Method for synchronous desulphurization, denitration dedusting and emission reduction of carbon dioxide by fire coal and flue gas
A technology of carbon dioxide, desulfurization and denitrification, applied in the directions of carbon monoxide, chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, etc., can solve the problems of inability to change the growth trend of total carbon dioxide emissions, impossible to implement in power plants, and ineffective for fine dust. , to avoid huge costs and corresponding risks, avoid transshipment costs and storage risks, and reduce capture costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
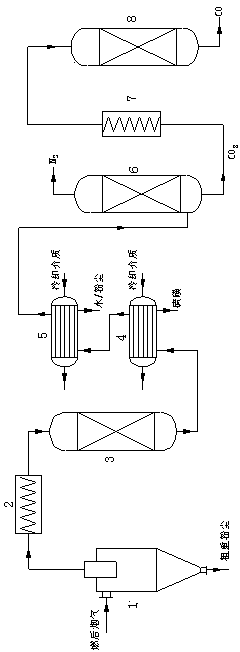
[0038] Using carbonized corncobs as inorganic carbon, simulated flue gas (CO 2 Content 10.13%, SO 2 Content 1500ppm, NO content 360ppm, the rest is N 2 ) for reduction experiments. The simulated flue gas does not contain solid dust.
[0039] 1. Gas heating up
[0040] Raise the simulated flue gas temperature to 700-745°C.
[0041] 2. Reduction reaction
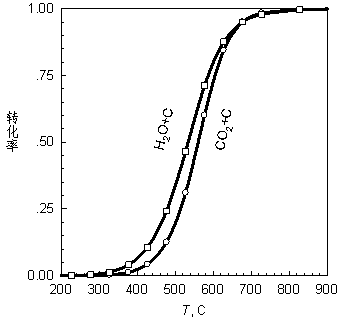
[0042] The heated gas enters the reactor filled with carbonized corn cobs. The temperature of the reactor is 700-745°C. Part of the carbon dioxide in the gas undergoes a reduction reaction with the carbon filled in the reactor to generate carbon monoxide. The resulting reducing atmosphere will simulate the carbon monoxide in the flue gas. Trace SO 2 and NO x Complete reduction, since SO is no longer detectable after the gas-solid reactor 2 and NO.
[0043] 3. Step by step cooling
[0044] The gas at the outlet of the reactor enters the first cooler to cool down to 200-400 °C, the water vapor does not condense, but th...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Using carbonized corncobs as inorganic carbon, simulated flue gas containing oxygen (CO 2 Content 7.48%, O 2 Content 4.61%, SO 2 The content is 830 ppm, the NO content is 700 ppm, and the rest is N 2 ). Repeat the above experiment, the operation steps are the same as in Example 1, and the results are also the same.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Using carbonized corncobs as inorganic carbon, simulated flue gas containing water (CO 2 Content 10.32%, SO 2 Content 1500ppm, NO content 360ppm, the rest is N 2 ) to repeat the above experiment. Water was added using a microsyringe in an amount equal to half the moles of carbon dioxide. First 2 operation steps are identical with embodiment 1, namely:
[0051] 1. Gas heating up
[0052] Raise the simulated flue gas temperature to 700-745°C.
[0053] 2. Reduction reaction
[0054] The heated gas enters the reactor filled with carbonized corncobs. The temperature of the reactor is 700-745°C. Part of the carbon dioxide in the gas undergoes a reduction reaction with the carbon filled in the reactor to generate carbon monoxide, and part of the water vapor is reduced to hydrogen. The resulting reducing atmosphere will simulate the trace amount of SO in the flue gas 2 and NO x Complete reduction, since SO is no longer detectable in the gas after the gas-solid reactor ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com