Sensor device capable of controlling insertion angle in subcutaneous tissue
A sensor device and subcutaneous tissue technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of restricting the promotion and application of subcutaneous dynamic monitoring products, unfavorable, high signal-to-noise ratio and background elimination, etc., to achieve rapid withdrawal, good effect and fast implantation speed Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0074] The following descriptions are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and do not limit the scope of the present invention.
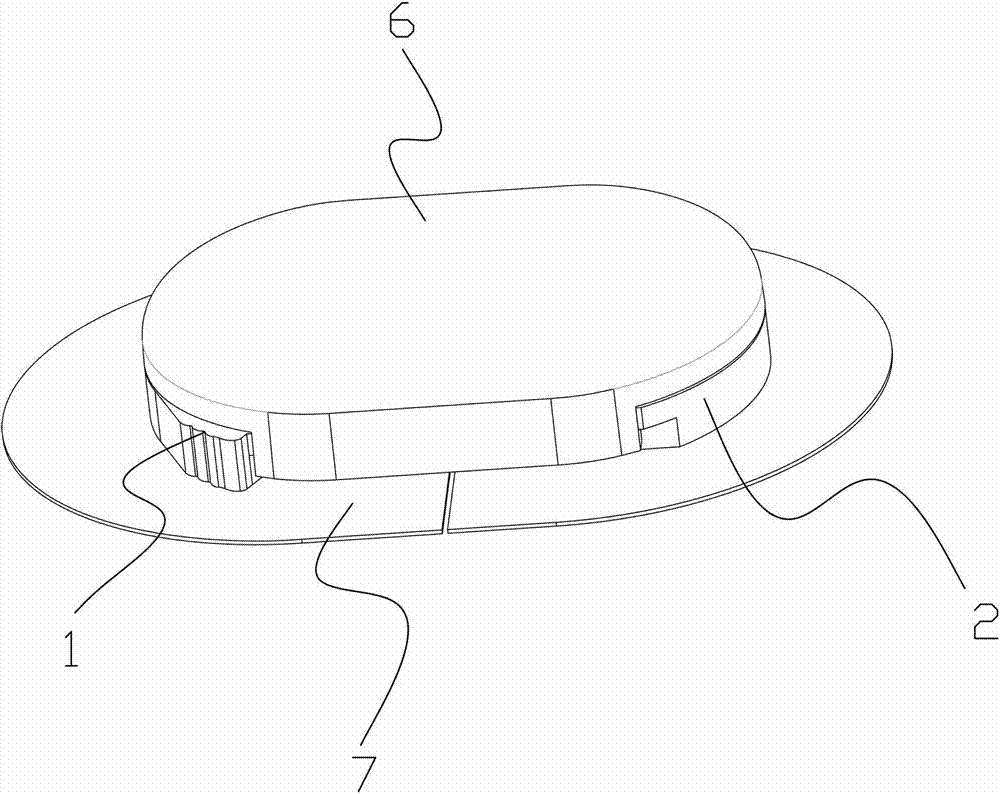
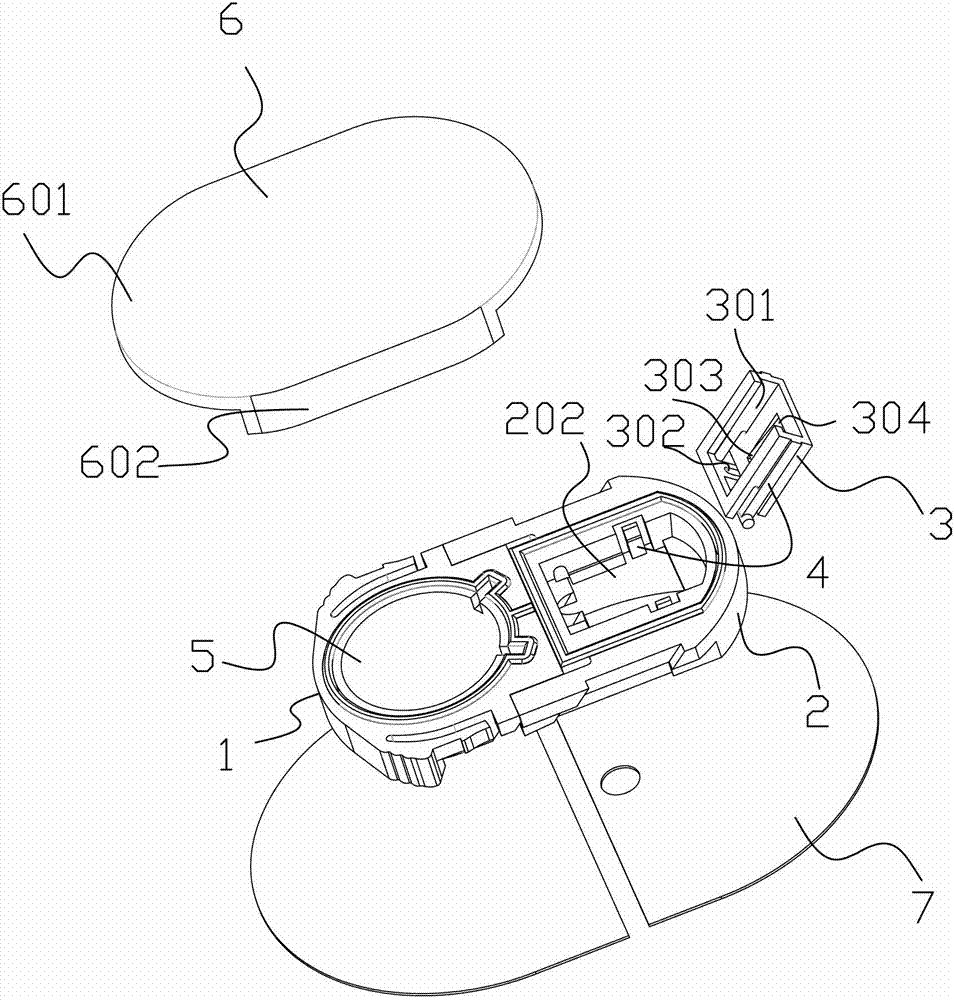
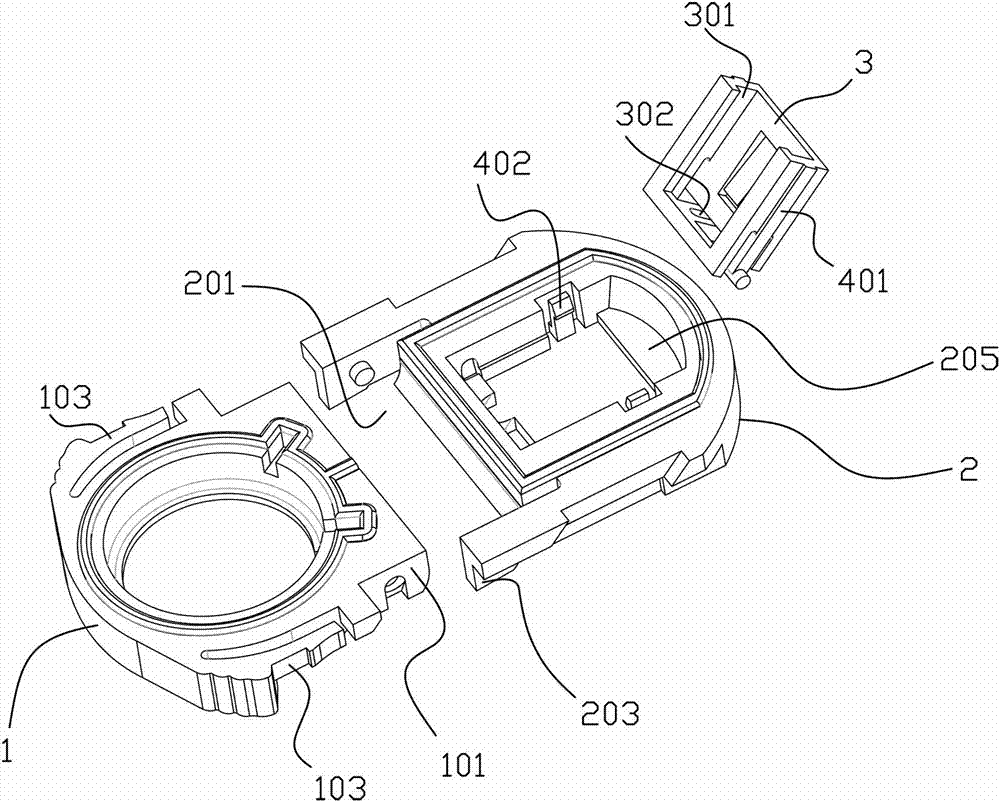
[0075] Examples, see attached figure 1 , 2 , 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, the sensor device in the subcutaneous tissue that can control the implantation angle, including the fixing base 1 that can be fixed with the skin and the The implant seat 2 is provided with a hard needle tube passage port 204 on the implant seat 2, which is convenient for the passage of the hard needle tube and the implanted biosensor; the implant seat and the fixed seat are made of sheet-shaped plastic, which are transparent, rounded corners; the implant base 2 and the fixed base 1 can be rotatably connected, can be hinged, pivoted, etc., can also be connected by hinges, or connected by materials that are easy to bend, such as rubber sheets, polyurethane sheets etc., so that the implant base 2 can rotate around the fixed base 1; The opening part 201...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com