A method for detecting free hydrochloric acid content in titanium tetrachloride aqueous solution
An aqueous solution and content technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of less aqueous solution and unsuitable detection and analysis of extremely acidic system of aqueous solution, and achieve the effect of mild process, simple and practical method, and strong operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
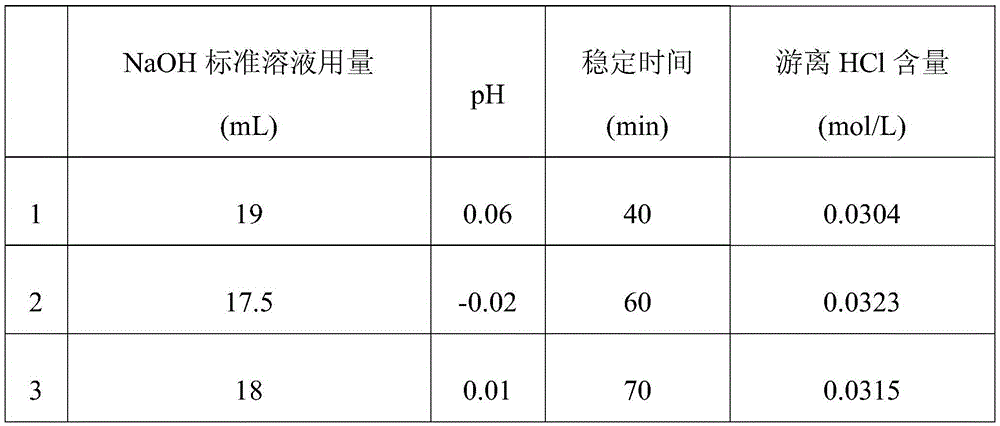
[0035] Take 5 mL of TiCl with a concentration of 1.99 mol / L 4 Put the aqueous solution in a beaker; slowly add 0.5mol / L NaOH standard solution drop by drop, and use a pH meter to measure the pH value of the solution while dropping, and control the pH value of the end point of the solution to be less than 0.1, according to the amount of NaOH standard solution added and the end point of the solution pH value, calculated to get the original TiCl 4 The content of free HCl in the aqueous solution; three groups were measured repeatedly under the same conditions for comparison. The calculation results are shown in Table 1.
[0036] Table 1
[0037]
[0038] As can be seen from Table 1, the free hydrochloric acid content that the 3 repeated tests of embodiment 1 detects is respectively 0.0304mol / L, 0.0323mol / L, 0.0315mol / L, after calculation, the relative deviation of its sample measurement result is 3.04 %.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Take 5 mL of TiCl with a concentration of 2.55 mol / L 4 Put the aqueous solution in a beaker; slowly add 0.5mol / L NaOH standard solution drop by drop, and use a pH meter to measure the pH value of the solution while dropping, and control the pH value of the end point of the solution to be less than 0.1, according to the amount of NaOH standard solution added and the end point of the solution pH value, calculated to get the original TiCl 4 The content of free HCl in the solution; three groups were measured repeatedly under the same conditions for comparison. The calculation results are shown in Table 2.
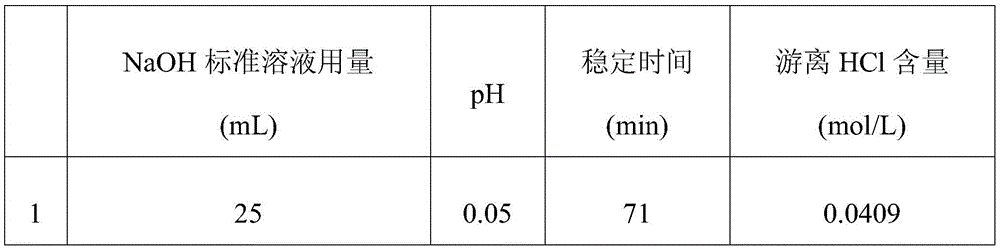
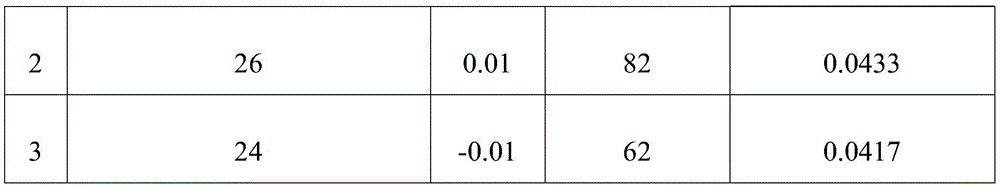
[0041] Table 2
[0042]
[0043]
[0044] As can be seen from Table 2, the free hydrochloric acid content that the 3 repeated tests of embodiment 2 detects is respectively 0.0409mol / L, 0.0433mol / L, 0.0417mol / L, after calculation, the relative deviation of its sample measurement result is 2.91 %.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Take 5 mL of TiCl with a concentration of 2.90 mol / L 4 Put the aqueous solution in a beaker; slowly add 0.5mol / L NaOH standard solution drop by drop, and use a pH meter to measure the pH value of the solution while dropping, and control the pH value of the end point of the solution to be less than 0.1, according to the amount of NaOH standard solution added and the end point of the solution pH value, calculated to get the original TiCl 4 The content of free HCl in the aqueous solution; three groups were measured repeatedly under the same conditions for comparison. The calculation results are shown in Table 3.
[0047] table 3
[0048]
[0049] As can be seen from Table 3, the free hydrochloric acid content that the 3 repeated tests of embodiment 3 detects is respectively 0.0478mol / L, 0.0493mol / L, 0.0500mol / L, after calculation, the relative deviation of its sample measurement result is 2.29 %.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com