Method for taking glucose as substrate to continuously produce polyhydroxylbutyrate valerate (PHBV) in one step by using halophilic mixed bacteria
A technology of mixed halophilic bacteria and glucose, applied in fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of complex process control, inability to realize continuous production and operation, etc., and achieve the effects of easy engineering operation, increased commercial utilization value, and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
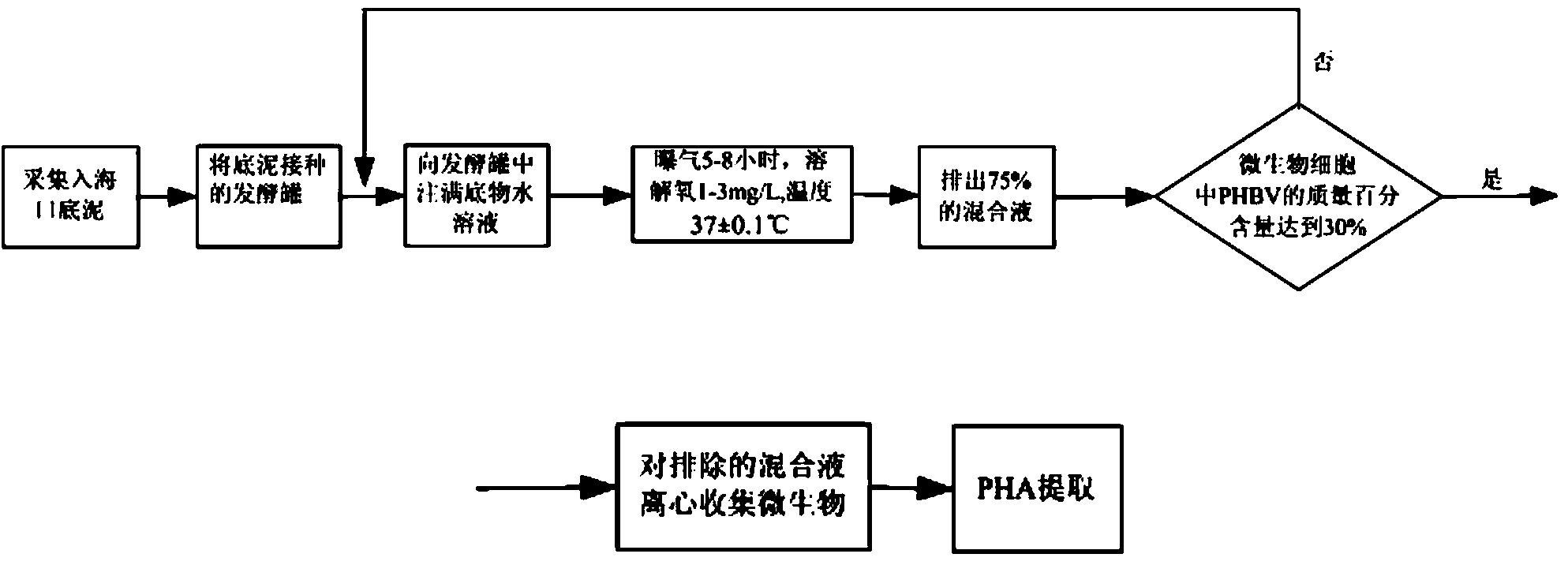
[0028] Step 1: Collect estuary sediment at the mouth of Tanghe River in Qinhuangdao City, Hebei Province. The sampling site is located 600 meters away from the Bohai Sea. The collected bottom mud is inoculated into the fermenter after sand removal. Inject the substrate aqueous solution to 2L in the fermenter, and the inoculum concentration is 0.102g / L;
[0029] Step 2: Control the temperature of the fermenter at 37±0.1°C, pH=7.2. Open the aeration device and feed air into the fermenter to maintain the dissolved oxygen in the mixed solution in the fermenter at 2 mg / L. Continuous aeration operation for 6 hours, stop aeration;
[0030] Step 3, remove 1.5L of the mixed solution, and the remaining 0.5L is used for the next fermentation;
[0031] Step 4, inject 1.5L substrate into fermenter again,
[0032] Step 5, repeat steps 2-480 times, the mass percentage of PHBV in the reaction solution is not less than 30%;
[0033] Step 6, continue to repeat steps 2-4176 times continuous...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com