High-efficiency phosphate-solubilizing aspergillus japonicus with heavy metal tolerance
A technology of Aspergillus and heavy metals, applied in the field of environmental biology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Example 1: Screening and Identification of Phosphorus Solubilizing Aspergillus japonicus
[0016] The Aspergillus japonicus strain of this embodiment is isolated and screened from the surface soil of a lead-zinc mine in Huayuan County, Xiangxi Prefecture, Hunan Province. The screening is carried out as follows: the collected soil is immediately brought back to the laboratory, air-dried, ground, and sieved, and 10.0 g of the sieved soil is placed in 100 ml of sterile water with glass beads to make a soil suspension , the concentration of this suspension is 10 -1 ,. Place the suspension on a constant temperature oscillator at 150 rpm for 30 minutes, take it out and let it stand for a while, take 10ml from the sample suspension and add it to 90ml of sterile water, and the concentration of the suspension is 10 -2 , and then perform 10-fold serial dilution in this way until the concentration of the diluent is 10 -4 until. take 10 -4 Concentration of bacterial suspensio...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Embodiment 2: Phosphorus-solubilizing test of phosphorus-solubilizing Aspergillus japonicus to insoluble phosphate
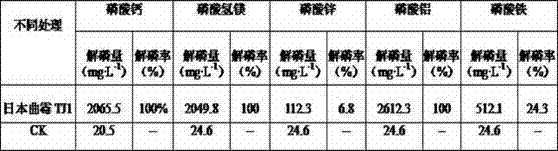
[0018] Select five insoluble phosphates and make the following medium
[0019] Phosphate-dissolving medium 1: glucose 10.0g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.5g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3g, NaCl 0.3g, KCl 0.3g, FeSO 4 0.03g, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.03g, yeast powder 0.5g, Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 10g, distilled water l000ml, pH7.0.
[0020] Phosphate-dissolving medium 2: Magnesium hydrogen phosphate (MgHPO 4 ) instead of Ca in phosphate-solubilizing medium 1 3 (PO 4 ) 2 , other components and contents remain unchanged.
[0021] Phosphate-dissolving medium 3: zinc phosphate (Zn 3 (PO 4 ) 2 Instead of Ca in Phosphorus Solubilizing Medium 1 3 (PO 4 ) 2 , other components and contents remain unchanged.
[0022] Phospholytic medium 4: with aluminum phosphate (AlPO 4 ) instead of Ca in phosphate-solubilizing medium 1 3 (PO 4 ) 2 , other components and contents remain uncha...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Embodiment 3: the dynamic change of phosphorus solubilizing property of Aspergillus japonicus
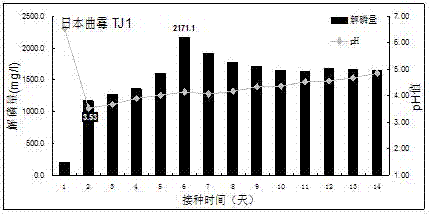
[0030] The above strains were inoculated on a PDA plate, and after culturing for 5 days, a spore suspension was prepared with sterile water, and the concentration of the spore suspension was determined to be 1.6×10 by hemocytometer. 7 spores / mL, inoculated into 50ml modified Montina liquid medium according to the inoculation amount of 1mL / bottle, and set as blank control group with no inoculation at the same time, add 1ml sterile water in each bottle of blank group, each treatment Repeat for three bottles. Place in a shaker at 28° C., shake culture at 150 rpm, detect the content of soluble phosphorus in the supernatant and the pH value of the medium every 24 hours, and measure continuously for 14 days. see results figure 1 shown.
[0031] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the phosphorus-dissolving ability of the above-mentioned strains has been tested for 14 days. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com