Carrier plant system for protecting and increasing number of rice field rice planthopper parasitic wasps
A carrier plant system and carrier plant technology are applied in the field of crop pest biological control, which can solve the problems of excessive use of chemical pesticides, excessive pesticide residues in rice, and ecological imbalance in rice fields, and achieve the effects of improving the control effect, low cost and reducing use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
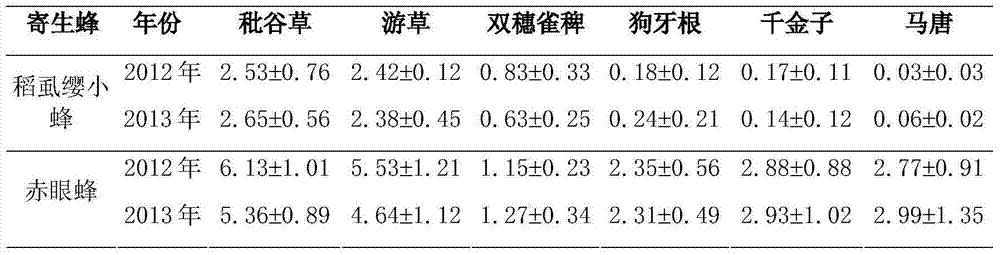
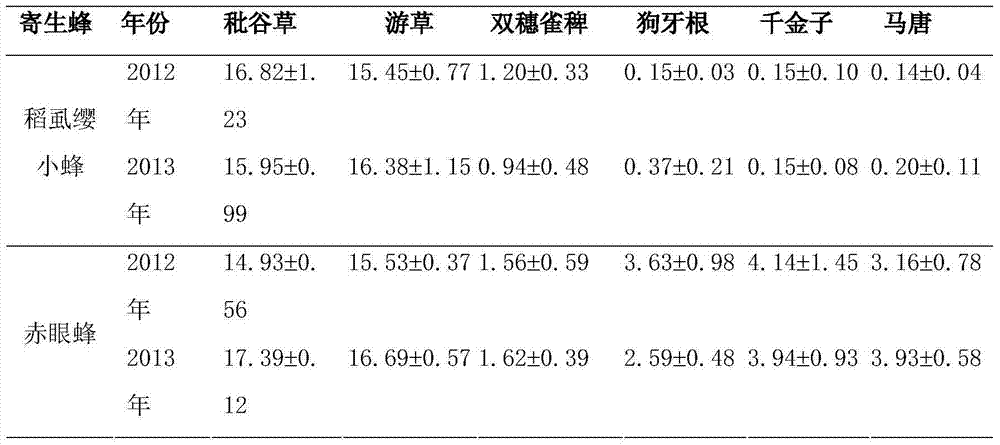
[0024] Embodiment 1, the investigation of the number of populations of Trichogramma and Trichogramma on weeds in the rice field ecosystem
[0025] In 2012 and 2013, the survey and sampling of rice planthopper parasitoids (M. japonica and Trichogramma) on common grass weeds in rice field ecosystems were carried out in Yinxian County, Ningbo, Zhejiang Province, and Wucheng District, Jinhua City, respectively. From March to May, the winter slack period is used for sampling, once every half month, a total of 4 times. The rice was sampled during the rice growth period from June to October, and the samples were taken once a month, a total of 5 times. When sampling, Qi Ni cuts various gramineous weeds, takes them back to the room and weighs them, and then puts them in a conical cage, which is covered with black cloth. Collect the eclosion parasitoids and collect them once a day until all the parasitoids have emerged. The parasitic wasp specimens were preserved with 70% alcohol, and...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Effects of Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Levels on the Growth, Development and Population Reproduction of Pseudo-Nilaparvata lugens on P.
[0032] Different levels of nitrogen fertilizer (0, 125, 250kg / ha) were applied to the potted corngrass and freegrass. A single plant of corngrass and freeweed was placed in a test tube with nutrient solution, and pseudo-N. lugens was raised in a single tube. One newly hatched worm was connected to each tube, and the molting and survival conditions were recorded every day. After eclosion, the weight of the first feathered female was weighed, and the male and female were paired to lay eggs, and the life span and egg production were recorded. When the eggs were completely hatched, the number of hatched eggs was recorded, and the unhatched eggs were dissected to record the hatching rate. Based on the above observations of adults, eggs and nymphs, the population trend index of the two species of BPH on different plants was cal...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3, lifespan, oviposition and reproduction of brown planthopper and pseudo brown planthopper on different plants
[0040] Nitrogen fertilization levels of rice (variety TN1), corngrass and free grass are all 250kg / ha, potted seedlings are covered with polyethylene cages, and each cage is inserted with one adult female and one male adult of the same species of brown planthopper or pseudo brown planthopper. For pairing, more than 15 pairs were observed repeatedly for each plant. After connecting the test worms, observe and record their survival every day. After the nymphs began to hatch, the hatched nymphs were counted every other day. After no nymphs hatched until 5 days, the number of unhatched eggs on the plants was observed and recorded under a dissecting microscope. Calculate the total egg production (the sum of the number of hatched nymphs and unhatched eggs), the hatching rate of eggs and the life span of male and female adults.
[0041] For plants capa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com