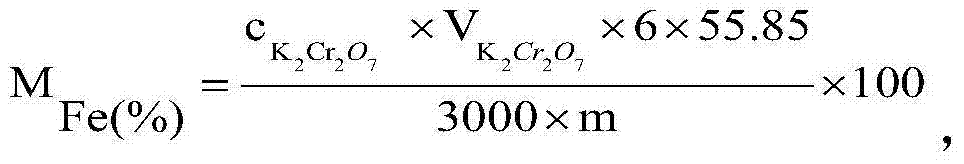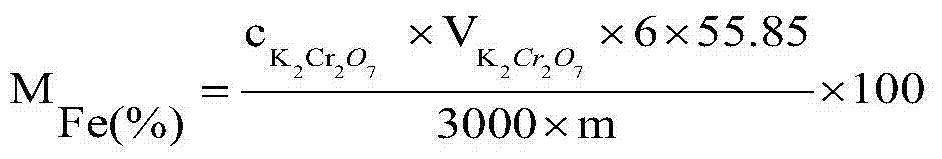Method for measuring iron content in direct reduction iron of steelmaking auxiliary material
A determination method and technology for reducing iron, applied in the direction of chemical analysis by titration, can solve the problems of large measurement error, difficult determination of metallic iron content, incomplete sample dissolution, etc., to avoid oxidation loss, improve accuracy and The effect of precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for measuring total iron content in steelmaking auxiliary material direct reduced iron, comprising the following steps:
[0026] 1) Sample particle size, blank test and measurement times
[0027] 1.1) Sample particle size: The sample particle size should be less than 0.125mm (less than 120 mesh).
[0028] 1.2) Blank test: do a blank test together with the sample, and the reagents used must be taken from the same reagent bottle.
[0029] 1.3) Measurement times: the same sample, in the same laboratory, should be measured twice by the same operator.
[0030] 1.4) Calibration test: analyze the standard sample with similar content of the same type along with the sample.
[0031] 2) Devices and reagents
[0032] 2.1) Erlenmeyer flask with stopper (200mL)
[0033] 2.2) S21-2 electromagnetic stirrer
[0034] 2.3) M-50 sand core filter movable device
[0035] 2.4) Qualitative filter paper
[0036] 2.5) Suction filter bottle (200mL)
[0037] 2.6) Burette with plu...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The method for measuring the total iron content in steelmaking auxiliary material direct reduced iron comprises the following steps:
[0062] 1) Sample particle size, blank test and measurement times
[0063] 1.1) Sample particle size: The sample particle size should be less than 0.125mm (less than 120 mesh).
[0064] 1.2) Blank test: do a blank test together with the sample, and the reagents used must be taken from the same reagent bottle.
[0065] 1.3) Measurement times: the same sample, in the same laboratory, should be measured twice by the same operator.
[0066] 1.4) Calibration test: analyze the standard sample with similar content of the same type along with the sample.
[0067] 2) Devices and reagents
[0068] 2.1) Erlenmeyer flask with stopper (100mL)
[0069] 2.2) S21-2 Electromagnetic Stirrer
[0070] 2.3) M-50 sand core filter movable device
[0071] 2.4) Qualitative filter paper
[0072] 2.5) Suction filter bottle (500mL)
[0073] 2.6) Burette with...
Embodiment 3
[0096] The method for measuring the total iron content in steelmaking auxiliary material direct reduced iron comprises the following steps:
[0097] 1) Sample particle size, blank test and measurement times
[0098] 1.1) Sample particle size: The sample particle size should be less than 0.125mm (less than 120 mesh).
[0099] 1.2) Blank test: do a blank test together with the sample, and the reagents used must be taken from the same reagent bottle.
[0100] 1.3) Measurement times: the same sample, in the same laboratory, should be measured twice by the same operator.
[0101] 1.4) Calibration test: analyze the standard sample with similar content of the same type along with the sample.
[0102] 2) Devices and reagents
[0103] 2.1) Erlenmeyer flask with stopper (100mL)
[0104] 2.2) S21-2 Electromagnetic Stirrer
[0105] 2.3) M-50 sand core filter movable device
[0106] 2.4) Qualitative filter paper
[0107] 2.5) Suction filter bottle (500mL)
[0108] 2.6) Burette with...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com