Separation and utilization method of NdFeB waste
A technology of neodymium iron boron and waste materials, which is applied in the direction of recycling technology, chemical instruments and methods, iron compounds, etc., can solve the problems of low recovery rate, impracticality, high resource consumption, etc., to reduce the cost of separation and recovery, improve recovery rate, High economical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The present invention comprises the following sequential steps:
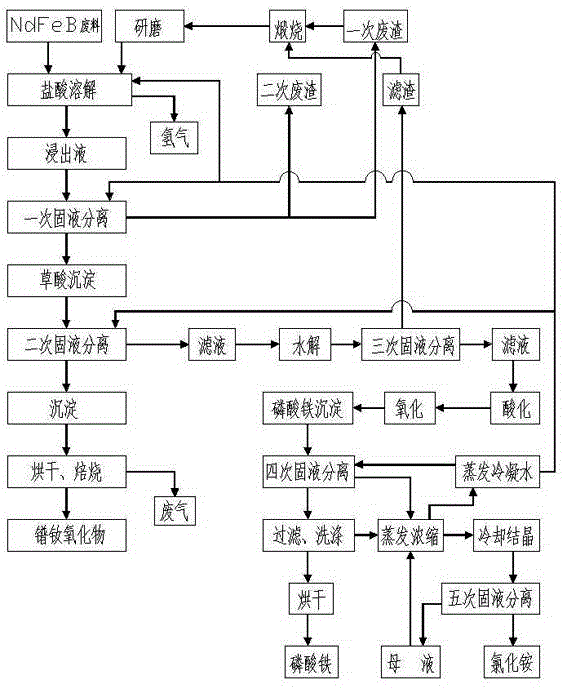
[0031] A. Hydrochloric acid dissolution: Add 20% hydrochloric acid to 1 ton of NdFeB waste (the total amount of rare earth is about 25%) for acid hydrolysis. The hydrochloric acid is obtained by diluting 32% industrial hydrochloric acid with deionized water. Hydrochloric acid The mass ratio to NdFeB waste is 2:1, the acid hydrolysis temperature is 95°C, and the acid hydrolysis time is 3 hours, so that the NdFeB waste is fully dissolved by hydrochloric acid, and the pH value at the end of the acid hydrolysis reaction is 2;
[0032] B. Primary solid-liquid separation: pass the solution in step A through a plate and frame filter press for solid-liquid separation to obtain about 150kg of primary filter residue (the total amount of rare earth is about 8%), and the primary filter residue is calcined at 450°C to fully oxidize the filter residue , to reduce the consumption of hydrochloric acid, after the high-t...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The present invention comprises the following sequential steps:
[0045] A. Hydrochloric acid dissolution: Add 20% hydrochloric acid to 1 ton of NdFeB waste (the total amount of rare earth is about 25%) for acid hydrolysis. The hydrochloric acid is obtained by diluting 32% industrial hydrochloric acid with deionized water. Hydrochloric acid The mass ratio to NdFeB waste is 2:1, the acid hydrolysis temperature is 100°C, and the acid hydrolysis time is 2.5 hours, so that the NdFeB waste is fully dissolved by hydrochloric acid, and the pH value at the end of the acid hydrolysis reaction is 1.8;
[0046] B. Primary solid-liquid separation: pass the solution in step A through a plate and frame filter press for solid-liquid separation to obtain a primary filter residue of about 150kg (the total amount of rare earth is about 8%), and the primary filter residue is calcined at 550°C to fully oxidize the filter residue , to reduce the consumption of hydrochloric acid, after the...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The present invention comprises the following sequential steps:
[0059] A. Hydrochloric acid dissolution: Add 23% hydrochloric acid to 1 ton of NdFeB waste (the total amount of rare earth is about 25%) for acid hydrolysis. The hydrochloric acid is obtained by diluting 32% industrial hydrochloric acid with deionized water. Hydrochloric acid The mass ratio to NdFeB waste is 2:1, the acid hydrolysis temperature is 105°C, and the acid hydrolysis time is 2.5 hours, so that the NdFeB waste is fully dissolved by hydrochloric acid, and the pH value at the end of the acid hydrolysis reaction is 1.6;
[0060] B. Primary solid-liquid separation: pass the solution in step A through a plate and frame filter press for solid-liquid separation to obtain a primary filter residue of about 150kg (the total amount of rare earth is about 8%), and the primary filter residue is calcined at a high temperature of 600°C to fully oxidize the filter residue , to reduce the consumption of hydroc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com