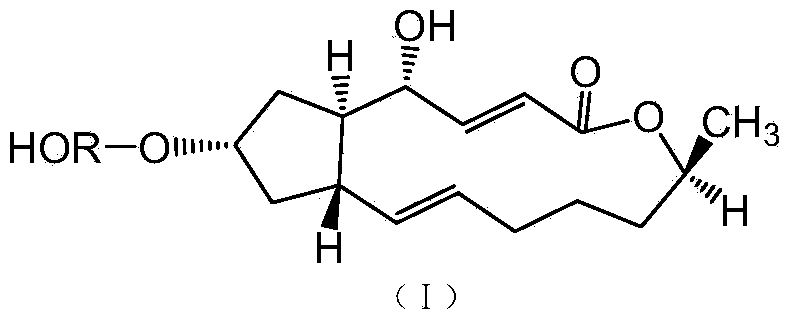
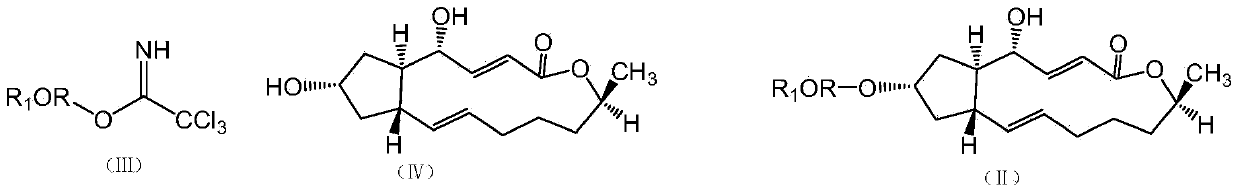
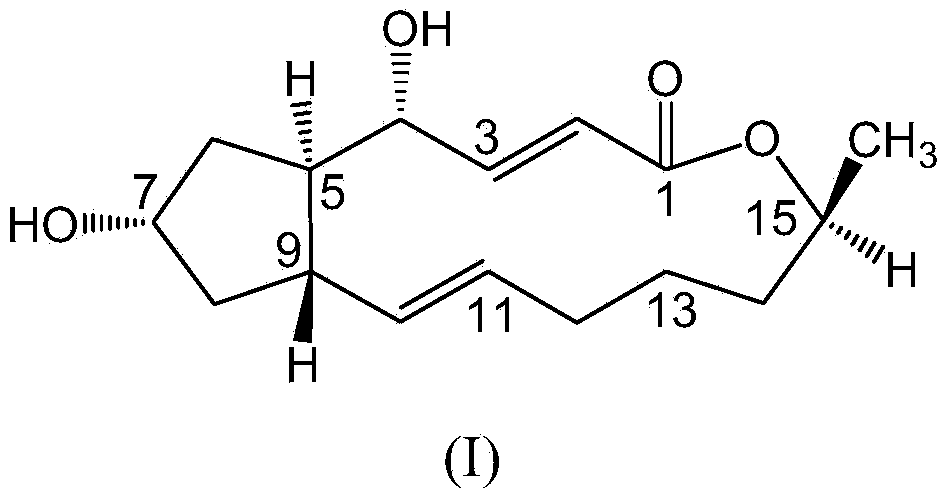
Brefeldin A glycosylated derivative and preparation and application thereof
A technology of brefeldin and brefeldin bacteria, applied in the field of preparation of brefeldin A glycosylated derivatives, can solve normal somatic cell toxicity, short half-life, brefeldin A water solubility Low-level problems, to achieve the effect of retaining tumor suppressor activity and enhancing water solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: 7-O-(D-α-glucose)-brefeldin A
[0028] (1) 7-O-(2,3,4,6-tetraacetyl-D-α-glucose)-brefeldin A
[0029]
[0030] Weigh 0.8 g of trichloroacetimidate-2,3,4,6-tetraacetyl-D-α-glucoside and 0.2 g of brefeldin A solid powder, dissolve in 30 ml of anhydrous di Chloromethane, add 0.5 g activated 4 Molecular sieves, stirred magnetically at room temperature (25°C) for 30 minutes to remove water, cooled methanol to reflux to -30°C, then added 40 microliters of boron trifluoride ether and 0.5 g of activated 4 Molecular sieves were reacted with magnetic stirring for 4 hours. After the reaction, the reaction solution was filtered to obtain filtrate c and filter cake, the filter cake was rinsed with 30 ml of dichloromethane, the washing liquid and filtrate c were combined, washed 3 times with saturated saline, and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate , filtered to obtain the filtrate d, the filtrate d was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the concentrate was...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: 7-O-(D-α-mannose)-brefeldin A
[0039] (1) 7-O-(2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-D-α-mannopyranose)-brefeldin A
[0040]
[0041] Weigh 0.5 g of 1-trichloroacetimidate-2,3,4,6-tetraacetyl-D-α-mannose, dissolve it in 30 ml of anhydrous dichloromethane, add 0.50 g of activated 4 Molecular sieves and 0.2 g of brefeldin A powder were magnetically stirred at room temperature (25°C) for 30 minutes, cooled and refluxed to -30°C with methanol, and then 40 μl of boron trifluoride ether and 0.5 g of activated 4 Molecular sieves, stirred and reacted at -30°C for 4 hours. Other operations were the same as in Example 1 to obtain 127 mg of light yellow powder.
[0042] Compound Characterization:
[0043] 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 )δ7.28(m,1H),5.92(d,J=15.6Hz,1H),5.82–5.57(m,1H),5.12(dd,J=8.7,4.5Hz,1H),4.85(dd,J =10.4,5.7Hz,1H),4.11(d,J=8.7Hz,1H),2.49–2.05(m,4H),2.20,2.07,2.09,2.29(12H),2.03(d,J=27.9Hz, 1H),1.93–1.78(m,3H),1.77–1.69(m,1H),1.67–1.57(m,1H),1.69–1.58(m,1H),1.5...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: 7-O-(D-α-glucosamine)-brefeldin A
[0050] (1) 7-O-(3,4,6-Triacetyl-2-deoxy-D-α-glucosamine)-brefeldin A
[0051]
[0052] Weigh 0.5 g of trichloroacetimidate glucosamine and 0.2 g of brefeldin A, dissolve in 30 ml of anhydrous dichloromethane, add 0.5 g of activated 4 Molecular sieves, stirred at 0°C for 30 minutes. Use methanol to cool and reflux to -30°C, then add 40 microliters of boron trifluoride ether and 0.5 grams of activated 4 Molecular sieves, react at -30°C for 4 hours. Other operations were the same as in Example 1 to obtain 84 mg of light yellow solid.
[0053] Compound Characterization:
[0054] 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 )δ7.28(m,1H),5.92(d,J=15.6Hz,1H),5.82–5.57(m,1H),5.12(dd,J=8.7,4.5Hz,1H),4.85(dd,J =10.4,5.7Hz,1H),4.11(d,J=8.7Hz,1H),2.49–2.05(m,4H),2.20,2.07,2.09,2.29(12H),2.03(d,J=27.9Hz, 1H),1.93–1.78(m,3H),1.77–1.69(m,1H),1.67–1.57(m,1H),1.69–1.58(m,1H),1.57–1.45(m,1H),1.26( t,J=6.2Hz,3H),0.92(dd,J=19.6,12.7Hz,1H). 13 C NMR ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com