Ferronickel-based alloy welding joint heat-affected zone grain boundary liquation crack control method
An iron-nickel-based alloy and heat-affected zone technology, applied in welding/welding/cutting articles, welding equipment, welding equipment, etc., can solve problems such as liquefaction cracks, achieve control of welding deformation, improve joint strength, and facilitate surface forming Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
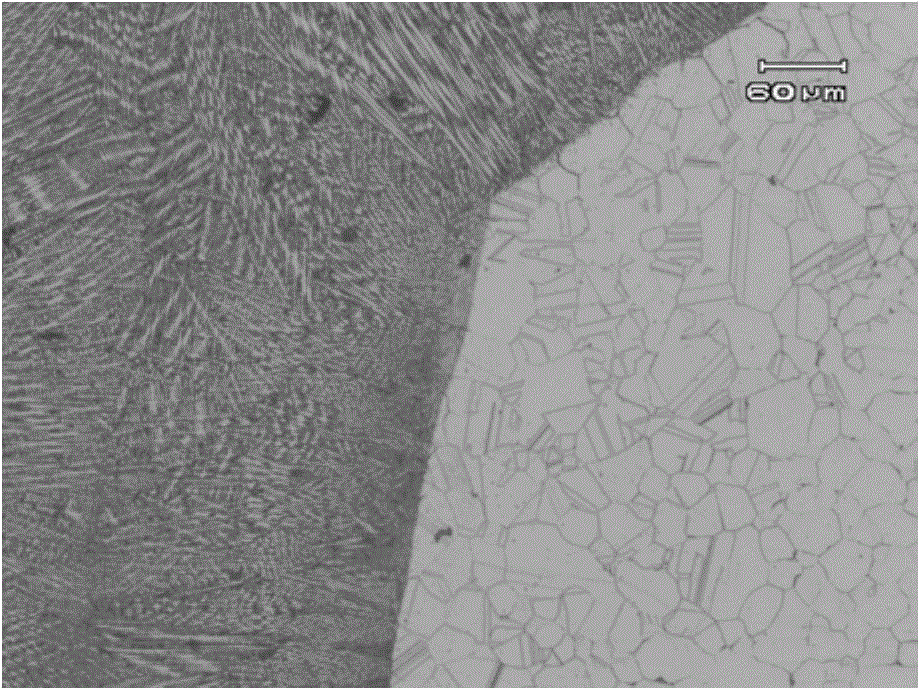
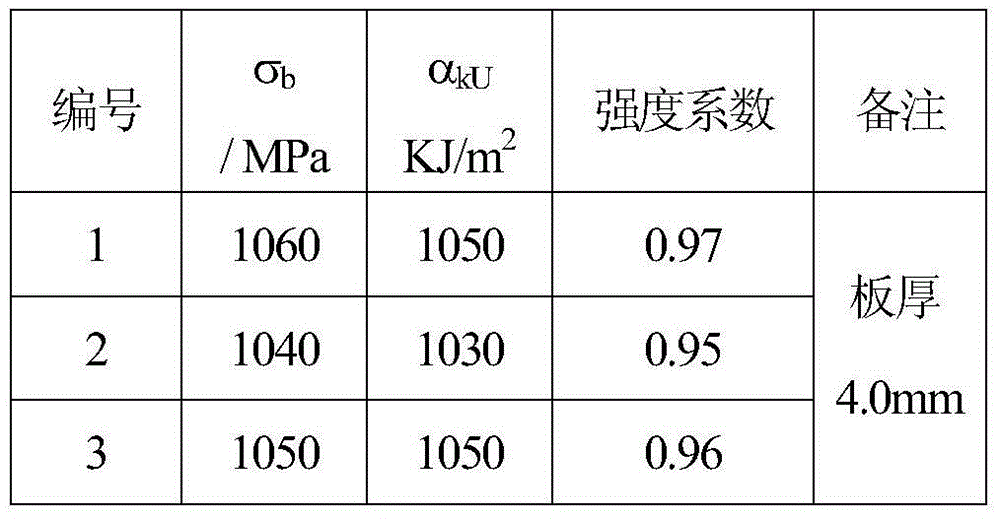
[0031] Vacuum electron beam welding of J75 alloy plates with specifications of 180mm (length) × 60mm (width) × 4.0mm (thickness), the specific implementation process is as follows:
[0032] 1. The J75 alloy plate blanks are all hot-rolled plates, and the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the hot-rolled plates meet the requirements of GJB 5724-2006 "Specification for Hydrogen-resistant Steel Bars". The J75 plate was treated at 980°C / 1h, water quenched +740°C / 8h, and air-cooled. The plate after heat treatment is machined to 3.5-4.5 mm (4.0 mm in this embodiment), and the length direction is machined to roughness Ra1.6 μm by grinding machine.
[0033] 2. Carry out decontamination treatment on the base metal after polishing treatment in step 1. During the treatment, petroleum ether is first used to degrease, and then alcohol is used to scrub. The decontamination treatment needs to be carried out within 30 minutes before welding;
[0034] 3. Clamp and fix the J75 a...
Embodiment 2
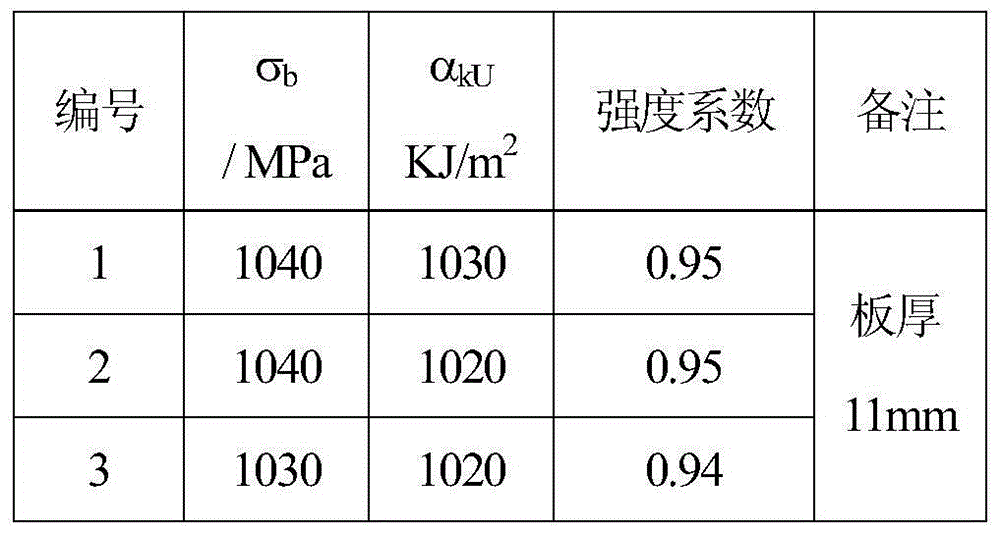
[0046] The vacuum electron beam welding of the J75 alloy plate with a specification of 120mm (length) × 60mm (width) × 11mm (thickness), differs from Example 1 in that the thickness of the welded J75 alloy plate is 11mm, and the welding process parameters are adjusted accordingly , Post-weld modification welding process parameters and electron beam scanning times.
[0047] The J75 alloy plate blank with the same heat treatment as in Example 1 was adopted, machined to a thickness of 11 mm after heat treatment, and processed to a roughness of Ra1.6 μm by a grinder in the length direction; petroleum ether was used to degrease 30 minutes before welding, and the grinding was scrubbed with alcohol. The base metal after light treatment; then use the butt joint and tight fit method to clamp and fix the two J75 alloy plates in the welding room, and keep the two base metals placed horizontally; close the vacuum welding room and pump the vacuum to 8×10 -3 After Pa, the positioning weldin...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The vacuum electron beam welding of the J75 alloy plate with a specification of 150mm (length) × 80mm (width) × 19mm (thickness), differs from Example 1 in that the thickness of the welded J75 alloy plate is 19mm, and the welding process parameters are adjusted accordingly , Post-weld modification welding process parameters and electron beam scanning times.
[0053] The J75 alloy plate blank with the same heat treatment as in Example 1 was adopted, machined to a thickness of 19 mm after heat treatment, and processed to a roughness of Ra1.6 μm by a grinder in the length direction; petroleum ether was used to degrease 30 minutes before welding, and the grinding was scrubbed with alcohol. The base metal after light treatment; then two pieces of J75 alloy plates are clamped and fixed in the welding room by means of butt joint and tight fit, and the two base metals are placed horizontally; the vacuum welding room is closed and the vacuum degree is evacuated to 5×10 -3 After ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com