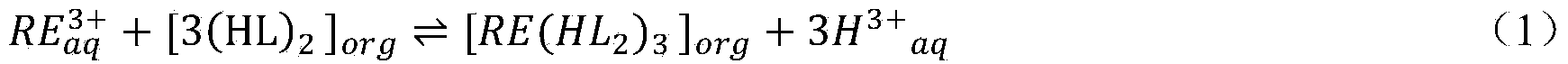Extraction system, extraction method and reextraction method
An extraction and system technology, applied in the direction of recycling materials, improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of poor separation of heavy rare earths, easy emulsification, and low purity of extractants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
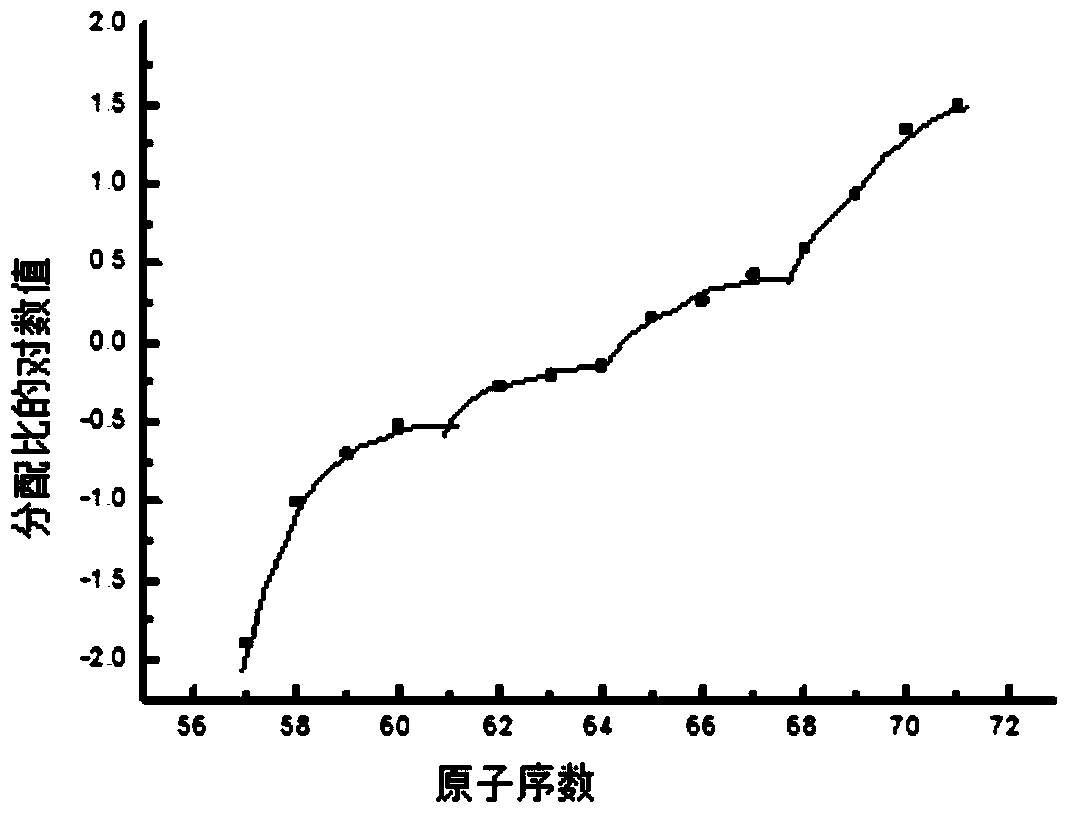
[0045] The molar concentration of extractant P227 in benzene is 0.2mol / L, wherein, the pH value in the aqueous phase containing rare earth ions is 2.5, the molar concentration of rare earth ions in water is 0.01mol / L, and the salting-out agent is sodium chloride, The molar concentration is 1mol / L, the ratio of the organic phase to the aqueous phase is 2:1, and the shaking time is 20min. After oscillating and equilibrating the phase separation, analyze the concentration of rare earth ions in the aqueous phase or back-extracted organic phase. The extraction data are shown in Table 1. Among them, the average separation coefficient is 3.16, which is much higher than the reported data, and its four-group effect is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the so-called four-group effect is: La, Ce, Pr, Nd are the first group; Sm, Eu, Gd are the second group; Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho are the third group; Y, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu belong to the fourth group, and Gd is a common element of the second group and...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The molar concentration of the sodium salt of extractant P227 in kerosene is 0.2mol / L, wherein, the pH value in the water phase containing rare earth ions is 2.5, the molar concentration of rare earth ions in the water phase is 0.01mol / L, and the salting-out agent is Sodium chloride, its molar concentration is 1mol / L, the ratio of organic phase to water phase is 2:1, and the shaking time is 20min. After oscillating and balancing phase separation, the concentration of rare earth ions in the aqueous phase or back-extracted organic phase was analyzed. The extraction data was the same as that of the experiment done in Example 1. The data are shown in Table 1. It can be seen that the results of saponification of the extractant are basically consistent with the experimental data without saponification, which provides a certain reference for industrial applications.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The molar concentration of extractant P227 in n-dodecane is 0.5mol / L, wherein, the pH value in the aqueous phase containing rare earth ions is 2.8, the molar concentration of rare earth ions in the aqueous phase is 0.01mol / L, and the salting-out agent is Sodium chloride, its molar concentration is 1mol / L, the ratio of the organic phase to the aqueous phase is 1:1, and the shaking time is 30min. After oscillating and equilibrating the phase separation, analyze the concentration of rare earth ions in the aqueous phase or back-extracted organic phase. The extraction data are shown in Table 2. Among them, the average separation coefficient is 3.32, which is much higher than the reported data, and its four-group effect is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the so-called four-group effect is: La, Ce, Pr, Nd are the first group; Sm, Eu, Gd are the second group; Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho are the third group; Y, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu belong to the fourth group, and Gd is a common element of the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com