Thin shell type catalyst and preparation method thereof
A catalyst and thin-shell technology, applied in the field of thin-shell catalysts, can solve the problems of shell precious metal loss and easy wear, and achieve the effect of excellent activity and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
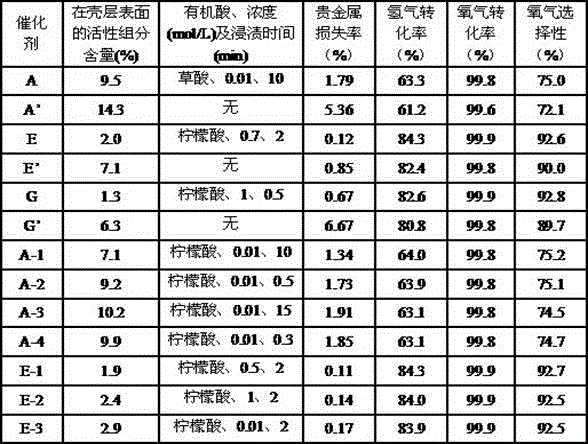
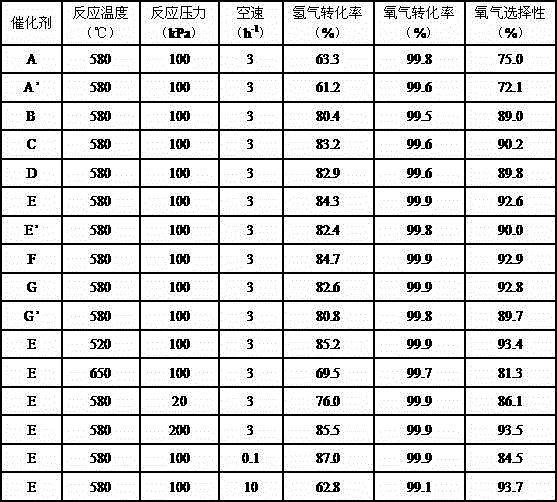
[0034] Put 10 grams of small spherical particle thin-shell carrier AI whose core is mullite, thin shell is γ-alumina, and the shell thickness is 0.21 mm, into 50 mL of oxalic acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.01 mol / L for 10 min. Afterwards, the pellets were filtered out, and dried in an oven at 120° C. for 14 hours to obtain the thin-shell carrier AII.
[0035] Dissolve ammonium chloroplatinate in water to prepare a solution. Put the thin-shell carrier AII impregnated with oxalic acid into 40mL ammonium chloroplatinate solution for impregnation, then dry at 90°C for 24 hours, then bake at 400°C for 20 hours, and cool to room temperature to obtain a non-uniform distribution of Pt in the shell The thin-shell catalyst A. Elemental analysis showed that the mass fraction of Pt in the catalyst was 0.0502%.
[0036] The attrition rate of the thin-shell catalyst A was determined to be 0.80% according to the method of the standard HG / T 2976-1999, and the mass fraction ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Put 10 grams of small spherical particle thin-shell carrier BI whose core is silicon carbide, thin shell is δ-alumina, and shell thickness is 0.33 mm into 50 mL of tartaric acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.05 mol / L for 8 minutes. After dipping The pellets were filtered out and dried in an oven at 100°C for 20 hours to obtain the thin-shell carrier BII.
[0046] Dissolve triruthenium dodecacarbonyl in water to prepare a solution. The thin-shell carrier BII impregnated with tartaric acid was immersed in 40 mL of triruthenium dodecacarbonyl solution, then dried at 100°C for 2 hours, then calcined at 300°C for 24 hours, and cooled to room temperature to obtain Ru in the shell. Evenly distributed thin-shell catalyst B. Elemental analysis showed that the mass fraction of Ru in the catalyst was 0.688%.
[0047] The attrition rate of the thin-shell catalyst B was determined to be 0.46% according to the method of the standard HG / T 2976-1999, and the mass fractio...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Put 10 grams of thin-shell carrier CI with spinel as the inner core, θ-alumina as the thin shell, and a shell thickness of 0.35 mm into 50 mL of citric acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.20 mol / L for 6 min. After impregnation, the pellets were filtered out and dried in an oven at 100°C for 5 hours to obtain the thin-shell carrier CII.
[0052] Dissolve ammonium hexachloroosmate in water to make a solution. Put the thin-shell carrier CII impregnated with citric acid into 40mL ammonium hexachloroosmate solution for impregnation, then dry at 100°C for 15 hours, then bake at 500°C for 8 hours, and cool to room temperature to obtain Os in the shell Non-uniformly distributed thin-shell catalyst C. Elemental analysis showed that the mass fraction of Os in the catalyst was 0.3040%.
[0053] The attrition rate of the thin-shell catalyst C was determined to be 0.27% by the method of the standard HG / T 2976-1999, and the mass fraction of Os in the catalyst with the a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com