the 'titanium-bone' interface by the diabetes environment, biological functions of cells are influenced, apoptosis damage is worsened, and bad osseointegration of a titanium metal implant and loosening of the titanium metal implant after a long term are finally caused, are solved, and the stability of the medical titanium metal implant is improved.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF THE NORTHERN WAR ZONE OF THE CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Preparation method of hydroxyapatite/polylactic acid composite coating on the surface of medical magnesium alloy
InactiveCN103933611BHigh strengthReduce corrosion ratePretreated surfacesMetallic material coating processesAcid etchingCalcium nitrate tetrahydrate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hydroxyapatite / polylactic acid composite coating on the surface of medical magnesium alloy, which comprises the following steps of polishing a magnesium alloy basal body to remove an oxidation layer on the surface; carrying out acid etching pretreatment and neutralizing treatment on the magnesium alloy basal body; preparing transfer solution from sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate and calcium nitrate terahydrate; preparing a biomimetic calcium-phosphate coating; dissolving polylactic acid in a chloroform solvent to prepare polylactic acid solution; immersing the prepared magnesium alloy / hydroxyapatite composite material in the polylactic acid solution, and coating the polylactic acid coating on the surface of the magnesium alloy / hydroxyapatite composite material by adopting the solution dip-coating method; and putting the magnesium alloy material for 2-3 days till chloroform in the polylactic acid solution is completely volatilized, thereby obtaining the composite material of which the surface of magnesium alloy is wrapped with the hydroxyapatite / polylactic acid composite coating. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method of the hydroxyapatite / polylactic acid composite coating on the surface of medical magnesium alloy overcomes the disadvantages of the single coating, and therefore, the corrosion resistance and the biocompatibility of magnesium alloy are obviously increased.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
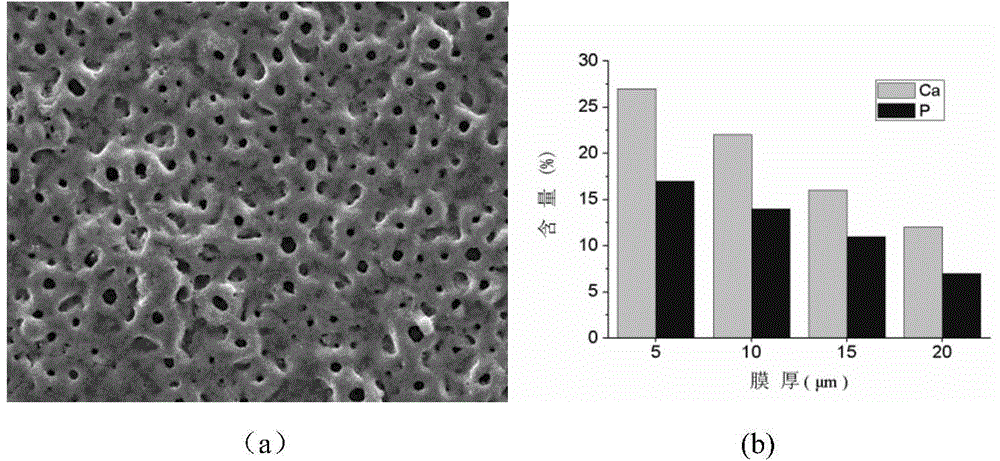
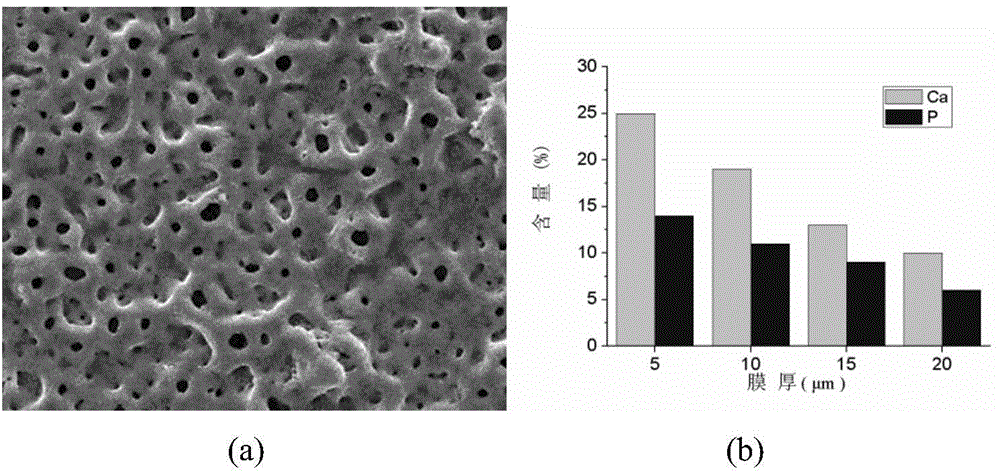
Preparation method of homoporous biological ceramic implant material having gradient calcium and phosphor content
InactiveCN103603021APromotes pore functionShort biocompatibilitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingIce waterMicro arc oxidation
The invention relates to a preparation method of a homoporous biological ceramic implant material having gradient calcium and phosphor content. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, low-temperature electrolyte preparation: preparing an electrolyte having a calcium ion concentration C(Ca) of 8-30mmol / L and a phosphorus ion concentration C(P) of 2-5mmol / L by deionized water, freezing deionized water and putting the freezed deionized water into the electrolyte to obtain an ice-water mixed low-temperature electrolyte, and 2, micro-arc oxidation treatment on titanium or a titanium alloy in the low-temperature electrolyte. Micropores of the ceramic membrane on the surface of the implant material have the same sizes and are uniform; gradient calcium and phosphor content is realized in the membrane and the inner membrane contains more calcium and phosphor elements; compared with a bone-implant interface mature period of the existing titanium implant tooth, a bone-implant interface mature period of the homoporous biological ceramic implant material is shortened to be within 3 months from 3-6 months; and biological properties satisfy prescribes of ISO, Chinese pharmacopoeia and American pharmacopeia.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A kind of surface micro-nano structure modification method of titanium and titanium alloy
ActiveCN109848546BEasy to integrateReduce usageSurface reaction electrolytic coatingLaser beam welding apparatusOrthopedics surgeryOsseointegration
Metal titanium and titanium alloy are widely applied to implants of oral prosthodontics, orthopedic surgery and plastic surgery at present, but have the problems of having poor osseous integration capability and being prone to have bacterial infection after implantation. The invention discloses a titanium and titanium alloy surface micro-nano structure modification method, and aims to improve theosseous integration capability and antibacterial capability of titanium and titanium alloy surfaces. The micro-nano structure modification method is characterized in that a femtosecond laser processing technology is adopted, the polished titanium alloy surface is ablated to form a micropost periodic structure with the spacing and the depth not greater than 200 microns, nanotubes with the diameterssmaller than 200 nm are prepared on the micropost periodic structure in an anodic oxidation mode after further acid pickling, and then annealing heat treatment is carried out to obtain a final sample. According to the method, the surface with a micro-nano structure can be prepared on the titanium and titanium alloy surfaces, and the titanium and the titanium alloy with such surfaces have good biocompatibility and antibacterial capability.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com