Process for indirectly drying brown coal through low-temperature steam and system device of process
A low-temperature steam and lignite technology, which is applied in the direction of drying solid materials, drying, dryers, etc., can solve the problems of uncontrollable adjustment of the drying system, no guarantee of industrial operation safety, unsuitable control of lignite temperature, etc., so as to facilitate industrial control, The effect of increasing the range of industrial applications and improving fluidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
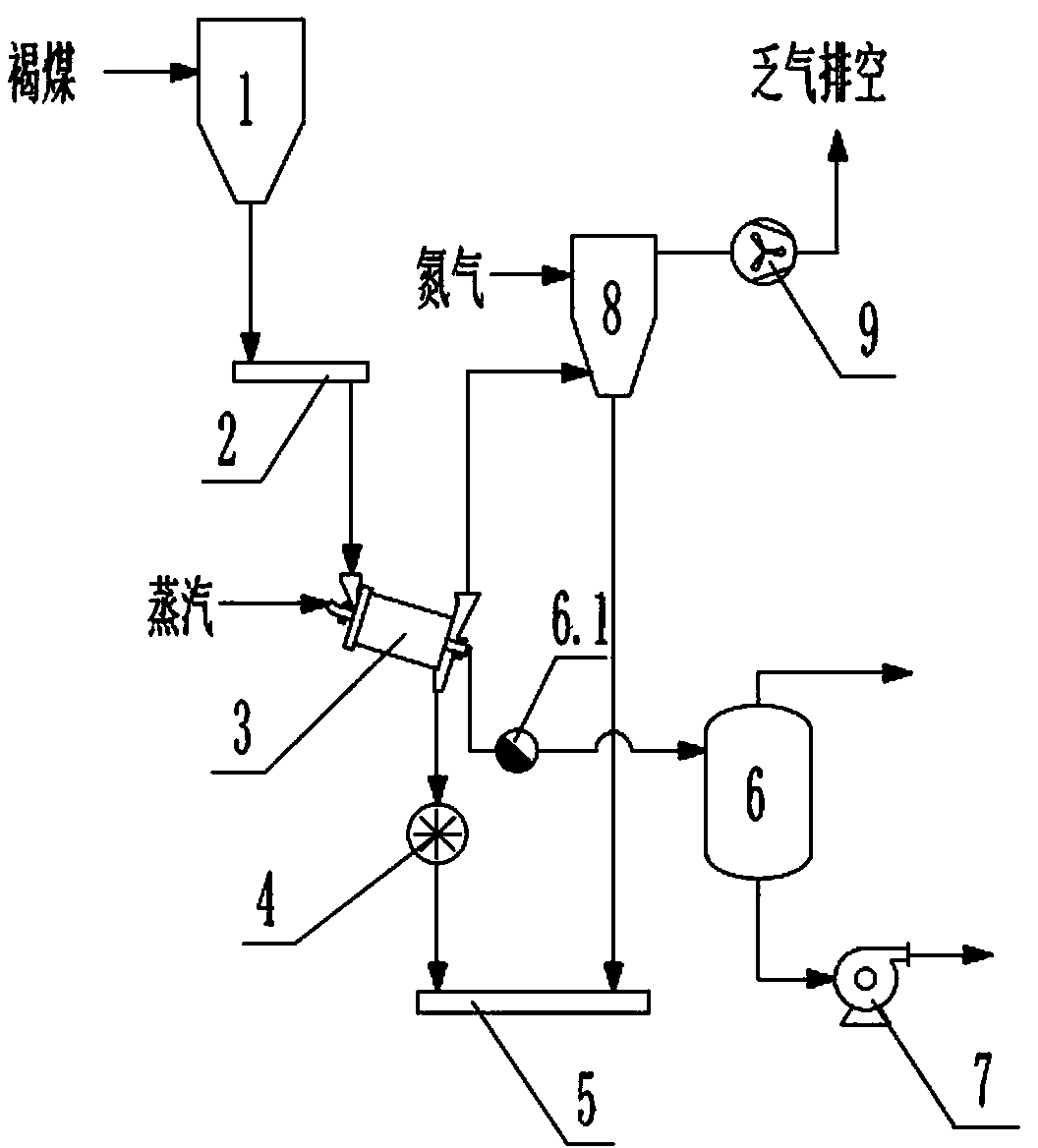
[0050] A process for indirectly drying lignite with low-temperature steam, such as figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0051] (a) Lignite with a water content of 35% by mass and a particle size of ≤20mm is put into the drying pipe of the dryer 3 from the raw coal bunker 1 through the coal feeder 2;
[0052] (b) passing the low-temperature steam to the outside of the drying pipe of the dryer 3 in step (a), so that the lignite in the drying pipe and the steam outside the drying pipe are subjected to indirect heat exchange, thereby achieving the purpose of drying the lignite;
[0053] (c) The condensate after heat exchange in step (b) enters the condensation tank 6 through the steam trap 6.1; the condensate is finally discharged by the condensate pump 7;
[0054] (d) The dried lignite in the step (b) comes out from the outlet of the dryer 3, and enters the buried scraper conveyor 5 through the rotary sealing feed valve 4;
[0055] (e) During the l...
Embodiment 2
[0069] A process for indirectly drying lignite with low-temperature steam, comprising the following steps:
[0070] (a) Lignite with a water content of 50% by mass and a particle size of ≤20 mm is fed from the raw coal bunker 1 through the coal feeder 2 into the drying pipe of the dryer 3;
[0071] (b) passing the low-temperature steam to the outside of the drying pipe of the dryer 3 in step (a), so that the lignite in the drying pipe and the steam outside the drying pipe are subjected to indirect heat exchange, thereby achieving the purpose of drying the lignite;
[0072] (c) The condensate after heat exchange in step (b) enters the condensation tank 6 through the steam trap 6.1; the condensate is finally discharged by the condensate pump 7;
[0073] (d) The dried lignite in the step (b) comes out from the outlet of the dryer 3, and enters the buried scraper conveyor 5 through the rotary sealing feed valve 4;
[0074] (e) During the lignite drying process described in step (...
Embodiment 3
[0088] A process for indirectly drying lignite with low-temperature steam, comprising the following steps:
[0089] (a) Lignite with a water content of 45% by mass and a particle size of ≤20mm enters the drying pipe of the dryer 3 from the raw coal bunker 1 through the coal feeder 2;
[0090] (b) passing the low-temperature steam to the outside of the drying pipe of the dryer 3 in step (a), so that the lignite in the drying pipe and the steam outside the drying pipe are subjected to indirect heat exchange, thereby achieving the purpose of drying the lignite;
[0091] (c) The condensate after heat exchange in step (b) enters the condensation tank 6 through the steam trap 6.1; the condensate is finally discharged by the condensate pump 7;
[0092] (d) The dried lignite in the step (b) comes out from the outlet of the dryer 3, and enters the buried scraper conveyor 5 through the rotary sealing feed valve 4;
[0093] (e) During the lignite drying process described in step (b), th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com