Plant-growth-promoting endophytic bacterium having polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degrading function and application thereof
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and degrading bacteria technology, applied in bacteria, microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as unseen patent research and application reports, and achieve the effect of ensuring the safety of agricultural products, reducing the risk of phenanthrene contamination, and achieving good removal effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
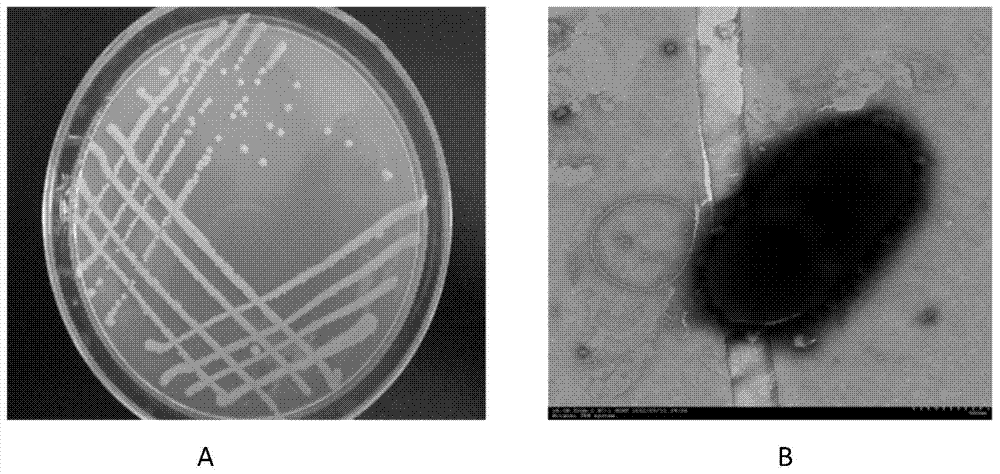
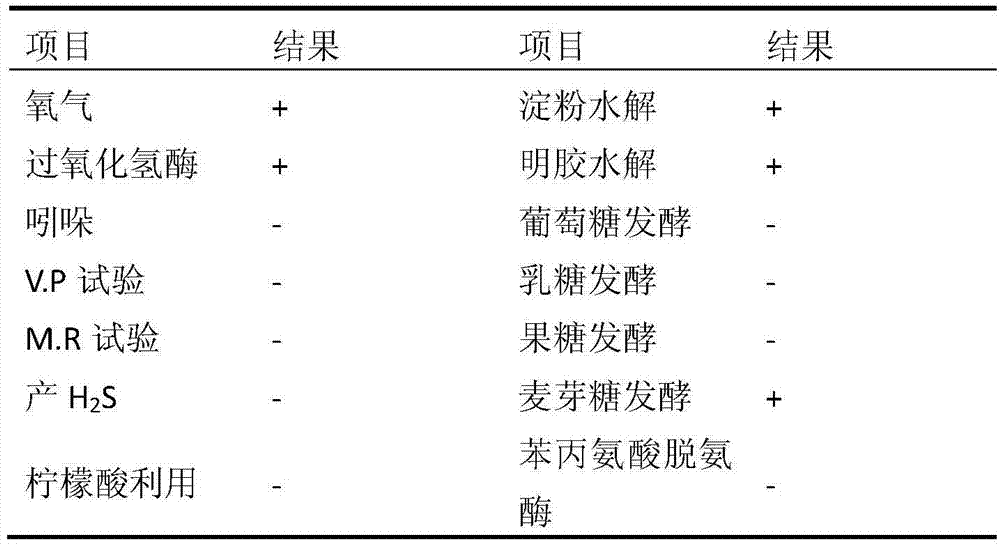
[0028] Example 1 Isolation and Identification of Bacterial Strains
[0029] Disinfect the fresh A. argentina plants collected from the sewage outlet of Nanjing Jiangning Yangzi Petrochemical Aromatics Plant: rinse the plants with tap water, rinse them with 75% alcohol in an ultra-clean bench for 3-5 minutes, and then rinse them with sterile water for 3-5 minutes. 4 times, then rinse with 1% sodium hypochlorite solution for 2 to 5 minutes, and finally rinse with sterile water several times. Transfer the surface-sterilized plant samples to LB solid plates, and after incubating them at 30°C for 24 hours, check whether there is bacterial growth on the plates. If no colony grows, it means that the surface of the plant is disinfected successfully.
[0030] Move the fully sterilized plants into a sterile mortar, cut them into pieces with sterilized scissors, add sterile water to grind them thoroughly, take the supernatant and add it to 100mL inorganic salt medium with 5% inoculum, a...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2 Fermentation of restoration bacterial agent
[0038] The process of using the above-mentioned strain Pn2 to produce the repairing bacterial agent is as follows: slant seed—shake bottle seed liquid—seed tank—product (the packaging dosage form is liquid bacterial agent).
[0039] 1) Inoculate the test tube species of Massilia sp. Pn2 with the preservation number CGMCC 1.12927 in the fermentation medium, and cultivate it to the logarithmic phase with shaking;
[0040] 2) Inoculate the above-mentioned cultured strains into the seed tank with an inoculation amount of 5%, and cultivate to the logarithmic phase;
[0041] 3) The seed liquid is connected to the production tank for cultivation according to the inoculum amount of 10%;
[0042] 4) During the cultivation process of seed tanks and production tanks, the ventilation rate of sterile air is 1:1.2, the stirring speed is 200 rpm, the cultivation temperature is 30°C, and the cultivation time of the whole proce...
Embodiment 3
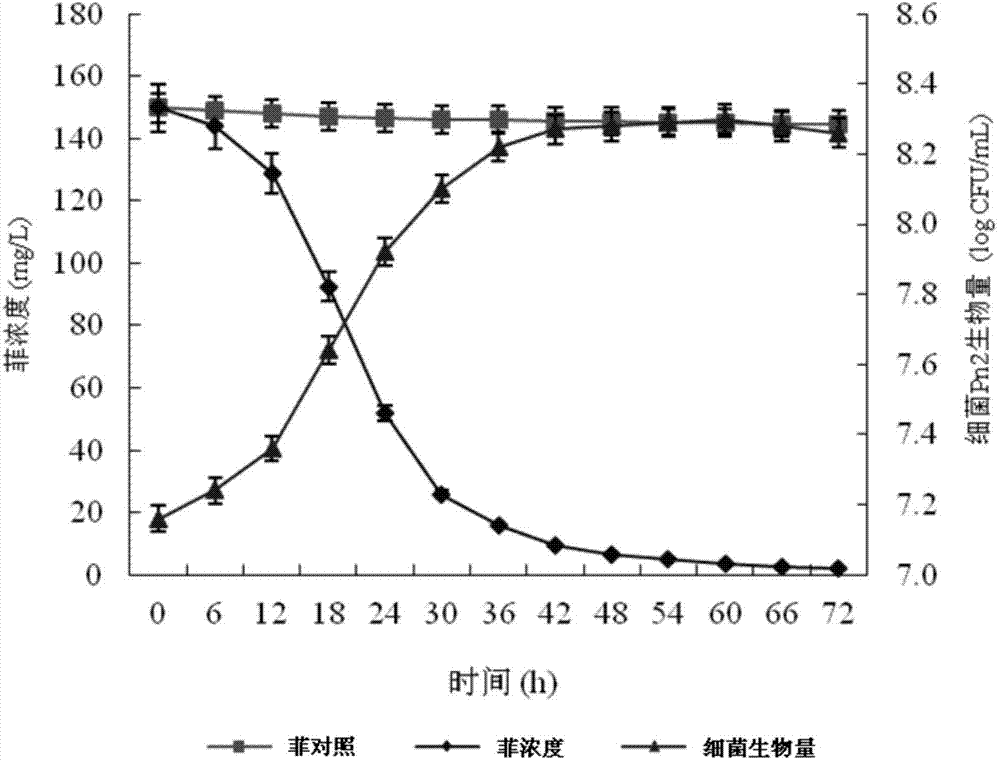
[0045] Example 3 Biodegradation experiment of PAHs by bacterial strain Pn2 in culture medium
[0046] In the inorganic salt culture medium (with embodiment 1), add final concentration and be 150mg L ‐1 The phenanthrene was inoculated into strain Pn2 (CGMCC 1.12927) with a 5% inoculum amount, and the inactivated strain Pn2 was used as a control, and cultured on a constant temperature shaker at 30°C. Take regular samples to detect the strain Pn2 at 150 mg·L ‐1 The growth of phenanthrene as the only carbon source and the degradation of phenanthrene, the results are shown in figure 2 . Strain Pn2 can grow well with phenanthrene as the sole carbon source, and within 3 days to an initial concentration of 150mg·L ‐1 The degradation rate of phenanthrene reaches more than 95%.
[0047] According to the above method, the bacterial strain Pn2 (CGMCC 1.12927) was sequentially inserted into the naphthalene-containing (100 mg·L ‐1 ), acenaphthyl (100mg·L ‐1 ), anthracene (50mg·L ‐1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com