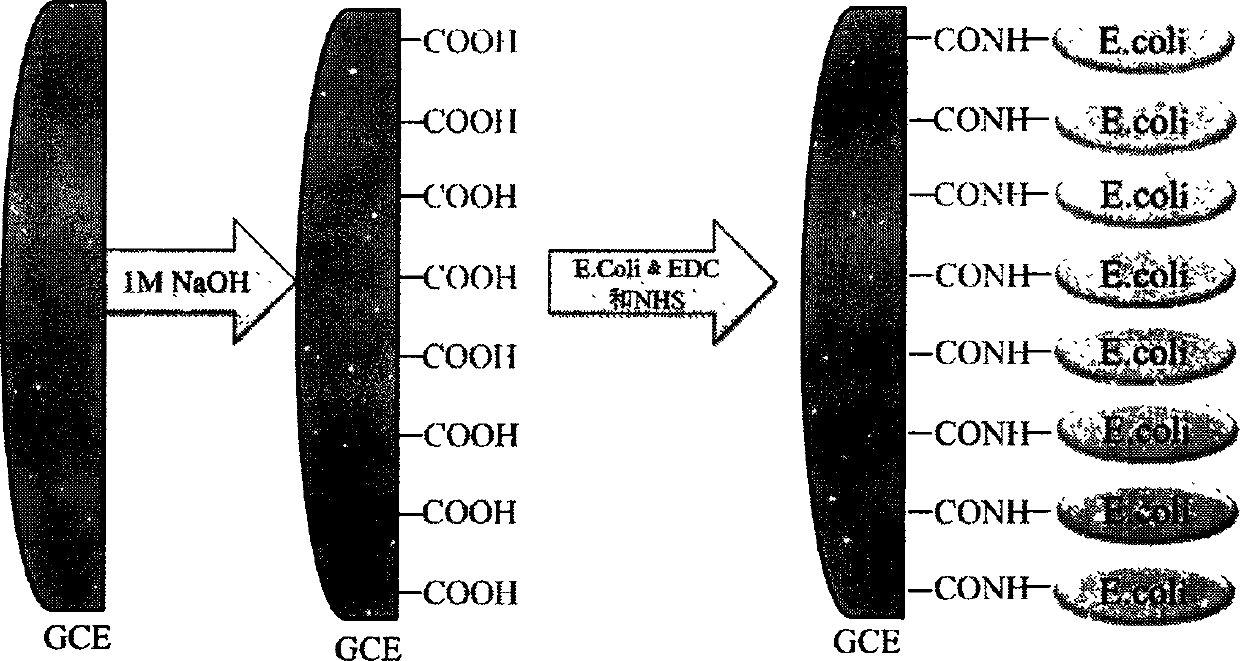
Preparation method of novel escherichia coli electrochemical sensor
An Escherichia coli, electrochemical technology, applied in the field of preparation of Escherichia coli electrochemical sensors, can solve the problems of unfavorable popularization and promotion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
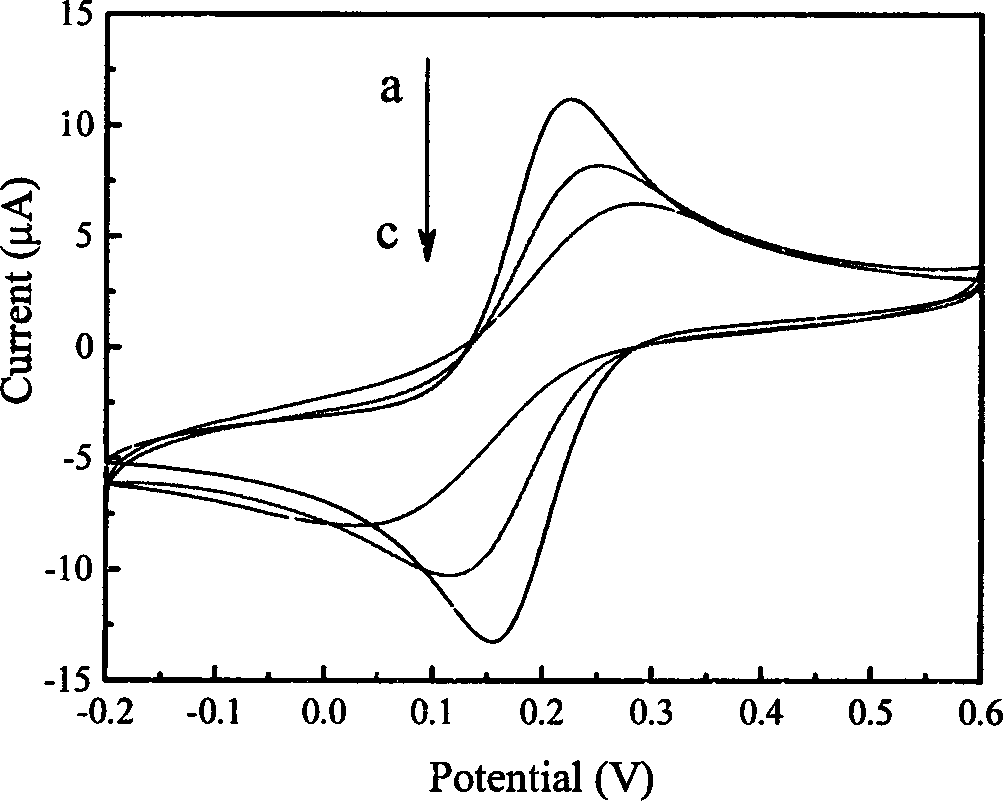
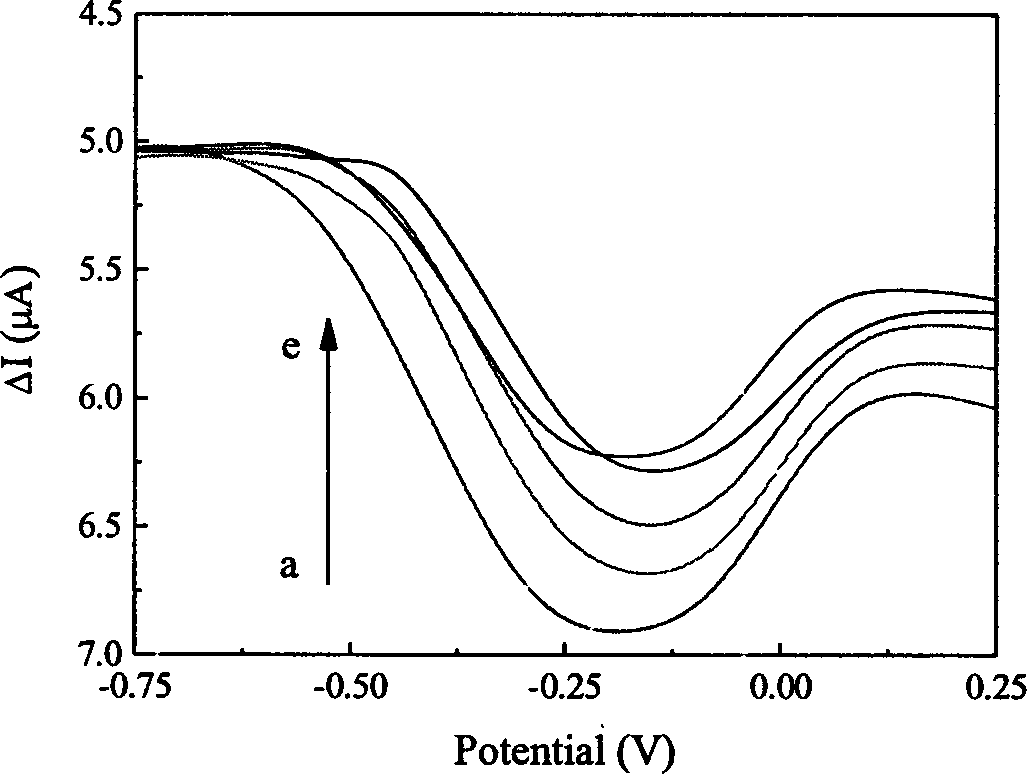
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] 1. The preparation of Escherichia coli electrochemical sensor comprises the following two steps:
[0021] 1.1 Carboxylation of glassy carbon electrodes: glassy carbon electrodes should be pretreated before use. The glassy carbon electrode was polished in alumina slurry with a particle size of 50nm for 5min, then ultrasonically cleaned in 0.1mol / L nitric acid, absolute ethanol and ultrapure water for 1min, and finally the electrode surface was dried with high-purity nitrogen. The cleaned glassy carbon electrode was activated by cyclic voltammetry in a 0.1mol / L sulfuric acid solution through an electrochemical workstation. After meeting the requirements, it was soaked in ultrapure water for later use. The above-mentioned treated glassy carbon electrode was immersed in 0.05mol / L sodium hydroxide solution for surface carboxylation, and cyclic voltammetry was used to scan for 1 circle, with a scanning speed of 50mV / s and a scanning range of -0.1 to 1.4V.
[0022] 1.2 Coupli...
Embodiment 2
[0026] 1. The preparation of Escherichia coli electrochemical sensor comprises the following two steps:
[0027] 1.1 Carboxylation of glassy carbon electrodes: glassy carbon electrodes should be pretreated before use. The glassy carbon electrode was polished in alumina slurry with a particle size of 50nm for 10min, then ultrasonically cleaned in 1.0mol / L nitric acid, absolute ethanol and ultrapure water for 3min, and finally the electrode surface was dried with high-purity nitrogen. The cleaned glassy carbon electrode was activated by cyclic voltammetry in a 1.0mol / L sulfuric acid solution through an electrochemical workstation. After meeting the requirements, it was soaked in ultrapure water for later use. The above-mentioned treated glassy carbon electrode was immersed in 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution for surface carboxylation, and was scanned by cyclic voltammetry for 5 cycles at a scanning speed of 100mV / s and a scanning range of -0.5 to 1.5V.
[0028] 1.2 Coupling of ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] 1. The preparation of Escherichia coli electrochemical sensor comprises the following two steps:
[0033] 1.1 Carboxylation of glassy carbon electrodes: Glassy carbon electrodes should be pretreated before use. The glassy carbon electrode was polished in alumina slurry with a particle size of 50nm for 10min, then ultrasonically cleaned in 0.5mol / L nitric acid, absolute ethanol and ultrapure water for 6min, and finally the electrode surface was dried with high-purity nitrogen. The cleaned glassy carbon electrode was activated by cyclic voltammetry in a 0.5mol / L sulfuric acid solution through an electrochemical workstation. After meeting the requirements, it was soaked in ultrapure water for later use. The above-mentioned treated glassy carbon electrode was immersed in 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution for surface carboxylation, and cyclic voltammetry was used to scan 10 cycles at a scanning speed of 150mV / s and a scanning range of -1 to 2V.
[0034] 1.2 Coupling of Esche...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com