Laser lift-off method for flexible electronic application of sapphire substrate of gallium nitride LED
A sapphire substrate, laser lift-off technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problem of lack of chemical etchant for sapphire, and achieve the effect of a simple and fast method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
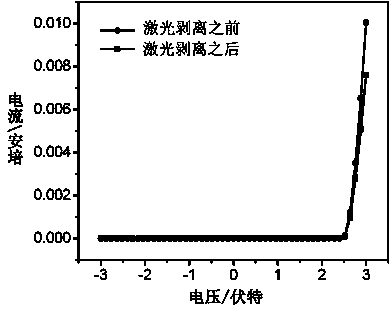
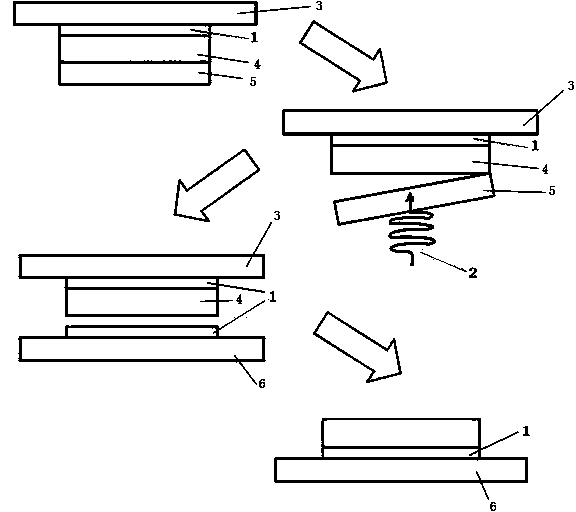
[0022] The principle of action of laser lift-off is based on the difference in bandgap between gallium nitride and sapphire. Sapphire has an optical bandgap of 8.7 eV, and GaN has an optical bandgap of 3.5 eV. Light with wavelengths between 143 nm and 354 nm will pass through sapphire but be absorbed by GaN. When light in this range is incident from the sapphire substrate, it will pass through the sapphire and be absorbed by the gallium nitride in the interface region to generate heat. If this light is emitted by a laser with high power and short action time, enough heat can be generated in the interface area to decompose gallium nitride into metal gallium and nitrogen, and because the laser action time is very short, the heat is too late to travel far. The decomposed GaN is only a few hundred nanometers thick near the interface and does not damage the core region of the GaN LED. After irradiation, the interface region will have only a layer of gallium metal left over from th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com