Degradable packaging plastic for electric power systems
A technology for degrading plastics and packaging plastics, applied in the field of power materials, can solve the problems of low mechanical and elastic properties of pure starch-based plastics, restrictions on popularization and application, and heavy products, and achieve simple and feasible preparation methods, good mechanical properties, and no breakage coefficient and the effect of improved barrier properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] A degradable packaging plastic used in power systems, which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30 parts of low-density polyethylene, 20 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 15 parts of polybutylene succinate, polyvinyl 12 parts of pyrrolidone, 9 parts of hydroxymethyl cellulose, 7 parts of polyglycolic acid, 6 parts of chitosan, 4 parts of polylactic acid, 3 parts of triethyl phosphate, 3 parts of mica powder, 2 parts of talcum powder, 2 parts of corn starch , 1 part of sodium succinate and 1 part of epoxidized soybean oil; the particle diameters of hydroxymethylcellulose, chitosan, mica stone powder, talcum powder, corn starch and sodium succinate are all controlled above 100 mesh.
[0017] The preparation method of the above-mentioned degradable packaging plastics comprises the following steps:
[0018] Take each raw material according to parts by weight for subsequent use;
[0019] Firstly, each raw material is added in the reaction tank in turn...
Embodiment 2
[0022] A degradable packaging plastic for power systems, which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40 parts of low-density polyethylene, 25 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 17 parts of polybutylene succinate, polyvinyl 15 parts of pyrrolidone, 11 parts of hydroxymethyl cellulose, 8 parts of polyglycolic acid, 7 parts of chitosan, 5 parts of polylactic acid, 4 parts of triethyl phosphate, 4 parts of mica powder, 3 parts of talcum powder, 3 parts of corn starch , 2 parts of sodium succinate and 2 parts of epoxidized soybean oil; the particle diameters of hydroxymethyl cellulose, chitosan, mica stone powder, talcum powder, corn starch and sodium succinate are all controlled above 100 mesh.
[0023] The preparation method of the above-mentioned degradable packaging plastics comprises the following steps:
[0024] Take each raw material according to parts by weight for subsequent use;
[0025] Firstly, each raw material is added in the reaction tank in turn...
Embodiment 3
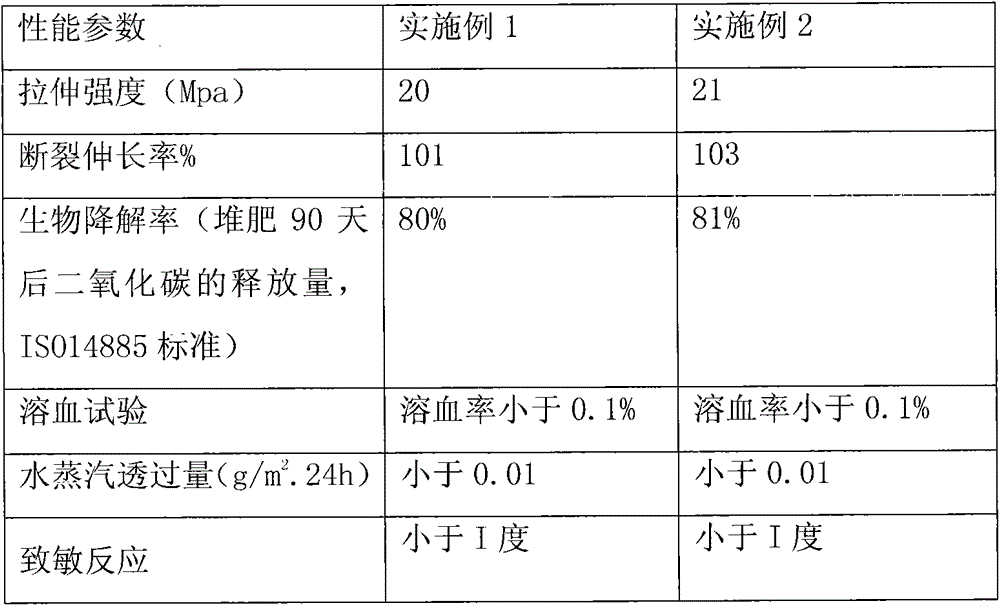
[0028] The performance test parameters of the degradable packaging plastic material prepared in Example 1 and Example 2 of the present invention are shown in Table 1 below, taking the thickness of 100 microns as an example:
[0029] Table 1
[0030]
[0031] Conclusion: Through the above performance test parameters, it can be found that the tensile strength, elongation at break and biodegradability of the packaging plastic material prepared by the present invention are better, and the pollution to the environment is greatly reduced.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com