Application of biological adsorbing agent
A biological adsorbent and application technology, applied in the direction of adsorption of water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, special compound water treatment, etc., can solve the problem that the filtrate is not fully utilized, and achieve waste reduction, good adsorption performance, and simple operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The tea dregs discarded in the beverage production factory are recovered, washed in hot water, dried in an oven at 80°C to constant weight, then crushed and sieved. Take 60-200 mesh tea residue powder, add it to 0.1mol / L citric acid solution, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:50 (g:mL), soak for 24 hours, then raise the temperature to 120°C under continuous stirring, and continue for 90 minutes, naturally Cool to room temperature, and the filtrate obtained by suction filtration is the filtrate produced by citric acid modified tea dregs.
[0034] Take 300 mL of the above filtrate, add 3.0 g of chitosan, and continue to stir at 50 ° C for 4 h, then adjust the pH value to 8 with 1 mol / L NaOH solution during stirring, and then continue to stir for 1 h; filter and wash after natural cooling, the obtained The solid particles are oven-dried and pulverized at 50°C to make the biosorbent.
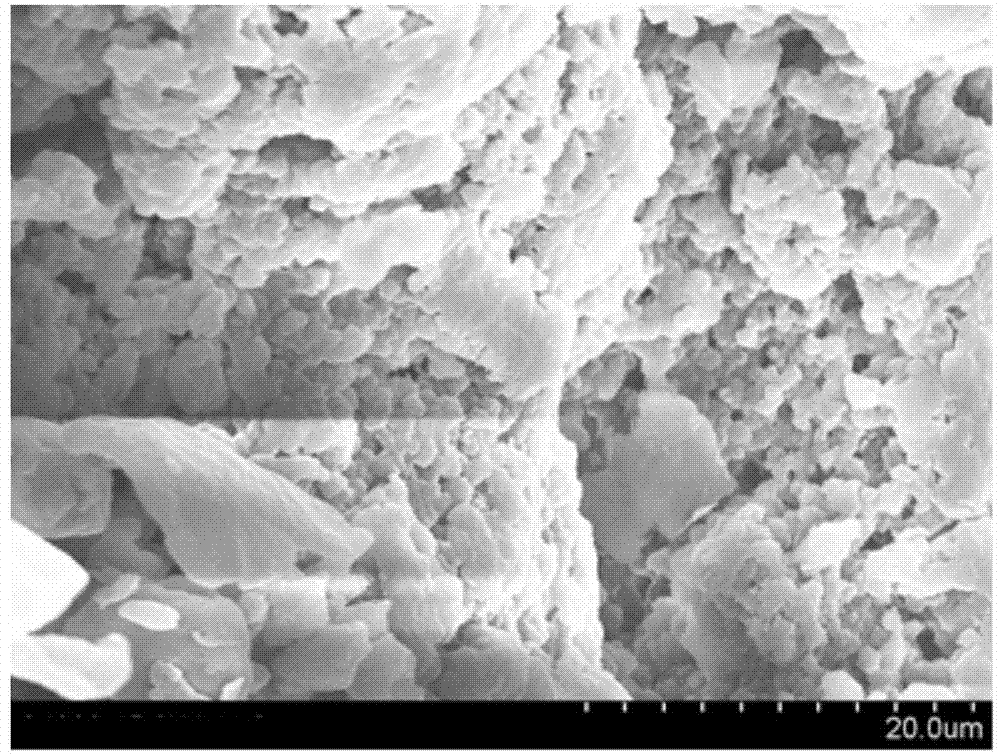
[0035] figure 1 The scanning electron micrograph of the biosorbent prepared for the presen...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The discarded bamboo shoot shells from the bamboo shoot processing factory were recovered, washed to remove the surface dust, dried in an oven at 80°C to constant weight, and then crushed and sieved. Take bamboo shoot shell powder of 40-200 mesh, add it to 0.5mol / L citric acid solution, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:100, after immersing for 6 hours, heat up to 80°C under continuous stirring, and continue for 90 minutes, and naturally cool to room temperature. The filtrate obtained by suction filtration is the filtrate produced by citric acid modified bamboo shoot shells.
[0038] Take 300mL of the above filtrate, add 6.0g chitosan, continue stirring at 80°C for 4h, then adjust the pH value to 8 with 1mol / L NaOH solution during stirring, and continue stirring for 1h; Wash with ionic water until the pH is constant, filter and wash after natural cooling, and dry and pulverize the obtained solid particles in an oven at 50°C to prepare the biosorbent.
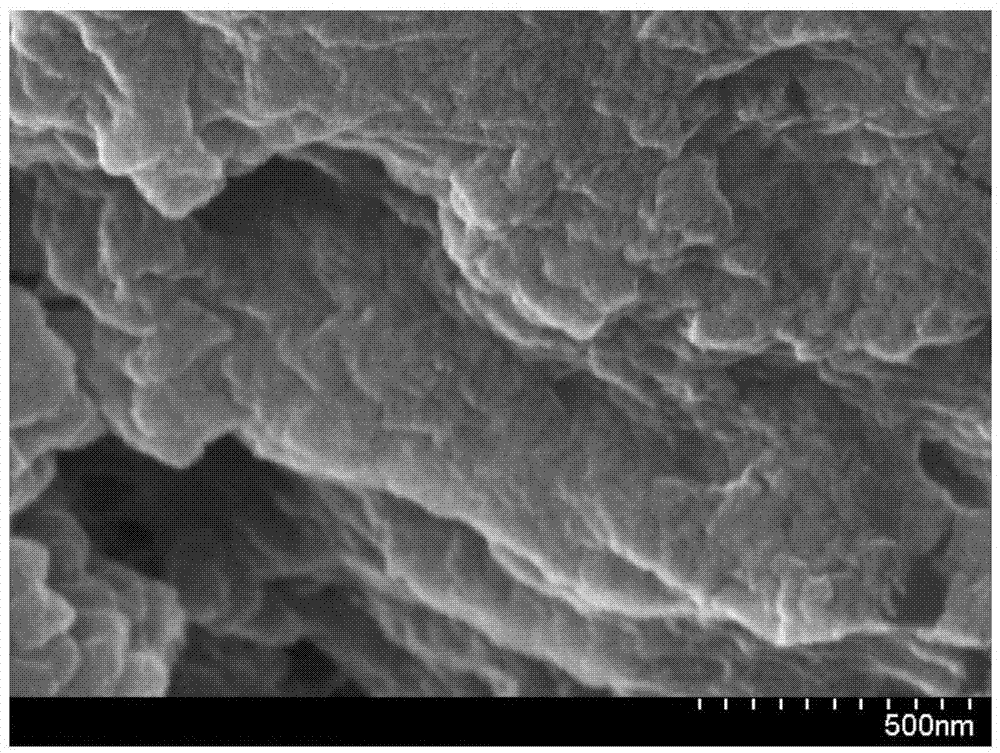
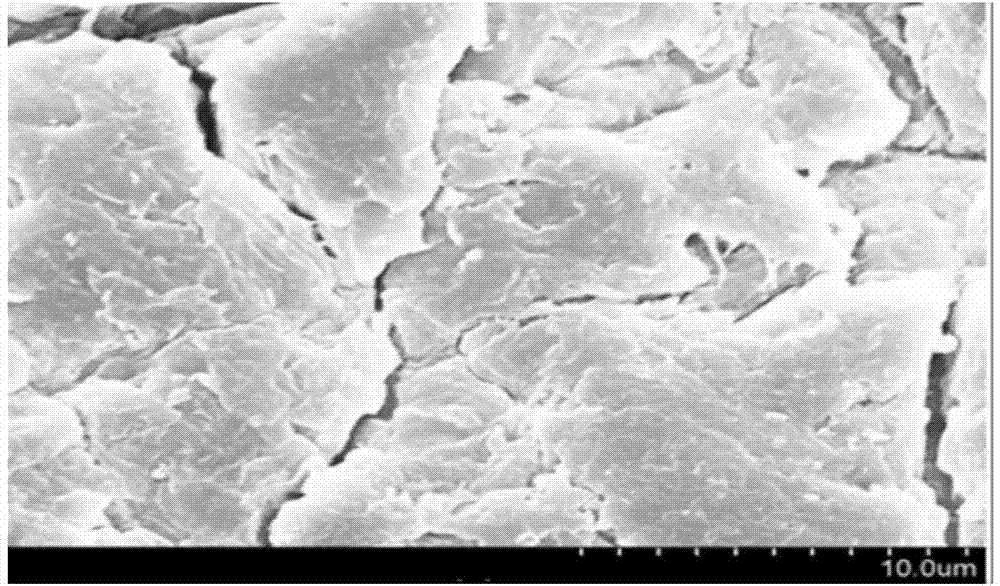
[0039] figure 2 T...
Embodiment 3
[0041] The discarded citrus peel residue after pectin extraction in pectin factory is recovered, washed and dried in an oven at 80°C to constant weight, then crushed and sieved. Take 40-200 mesh citrus peel powder and add it to 1.0mol / L citric acid solution with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:80. After soaking for 15 hours, raise the temperature to 100°C under continuous stirring for 90 minutes, and let it cool naturally to room temperature. , the filtrate obtained by suction filtration is the filtrate produced by citric acid modified citrus peel.
[0042] Take 300 mL of the above filtrate, add 4.5 g of chitosan, continue to stir at 60 ° C for 4 h, then adjust the pH value to 9 with 1 mol / L NaOH solution during stirring, and then continue to stir for 1 h; filter and wash after natural cooling, the obtained The solid particles are oven-dried and pulverized at 50°C to make the biosorbent.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com