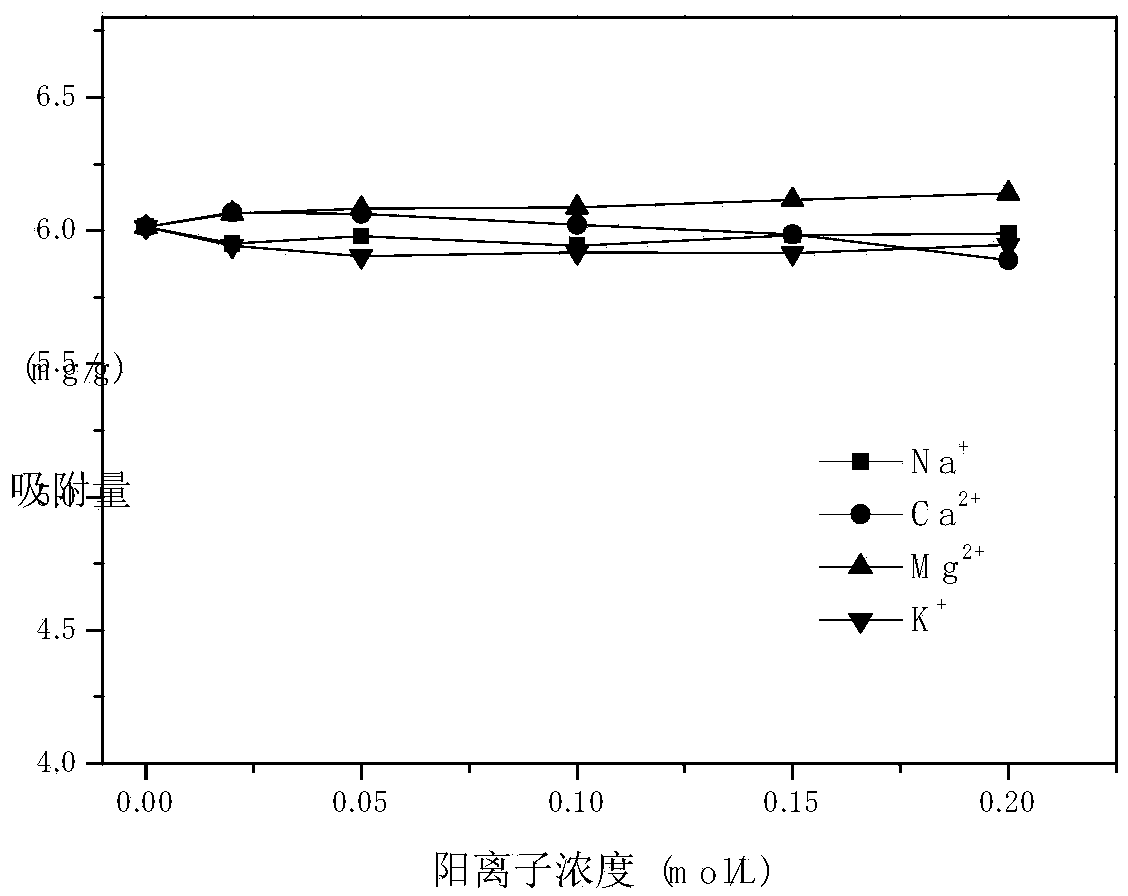
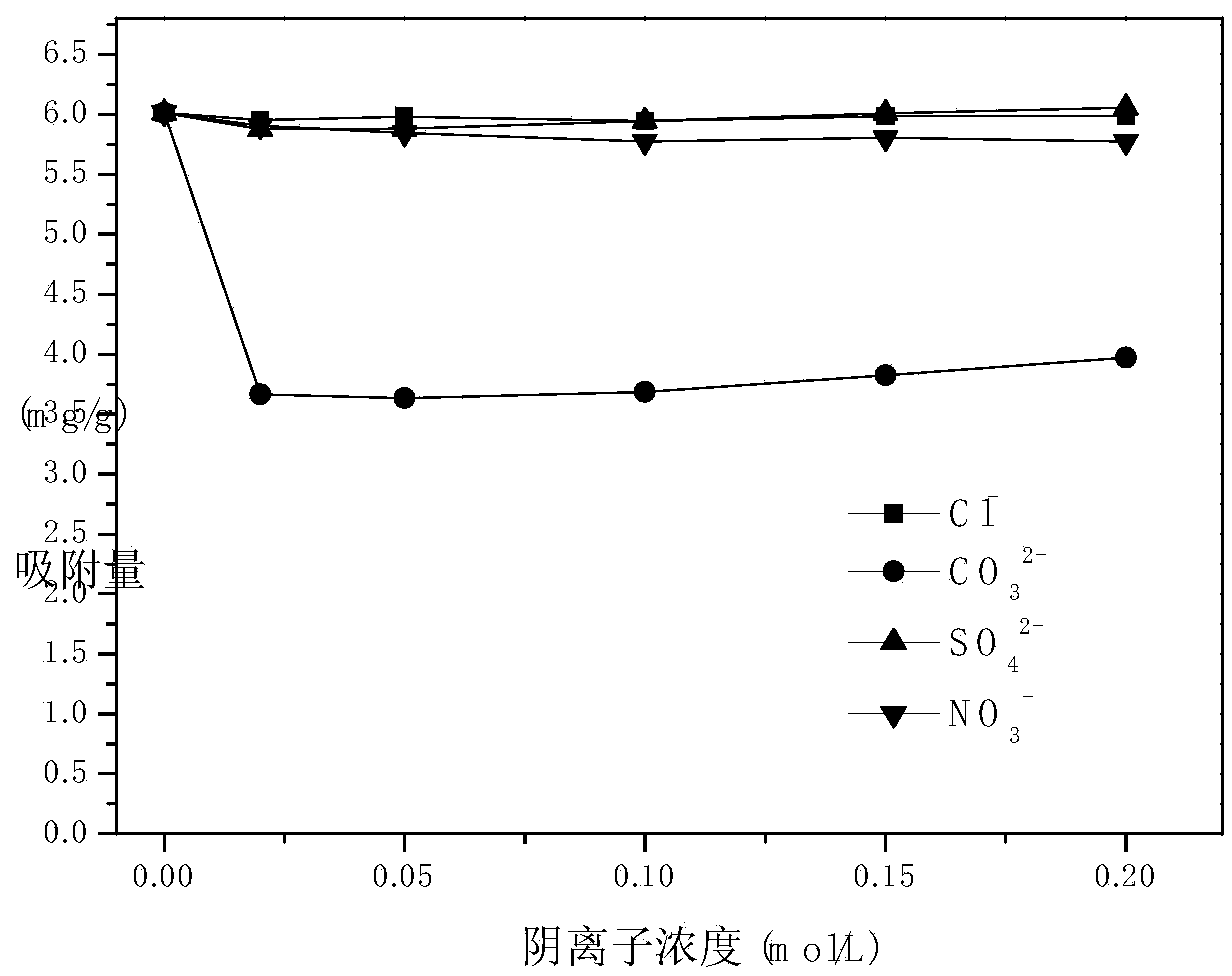
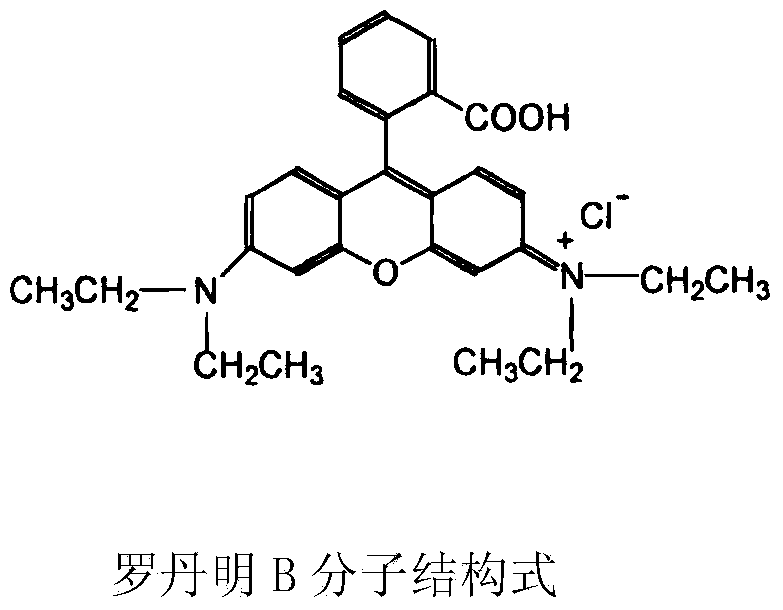
Biomass absorbing agent for treating rose-bengal dyeing wastewater as well as preparation method and application of biomass absorbing agent
A technology for biomass adsorbents and dye wastewater, applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of biosorbents that adsorb rhodamine B molecules, increase manufacturing costs, and lengthy chemical modification In order to achieve broad application prospects and economic value, low cost and excellent adsorption performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The camphor leaves collected are cleaned with tap water for deposits such as silt and soil on the surface of the leaves, soaked in 10% NaCl aqueous solution for about 1 hour, and then washed 2 to 3 times with ultrapure water, using a blast drying box. Dry at 100°C for about 12 hours, pulverize in a pulverizer, and sieve through a 100-mesh standard inspection sieve to obtain camphor leaf powder with a pore size of less than 0.15 mm, which is bagged for later use.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Pipette 100mL of rose bengal solution with an initial concentration of 20mg / L and place it in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, pass through 0.1mol / L NaOH solution (or 0.1mol / L HNO 3 solution) to adjust the initial pH value of the rose bengal solution, add 300mg of the prepared camphor leaf powder as an adsorbent, at a temperature of 30°C, and after oscillating at a constant temperature at a speed of 170rmp for 150min, absorb 3ml of the reaction solution and centrifuge twice at 9000r / min , using a spectrophotometer to measure the rose bengal concentration in the supernatant, the results are shown in Table 1:
[0030] Table 1 The adsorption inspection data of rose bengal dye wastewater solution with different pH values
[0031]
[0032] It can be seen from Table 2 that with camphor leaf powder as the biomass adsorbent, as the initial pH value of the rose bengal solution increases, the removal rate of rose bengal in the solution gradually decreases, but the removal rate does n...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Pipette 100mL of rose bengal solution with an initial concentration of 20mg / L and place it in a 250mL conical flask, add 300mg of prepared camphor leaf powder as an adsorbent, and absorb 3ml of Reaction solution, 9000r / min centrifugal separation 2 times, adopt spectrophotometer to measure rose bengal concentration in the supernatant, the result is as shown in table 2:
[0038] Table 2 The adsorption inspection data of the initial concentration of different rose bengal solutions
[0039]
[0040] As can be seen from Table 2, with the camphor tree leaf powder as the biomass adsorbent, with the increase of the initial concentration of the rose bengal solution, the adsorption capacity of the biomass adsorbent also increased thereupon, but the removal of rose bengal in the solution When the concentration of rose bengal solution was 20mg / L, camphor tree leaf powder had the highest removal rate of biomass adsorbent, which could reach 92.7%.
[0041] The adsorption capacity...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com