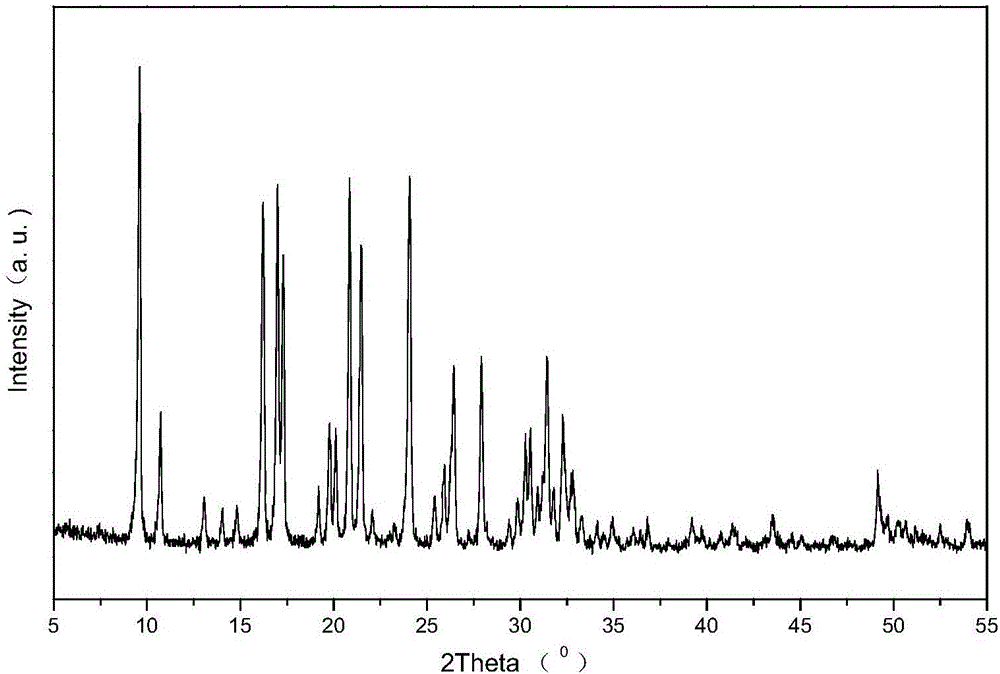
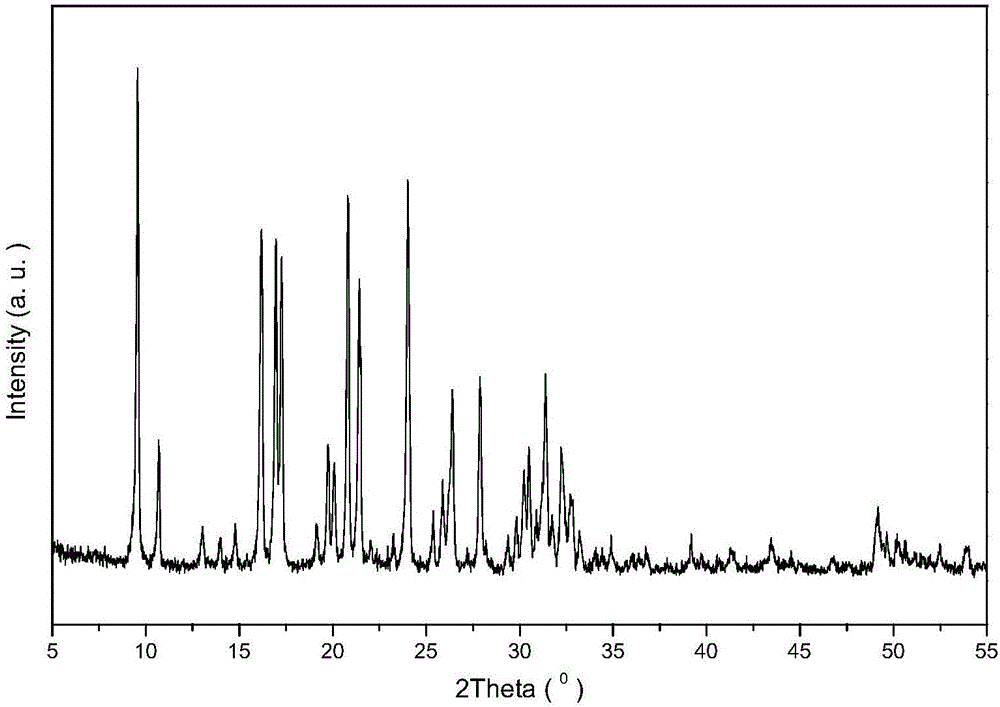
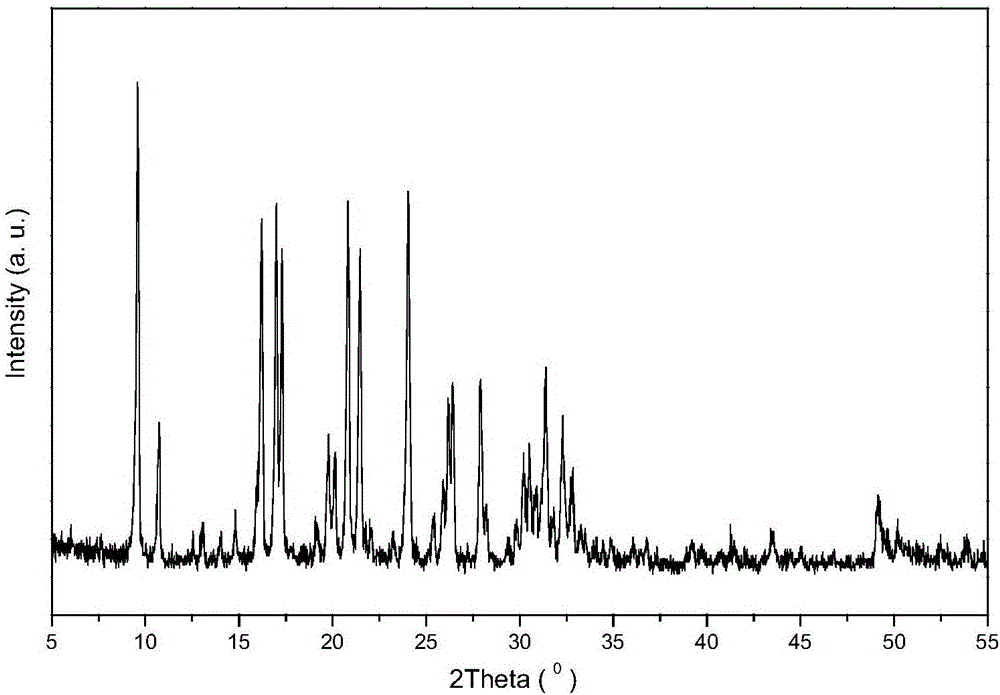
High-silica-alumina-ratio SSZ-39 zeolite, and synthesis and application thereof
A technology of SSZ-39 and synthesis method, which is applied in the direction of crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, other chemical processes, carbon compound catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the use efficiency of nano-zeolite, easy agglomeration, etc., and achieve the suppression of hydrogen transfer and aluminum content The effect of low and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Add 774.12g of water glass to 178.38g of 25wt% N,N-dimethyl-3,5-dimethylpiperidine (DMDMPOH, represented by "T") in an aqueous solution and stir well, then add 18.49g HY molecular sieve with a silicon-aluminum ratio of 5.2 and 0.4051g of NH4F powder, then sequentially add 2.32g of NaOH particles and 0.1746g of polyethylene glycol PEG-600 as a crystal growth inhibitor, add 294.80g of deionized water and stir thoroughly. The resulting mixed slurry was continuously stirred in a sealed container at room temperature for 2 hours until all the raw materials were mixed evenly, and there was a mixed sol with the following molar composition: 0.29Na 2 O: SiO 2 : 0.0125A1 2 o 3 :0.08T:0.003F:15H 2 O.
[0039] The resulting solid mixture was transferred to Lined in a 2000ml hydrothermal crystallization kettle, stirred at 60rpm, crystallized at 120°C for 24 hours, then raised the temperature to 140°C for 48 hours. After the crystallization is complete, the product is cooled ra...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Using the same experimental method and experimental raw materials as in Example 1 to synthesize SSZ-39 molecular sieves, the difference is the difference in the amount of raw materials added, so that in the sol before the crystallization reaction, silicon source, sodium source, aluminum source, fluoride ion, The molar ratio ratio of the amount of template agent and deionized water constitutes the following molar composition: 0.31Na 2 O: SiO 2 : 0.00625A1 2 o 3 :0.09T:0.008F:25H 2 O.
[0043] By the same ammonium ion exchange method as in Example 1, the H-type SSZ-39 molecular sieve product was obtained by drying and roasting. The addition amount of various raw materials for crystallization synthesis is shown in Table 1, and the molecular sieve sample is marked as B, and its physical and chemical properties are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Using the same experimental method and experimental raw materials as in Example 1 to synthesize SSZ-39 molecular sieves, the difference is the difference in the amount of raw materials added, so that in the sol before the crystallization reaction, silicon source, sodium source, aluminum source, fluoride ion, The molar ratio ratio of the amount of template agent and deionized water constitutes the following molar composition: 0.34Na 2 O: SiO 2 : 0.00417A1 2 o 3 :0.15T:0.02F:35H 2 O.
[0046] By the same ammonium ion exchange method as in Example 1, the H-type SSZ-39 molecular sieve product was obtained by drying and roasting. The addition amount of various raw materials for crystallization synthesis is shown in Table 1, and the molecular sieve sample is marked as C, and its physical and chemical properties are shown in Table 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com