Antipollution modifying method of compound reverse osmosis membrane
A reverse osmosis membrane and anti-pollution technology, which is applied in the preparation of polymer composite membranes and the field of anti-pollution modification of composite reverse osmosis membranes, can solve the problems of complex modification process and difficult dissolution of polyamide composite reverse osmosis membranes, and achieve Improve anti-pollution performance, reduce chemical cleaning frequency, and produce obvious effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] The difference from Comparative Example 1 is that after the polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane is obtained, anti-pollution modification is carried out on it, and the specific steps include:
[0020] (1) Preparation of A solution: Dissolve 0.2kg of acetic acid in 99.74kg of water, then add 0.01kg of chitosan and 0.05kg of sodium dodecylsulfonate to the aqueous solution, and stir until chitosan and surface activity A solution is obtained after the agent is completely dissolved;
[0021] (2) Preparation of solution B: add 0.05kg of sodium hydroxide to 99.95kg of water, stir and dissolve to obtain solution B;
[0022] (3) First, the surface of the polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane is coated with solution A, and after removing excess solution A on the surface of the membrane, it is contacted with solution B to complete the anti-pollution modification of the composite reverse osmosis membrane.
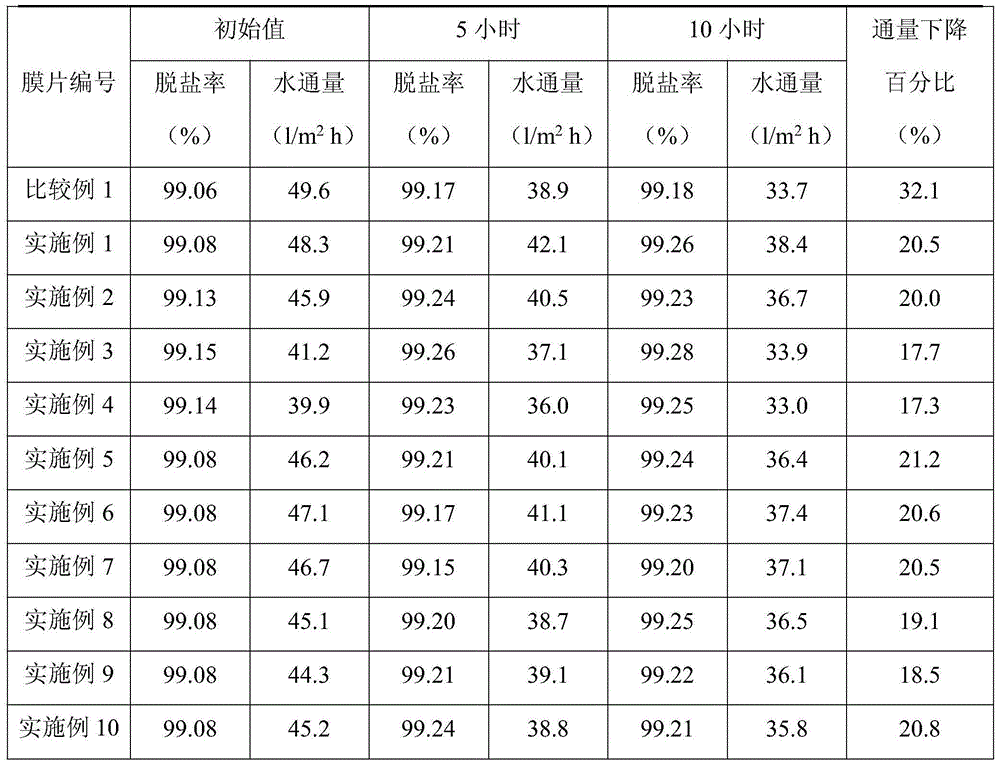
[0023] Measure the water contact angle of 50°, and then tes...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The difference from Comparative Example 1 is that after the polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane is obtained, anti-pollution modification is carried out on it, and the specific steps include:
[0026] (1) Preparation of solution A: Dissolve 0.2kg of acetic acid in 99.65kg of water, then add 0.1kg of chitosan and 0.05kg of sodium dodecylsulfonate to the aqueous solution, and stir until chitosan and surface activity A solution is obtained after the agent is completely dissolved;
[0027] (2) Preparation of solution B: add 0.05kg of sodium hydroxide to 99.95kg of water, stir and dissolve to obtain solution B;
[0028] (3) First, the surface of the polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane is coated with solution A, and after removing excess solution A on the surface of the membrane, it is contacted with solution B to complete the anti-pollution modification of the composite reverse osmosis membrane.
[0029] The water contact angle was measured to be 41°, and t...
Embodiment 3
[0031] The difference from Comparative Example 1 is that after the polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane is obtained, anti-pollution modification is carried out on it, and the specific steps include:
[0032] (1) Preparation of A solution: Dissolve 0.2kg of acetic acid in 99.25kg of water, then add 0.5kg of chitosan and 0.05kg of sodium dodecylsulfonate to the aqueous solution, and stir until chitosan and surface activity A solution is obtained after the agent is completely dissolved;
[0033] (2) Preparation of solution B: add 0.05kg of sodium hydroxide to 99.95kg of water, stir and dissolve to obtain solution B;
[0034] (3) First, the surface of the polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane is coated with solution A, and after removing excess solution A on the surface of the membrane, it is contacted with solution B to complete the anti-pollution modification of the composite reverse osmosis membrane.
[0035] Measure the water contact angle of 40°, and then test...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com