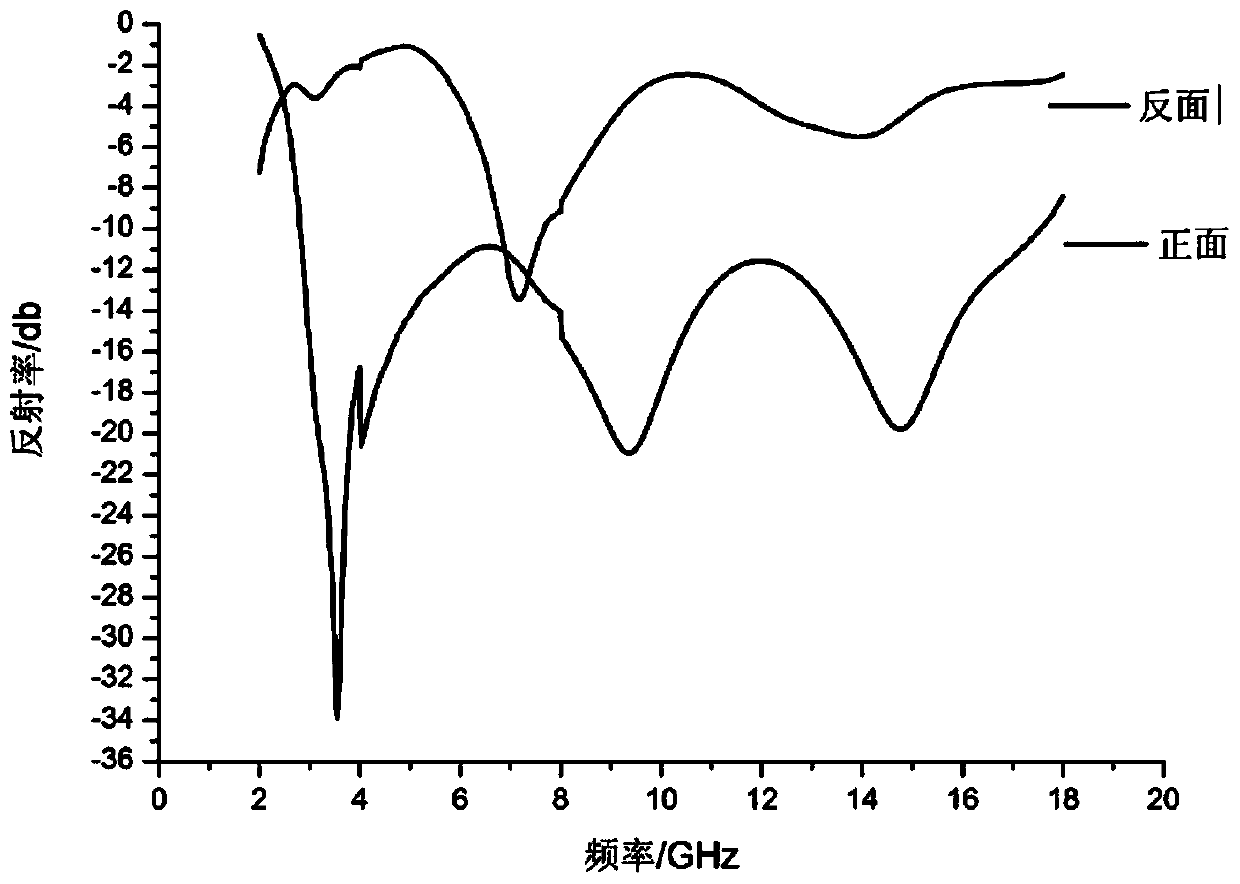
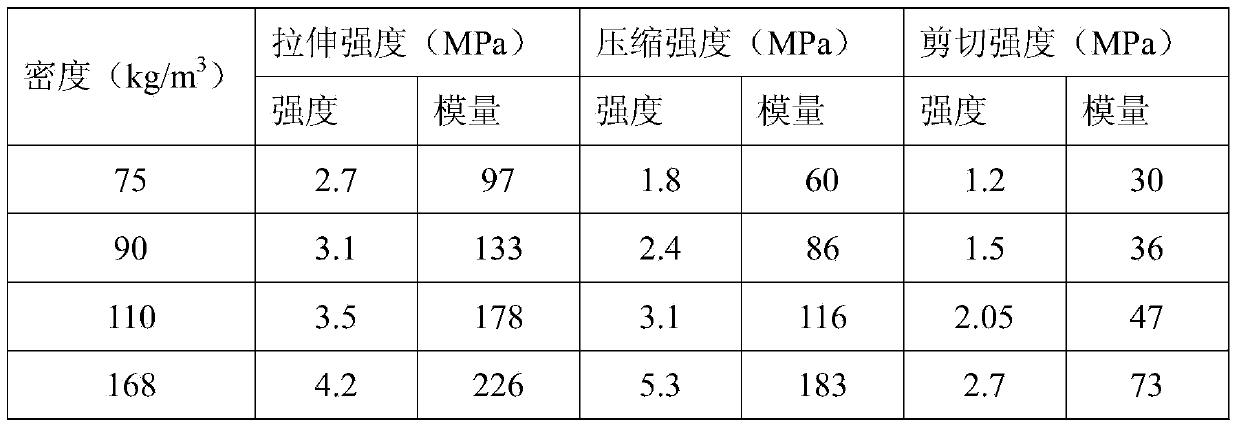
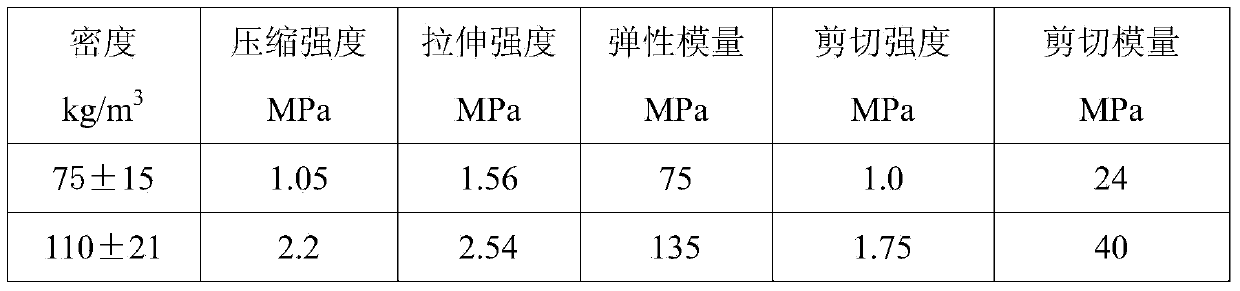
Wave-absorbing type polymethacrylimide foam/chopped fiber composite material and preparation method thereof
A polymethacrylic imine, methacrylic acid technology is applied in the field of wave absorbing functional materials, which can solve the problems of unguaranteed performance stability and inability to achieve uniform dispersion, and achieves low cost, excellent wave absorbing performance, and preparation method. simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] First prepare raw materials according to the following quality: 42 parts of methacrylic acid, 58 parts of methacrylonitrile, 0.25 parts of azobisisobutyronitrile, 3 parts of formamide, 2 parts of acrylamide, 1 part of carbonamide, and 0.5 parts of methyl silicone oil share. The above reagents were mixed and stirred thoroughly to obtain solution A.
[0036] Add 4 parts of polymethyl methacrylate with a molecular weight of 1.5 million to solution A, and dissolve the thickener by stirring at a high speed at a temperature of 50°C to obtain viscous solution B.
[0037] Add 1 part of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber with a length of 2 mm into solution B, and uniformly disperse polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber in solution B by low-speed vibration and power ultrasound to obtain solution C in which chopped fibers are dispersed.
[0038] The solution C was injected into a sealed glass plate mold of 100mm×100mm×10mm, and reacted at a temperature of 50°C for 72h to obtain ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] First prepare the raw materials according to the following mass percentages: 50 parts of methacrylic acid, 50 parts of methacrylonitrile, 0.4 parts of azobisisobutyronitrile, 8 parts of formamide, 2 parts of acrylamide, 1 part of carbonamide, and 0.5 parts of methyl silicone oil share. The above reagents were mixed and stirred thoroughly to obtain solution A.
[0047] Add 6 parts of polymethyl methacrylate with a molecular weight of 1.5 million to solution A, and dissolve the thickener by high-speed stirring at a temperature of 40°C to obtain viscous solution B.
[0048]Add 0.5 parts of aramid fibers with a length of 4mm into solution B, and disperse the aramid fibers evenly in solution B by low-speed vibration and power ultrasound to obtain solution C in which chopped fibers are dispersed.
[0049] The solution C was injected into a sealed glass plate mold of 100mm×100mm×10mm, and reacted at a temperature of 60°C for 48h to obtain a polymethacrylic acid imide copolyme...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Prepare raw materials according to the following mass percentages: 58 parts of methacrylic acid, 42 parts of methacrylonitrile, 0.5 parts of diacetyl peroxide, 6 parts of formamide, 2.5 parts of acrylamide, 1.5 parts of carbonamide, and 0.5 parts of methyl silicone oil. The above reagents were mixed and stirred thoroughly to obtain solution A.
[0054] Take 8 parts of polymethyl methacrylate with a molecular weight of 1.5 million and add it to solution A, and dissolve the thickener by stirring at a high speed at a temperature of 50°C to obtain viscous solution B.
[0055] Add 0.3 parts of carbon fibers with a length of 10 mm into solution B, and disperse the carbon fibers in solution B evenly through low-speed vibration and power ultrasonic to obtain solution C in which chopped fibers are dispersed.
[0056] The solution C was injected into a sealed glass plate mold of 100mm×100mm×10mm, and reacted at a temperature of 50°C for 72h to obtain a polymethacrylic imide copol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com