Improved nitric acid production
A nitric acid, production process technology, applied to the separation of nitric acid, nitrogen oxides/oxyacids, dispersed particles, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
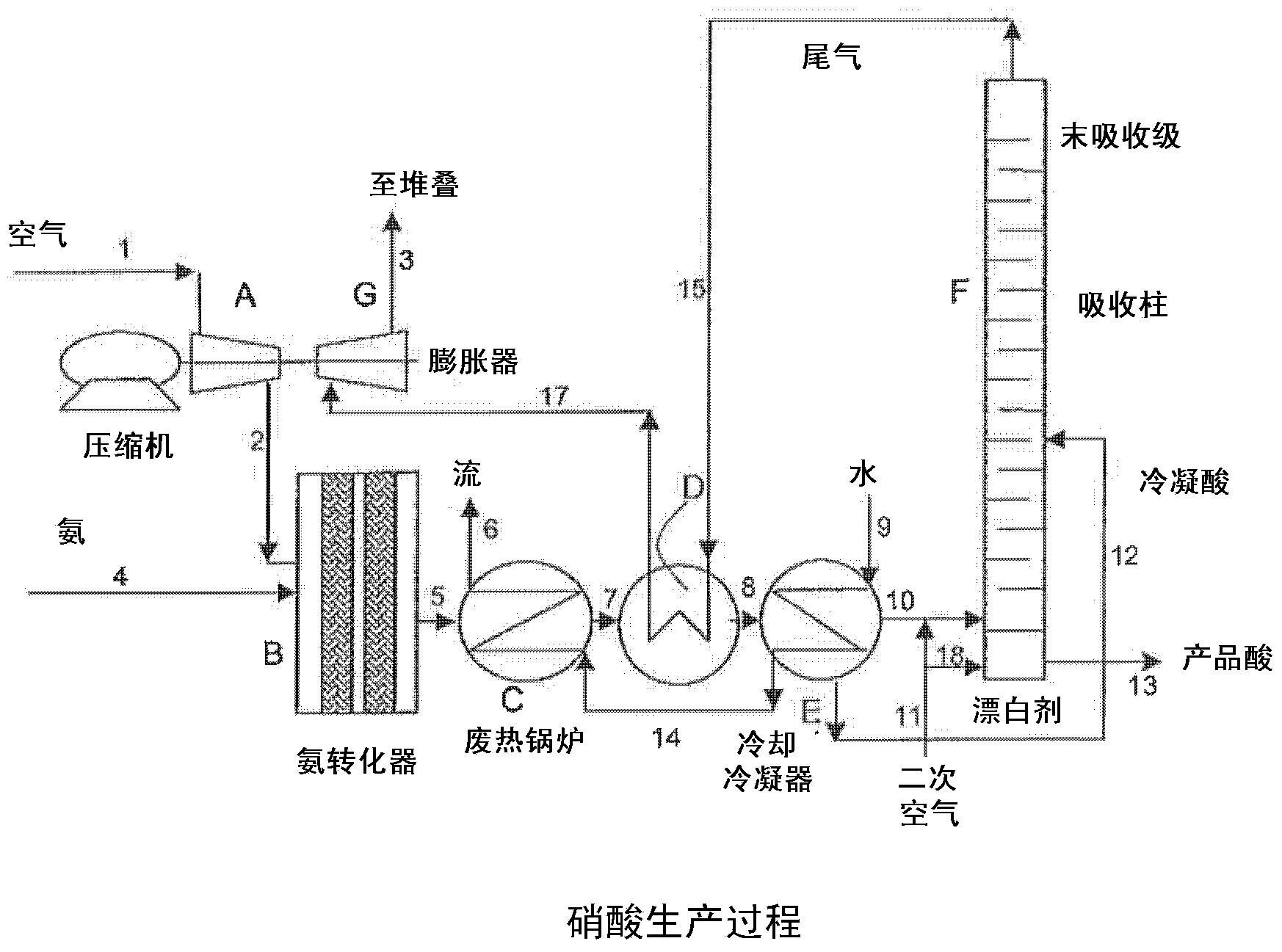
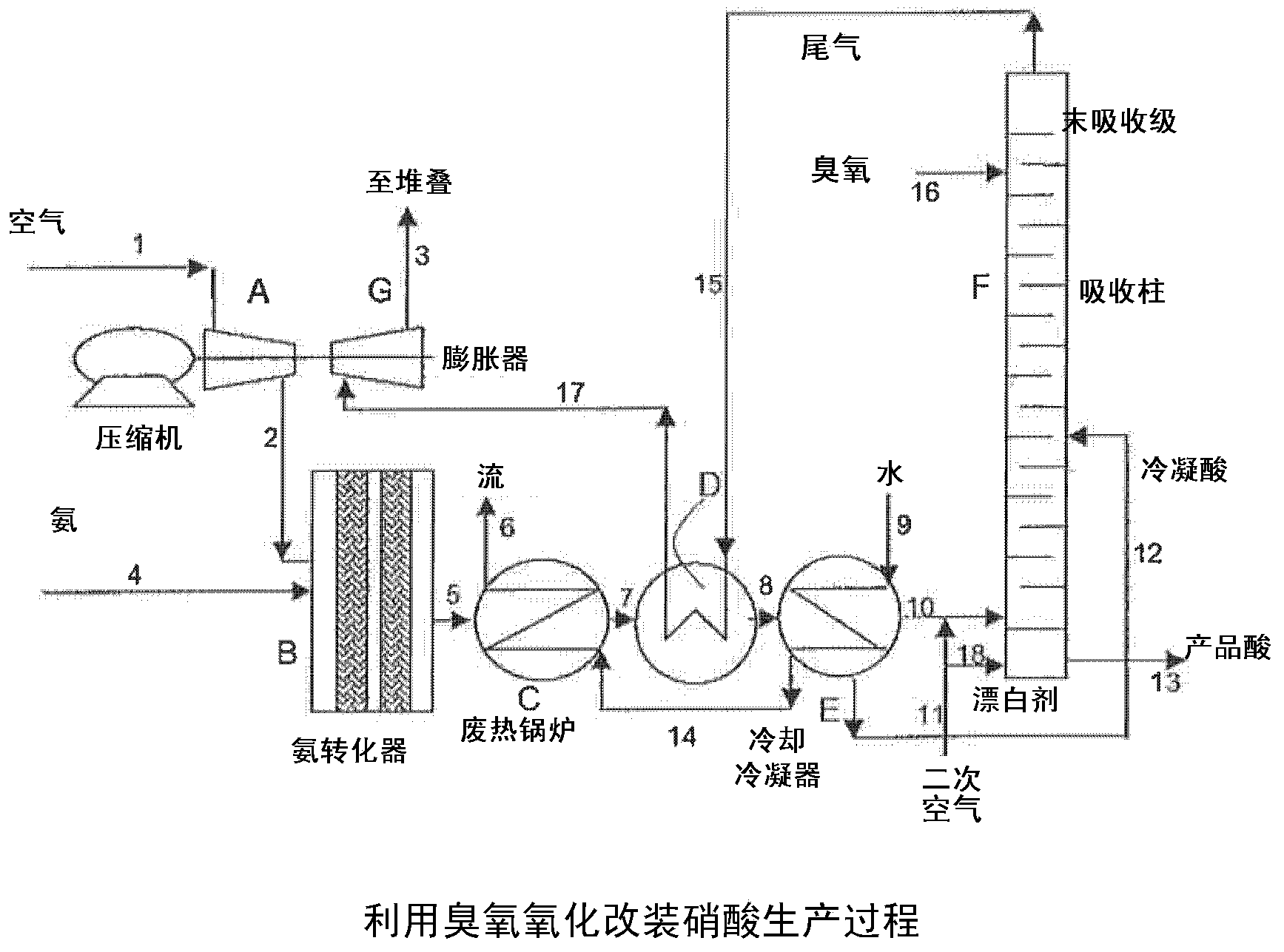
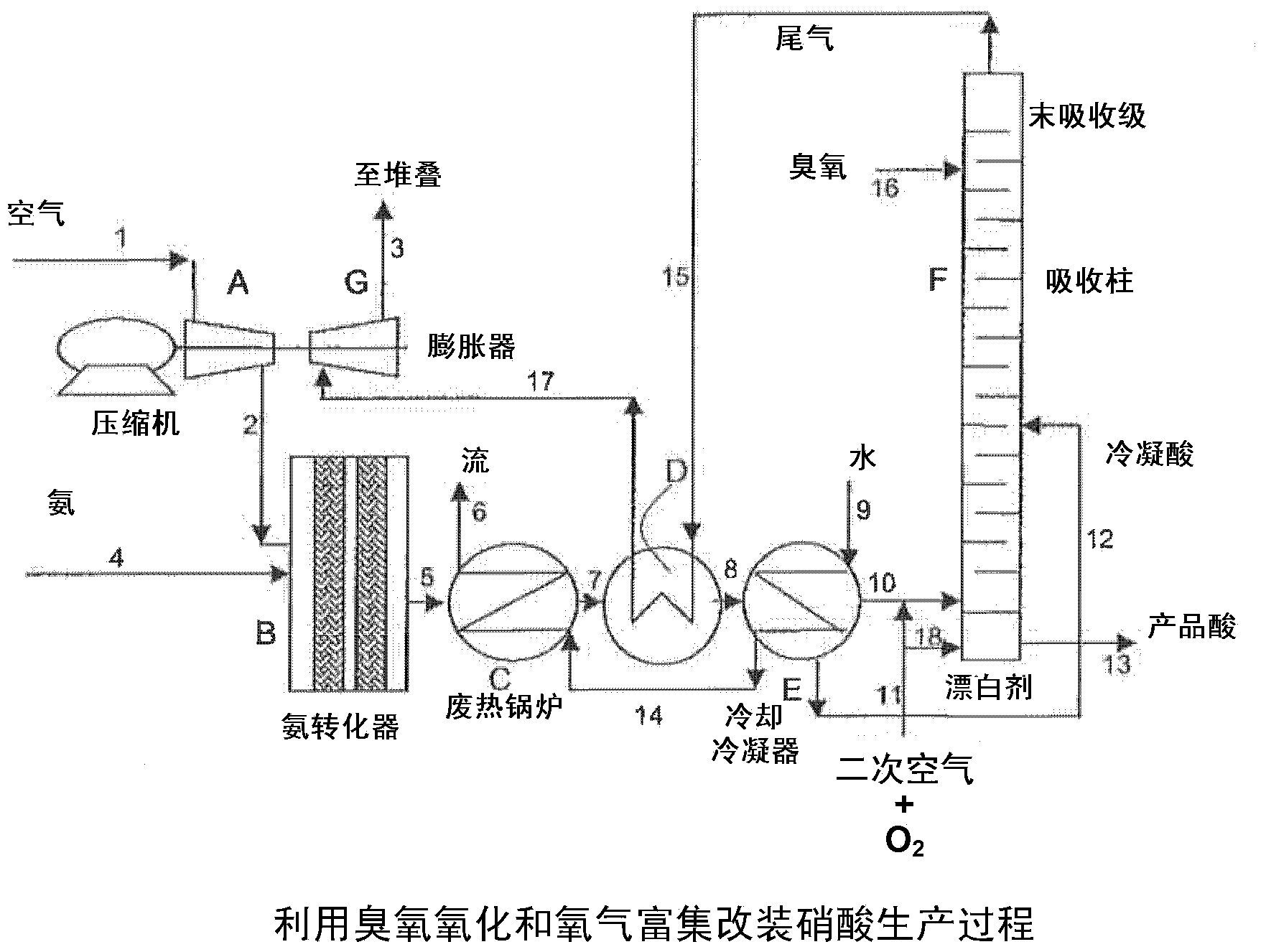
[0036] turn to figure 1, showing a schematic diagram of the nitric acid production process. Air is fed via line 1 to compressor A which feeds compressed air to ammonia converter B via line 2. Ammonia is fed to the premix with air via line 4 and the ammonia is subjected to high temperature oxidation present in ammonia converter B on the surface of the noble metal catalyst. This oxidation reaction is highly exothermic and converts ammonia to nitrogen oxides. The process gas stream leaving ammonia converter B via line 5 consists mainly of nitrogen with residual oxygen, water in vapor form and nitrogen oxides (especially NO). Heat from the process gas stream leaving the ammonia converter is recovered from the waste heat in the waste heat recovery unit C to form a high pressure gas stream in line 6, the tail gas is heated in the heat exchanger D and further eliminated in the cooling condenser E. At this point, the high temperature heat recovered as a gas stream in line 6 can be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com