Magnesium stabilized ultra low soda cracking catalysts
A catalyst, catalytic cracking technology, applied in physical/chemical process catalysts, molecular sieve catalysts, catalyst activation/preparation, etc., can solve problems such as reducing catalytic activity, stability and yield, affecting bottom-line profit generation, reducing catalyst performance, etc. Achieve activity and hydrothermal stability, good coke and hydrogen selectivity, improved FCC process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
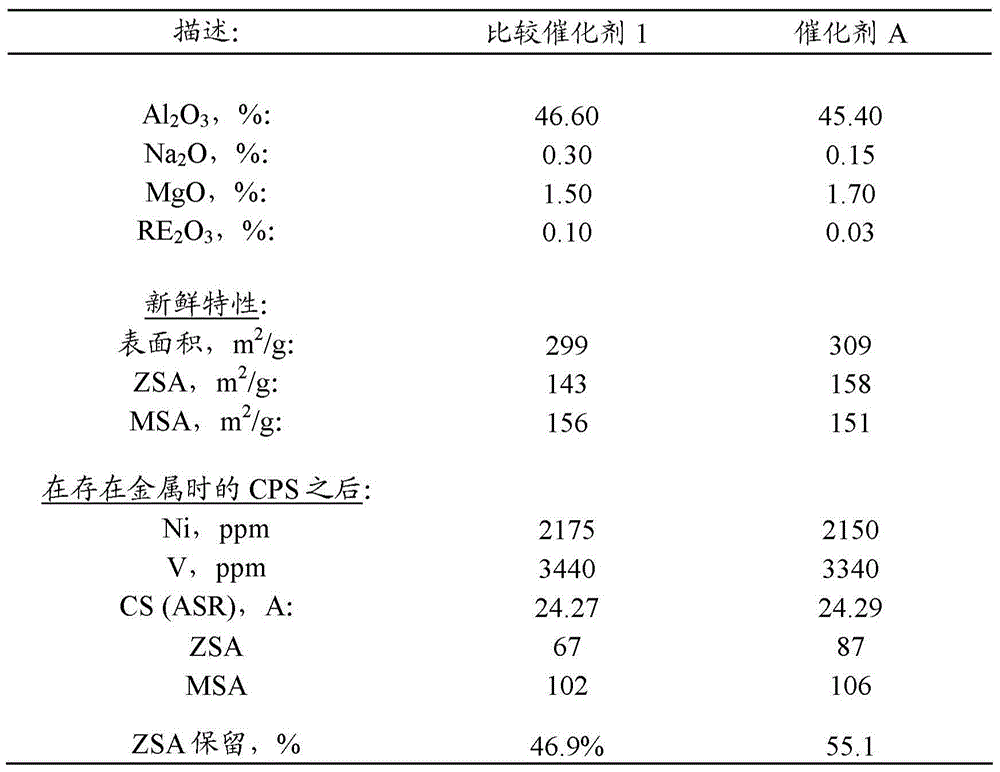
[0070] Example 1: Ultra-low Na with 1.6% MgO 2 O catalyst
[0071] with containing 0.9 wt% Na 2 Catalyst A was prepared from the USY zeolite of O. will contain 25% USY zeolite (0.9% Na 2 O), a slurry of 20% colloidal silica (Bindzil), 35% acid peptized alumina and 20% clay was ground in a Drais mill and subsequently spray dried in a Bowen spray dryer. The spray-dried catalyst was calcined at 400 °C for 40 minutes in a laboratory muffle furnace. Washing the calcined catalyst to remove Na 2 O. After the washing step, with enough MgSO 4 The solution impregnated the filter cake to form 1.6 wt% MgO on the catalyst. The resulting catalyst was designated Catalyst A. Catalyst A contains 0.15 wt% Na 2 O, which corresponds to 0.60 wt% Na based on zeolite 2 O. The characteristics of the catalyst are shown in Table 1 below.
example 2
[0077] Example 2: DCR Evaluation of Catalyst A
[0078] Using the cyclopropene steam (CPS) protocol (see ACS Symposium Series by Lori T. Boock, Thomas F. Petti and John A. Rudesill, 634, 1996, 171-183 (ACS Symposium Series, Vol. 634, 1996 , pp. 171-183)) deactivates Catalyst A and Comparative Catalyst 1. The catalyst was deactivated in the presence of 2000ppm Ni / 3000ppm V. After deactivation, the physical and chemical properties of Catalyst A and Comparative Example 1 are listed in Table 1 above.
[0079] Catalyst A exhibited significantly better retention of zeolite surface area (ZSA) after deactivation than Comparative Catalyst 1 . The deactivated catalyst was then run through a Davison Circulation Riser (DCR) unit with resid feed. The reactor temperature was 527°C. The DCR test results are reported in Table 2 below.
[0080] Table 2
[0081] Ultra-low sodium Mg-containing catalyst B after CPS in the presence of 2000ppm Ni / 3000ppm V The interpolated DCR yield o...
example 3
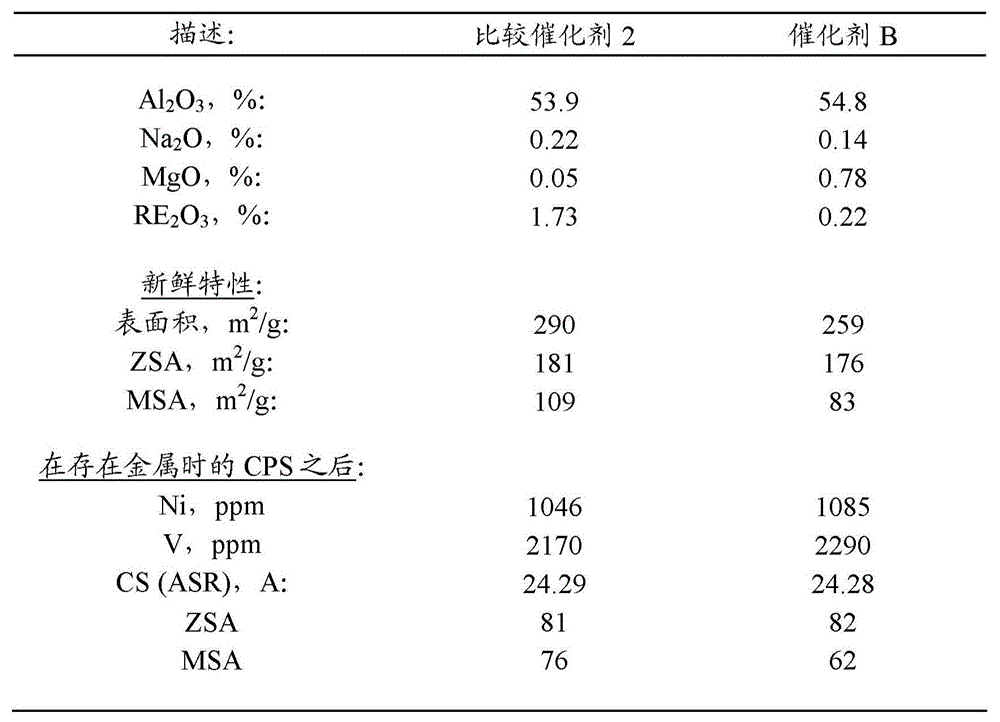
[0084] Example 3: Ultra-low Na with 0.8% MgO 2 O catalyst
[0085] with containing 0.9% Na 2 Catalyst B was prepared from the USY zeolite of O. A slurry comprising 25% USY zeolite, 15% boehmite alumina, 18% aluminum chlorohydrate and 42% clay was ground in a Drais mill and then spray dried in a Bowen spray dryer. The spray-dried catalyst was calcined at 400 °C for 40 minutes in a laboratory muffle furnace. Washing the calcined catalyst to remove Na2 O. After the washing step, with enough MgSO 4 The solution impregnated the filter cake to form 0.8 wt% MgO on the catalyst. The resulting catalyst was designated Catalyst B. Catalyst B contains 0.14 wt% Na 2 O, which corresponds to 0.56 wt% Na based on zeolite 2 O. The characteristics of the catalyst are shown in Table 3 below.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com