Organic electroluminescent device and preparation method thereof
An electroluminescence device and a luminescence technology, applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of low light-emitting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
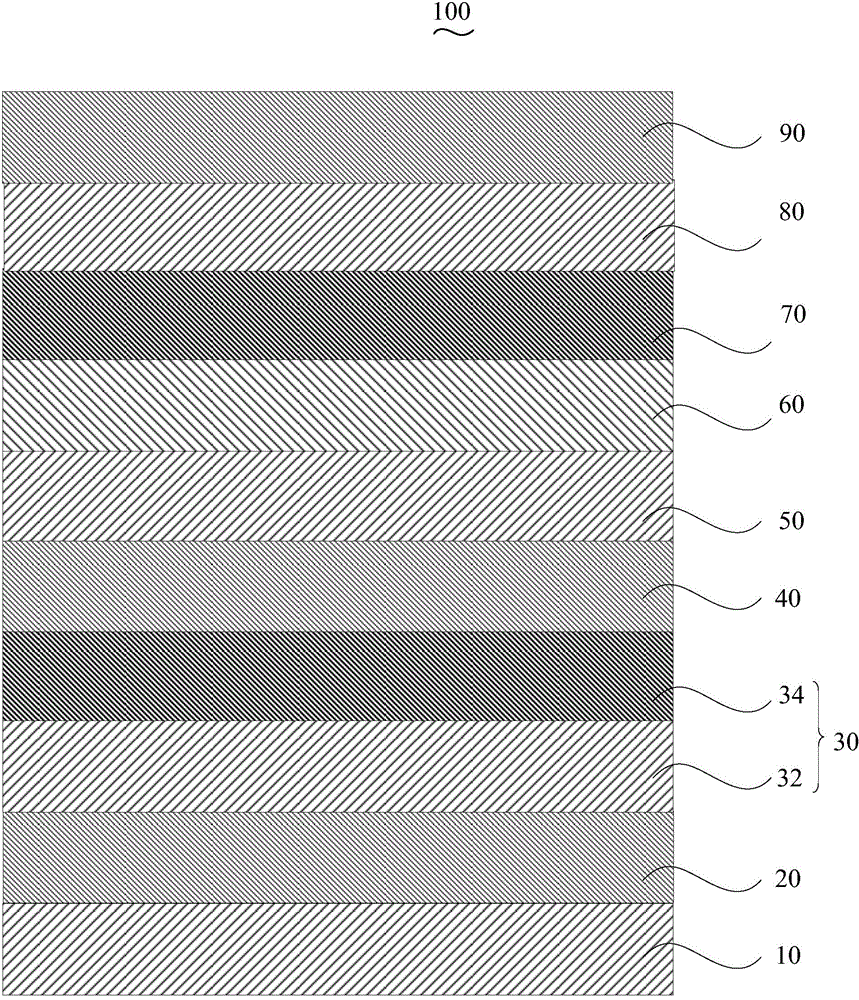
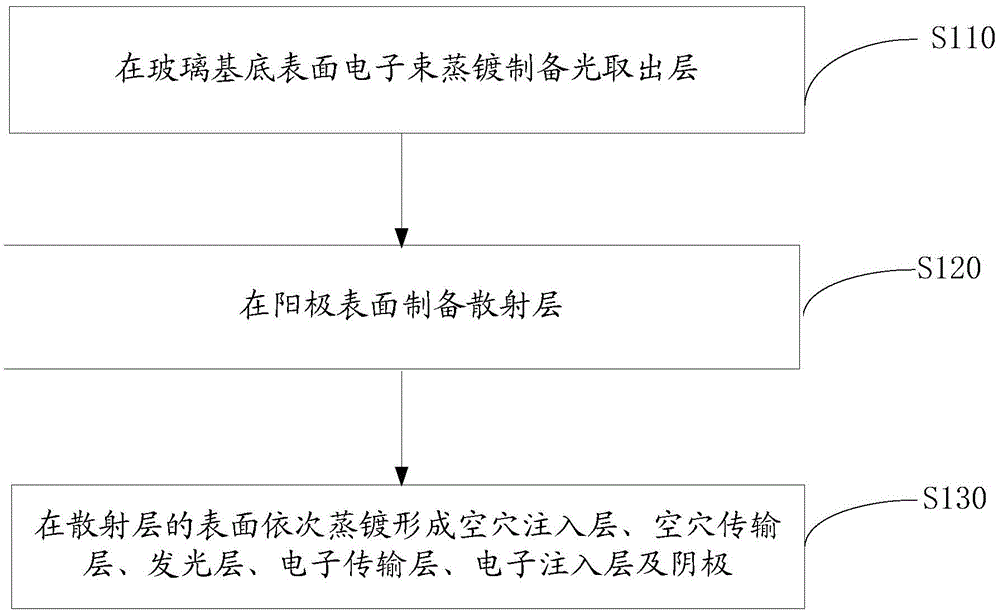
[0036] Please also see figure 2 , the preparation method of the organic electroluminescent device 100 of an embodiment, it comprises the following steps:
[0037] Step S110 , anode 20 on the surface of glass substrate 10 .
[0038] The glass substrate 10 is glass with a refractive index of 1.8-2.2, and the transmittance at 400 nm is higher than 90%. The glass substrate 10 is preferably glass with a grade of N-LAF36, N-LASF31A, N-LASF41A or N-LASF44.
[0039] The anode 20 is formed on one side surface of the glass substrate 10 . The material of the anode 20 is indium tin oxide (ITO), aluminum zinc oxide (AZO) or indium zinc oxide (IZO), preferably ITO. The thickness of the anode 20 is 80nm-300nm, preferably 120nm. The anode 20 is prepared by magnetron sputtering. The acceleration voltage of magnetron sputtering is 300-800V, the magnetic field is 50-200G, and the power density is 1-40W / cm 2 .
[0040] In this embodiment, the glass substrate 10 is rinsed with distilled wa...
Embodiment 1
[0058] The structure prepared in this example is glass / ITO / CaCO 3 :NPB / LiF:Zn / WO 3 / NPB / BCzVBi / TAZ / CsF / Ag organic electroluminescence device.
[0059] The glass substrate is N-LASF44. After rinsing the glass substrate with distilled water and ethanol, soak it in isopropanol for one night. Magnetron sputtering anode on the glass substrate, the material is ITO, the thickness is 120nm; prepare a scattering layer on the surface of the anode, the scattering layer includes a carbonate doped layer and a lithium compound doped layer, first prepare the carbonate doped layer, Materials including CaCO 3 and NPB, CaCO 3 and NPB 3 The mass ratio is 0.1:1, prepared by electron beam, the thickness is 45nm, and then the lithium compound doped layer is prepared, the material includes LiF and Zn, and the electron beam evaporation is used, the thickness is 10nm, and the mass ratio of Zn to LiF is 0.02: 1; The hole injection layer is prepared by evaporation, and the material is WO 3 , the t...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The structure prepared in this example is glass substrate / IZO / MgCO 3 :TCTA / Li 2 CO 3 :Zn / V 2 o 5 / TAPC / DCJTB / TPBi / CsN 3 / Pt organic electroluminescent devices.
[0065] The high refractive index glass is N-LAF36. After the glass is rinsed with distilled water and ethanol, soak it in isopropanol for one night. An anode film was prepared on a high refractive index glass substrate, the material was IZO, and the thickness was 80nm. Then a scattering layer is prepared, consisting of a carbonate doped layer and a lithium compound doped layer. Prepare the carbonate doped layer first, the material includes MgCO 3 and TCTA, MgCO 3 The mass ratio to TCTA is 0.05:1, prepared by electron beam, and the thickness is 60nm. Then prepare the lithium compound doped layer, the material includes Li 2 CO 3 And Zn, Zn and Li 2 CO 3 The mass ratio is 0.05:1, prepared by electron beam, and the thickness is 5nm. Evaporated hole injection layer: the material is V 2 o 5 , with a t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com