A kind of Schottky diode and its manufacturing method
A Schottky diode and anode technology, which can be used in diodes, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., and can solve problems such as large leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
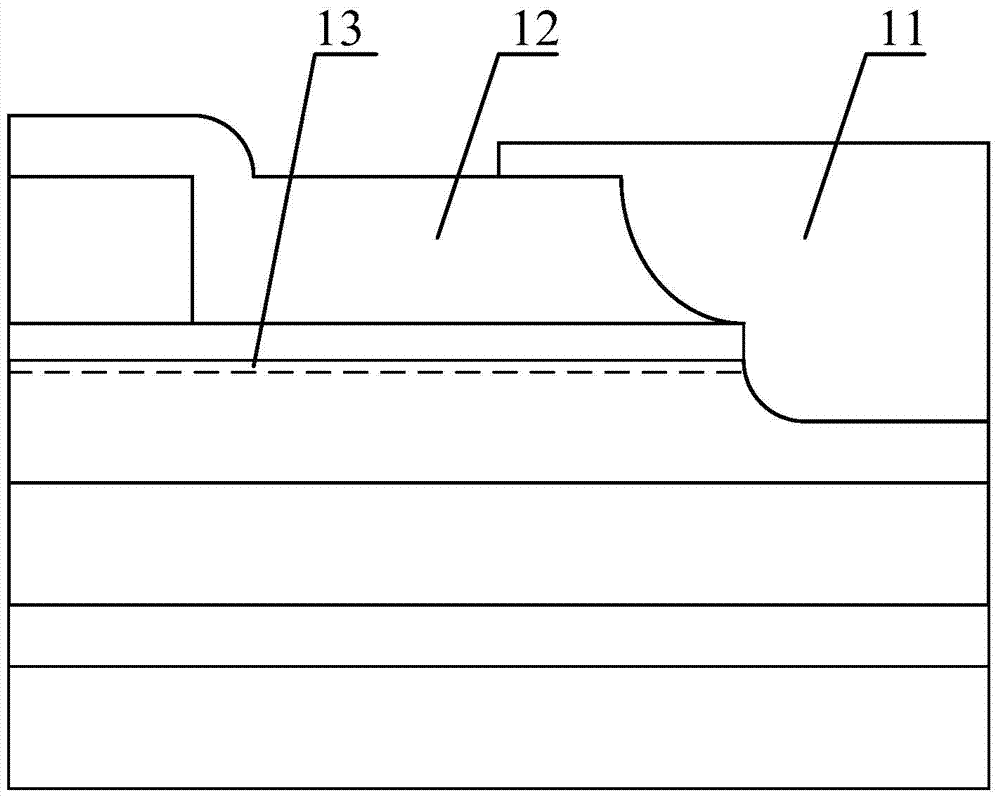
[0060] Figure 4 A schematic cross-sectional view of the Schottky diode provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention is given. Such as Figure 4 shown, the Schottky diode consists of:
[0061] A substrate 1, wherein the material of the substrate 1 can be gallium nitride, silicon, sapphire, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, SOI or other substrate materials that can epitaxially grow III-V group nitrides.
[0062] A nucleation layer 2, a buffer layer 3, a first semiconductor layer 4 and a second semiconductor layer 6 grown sequentially on a substrate 1, wherein the band gap of the first semiconductor layer 4 is smaller than the band gap of the second semiconductor layer 6 , the material of the nucleation layer 2 can be aluminum nitride or gallium nitride, the material of the buffer layer 3 can be a graded layer of aluminum gallium nitride or a superlattice material, and the material of the first semiconductor layer 4 can be gallium nitride, The material of the second sem...
Embodiment 2
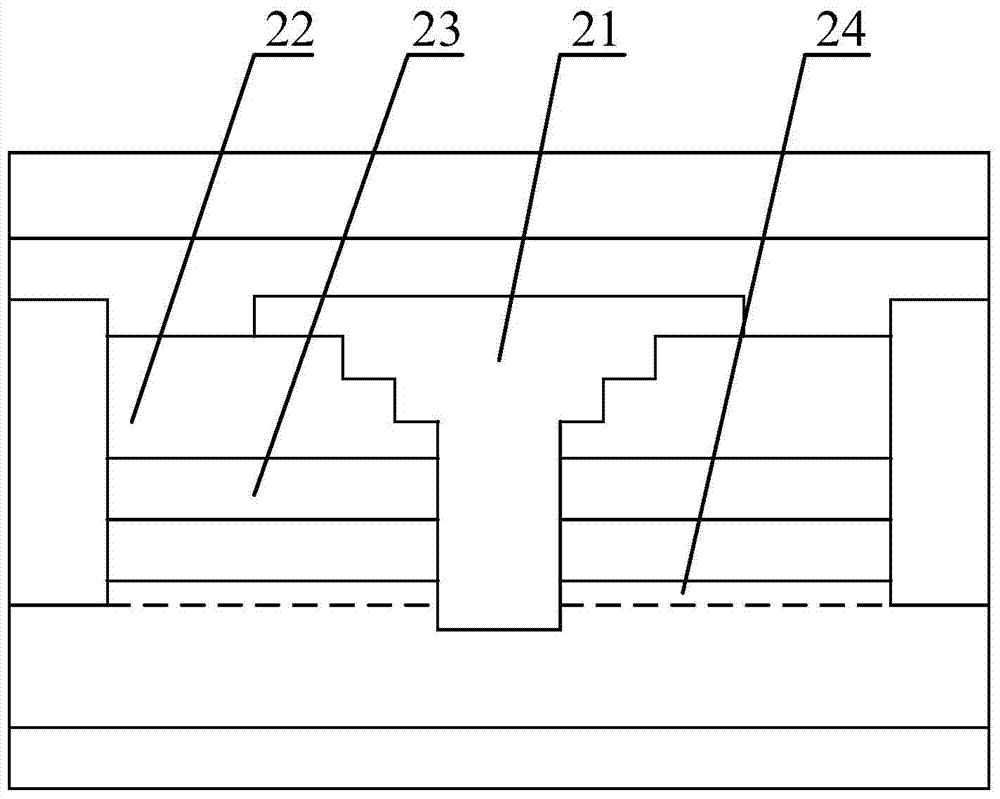
[0082] Figure 8 A schematic cross-sectional view of the Schottky diode provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention is given.
[0083] Such as Figure 8 As shown, different from the first embodiment, the anode trench of the Schottky diode provided by the second embodiment extends into the second semiconductor layer 6 , but does not exceed the second semiconductor layer 6 . After the second semiconductor layer is etched and thinned, the concentration of the two-dimensional electron gas under it will decrease, resulting in an increase in the on-resistance. If the etching depth is too deep, the two-dimensional electron gas will be depleted, and the diode’s The forward voltage will increase. Therefore, the etching depth of the field plate trench needs to be controlled within a reasonable range. Generally speaking, the distance between the bottom of the trench and the two-dimensional electron gas channel needs to be greater than 5 nm to ensure a normal conduction of two-dim...
Embodiment 3
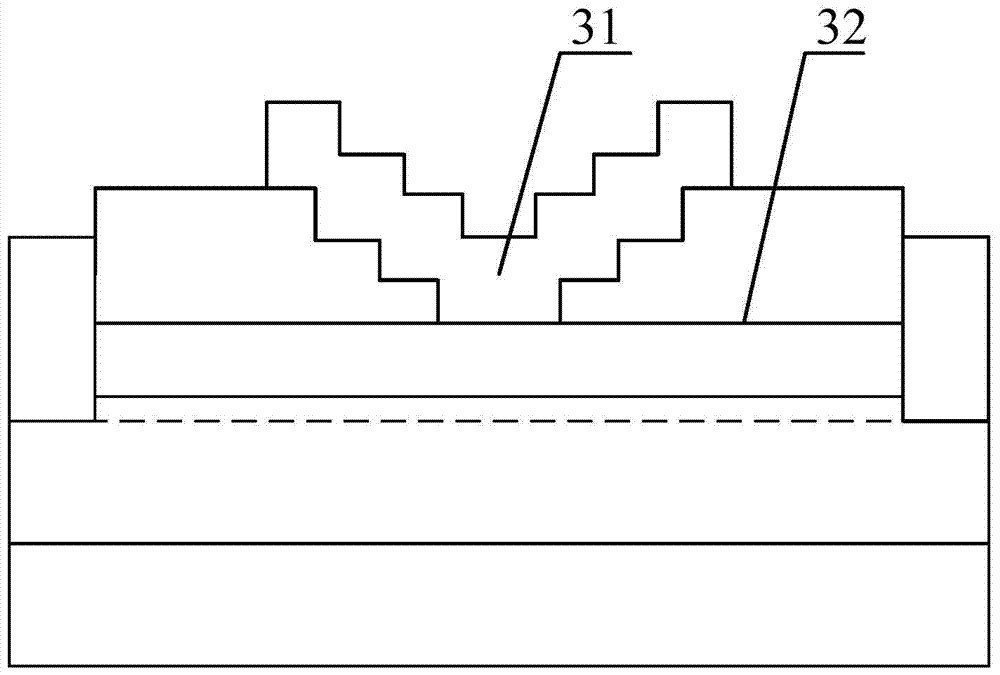
[0086] Figure 9 A schematic cross-sectional view of the Schottky diode provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention is given.
[0087] Such as Figure 9 As shown, different from Embodiment 1, the Schottky diode provided in Embodiment 3 also includes:
[0088] The field plate trench dielectric layer 10 is located on the passivation dielectric layer 8 and on the field plate trench.
[0089] In this embodiment, the material of the field plate trench dielectric layer 10 may be any one or a combination of at least two of silicon nitride, silicon dioxide, silicon oxynitride or aluminum oxide.
[0090] Compared with the Schottky diode provided in the first embodiment of the present invention, in the anode structure of the Schottky diode provided in the third embodiment of the present invention, a field plate trench dielectric layer is added between the field plate trench and the anode, which can further Reduces the leakage current flowing through the Schottky junction in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com