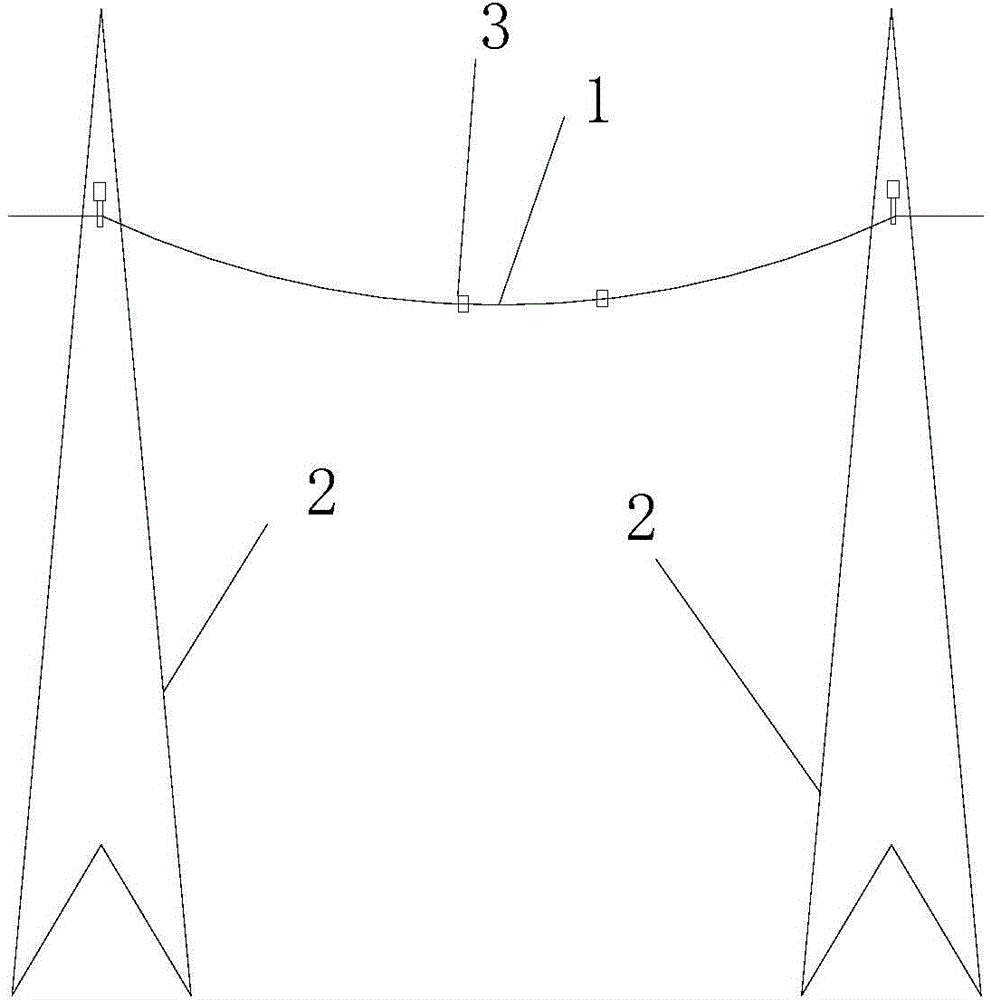
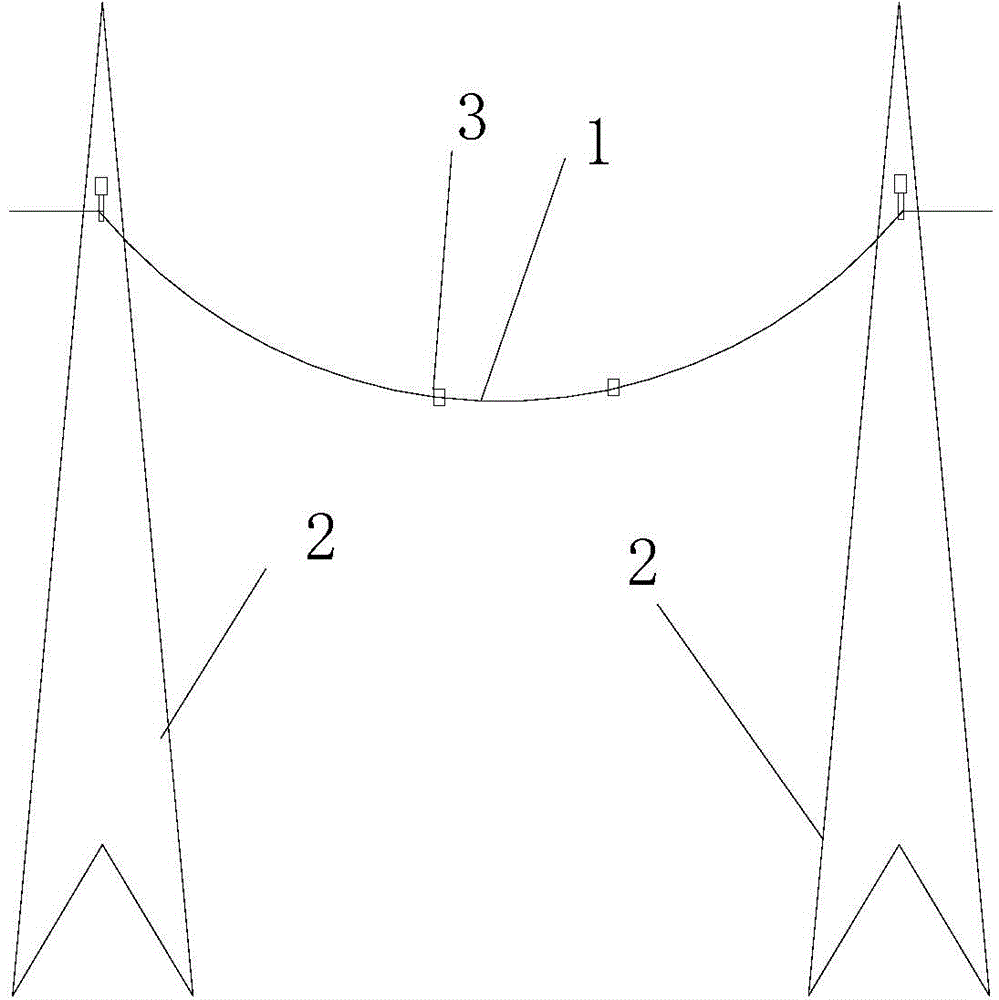
[0005] 1. Since the aluminum conductor layer is wrapped around the wire core by winding, it is difficult to make the wire core and the aluminum conductor layer fit tightly and firmly, that is, there will be a gap between the inner wall of the aluminum conductor layer and the outside of the wire core, that is The core can be pulled out of the aluminum conductor layer at will; in use, see figure 1 , 2 1. The power
transmission line 1 is erected between two support towers 2 for
electric energy transmission. Due to
thermal expansion and contraction, the aluminum conductor layer will expand or contract; and due to the characteristics of low expansion and high
temperature resistance of carbon fiber materials, in During use, the carbon fiber core basically maintains its original shape, without huge deformation, and its deformation is basically negligible; therefore, when the aluminum conductor layer expands, the length of the aluminum conductor layer will become longer and the
diameter will increase, and the core will be more It is easy to pull out from the aluminum conductor layer, so that the entire transmission wire will produce obvious sag phenomenon, and if it is more serious, the expansion of the aluminum conductor layer will generate a force to push the supporting
tower, prompting the supporting
tower to tilt outward, reducing the safety of use; When the aluminum conductor layer shrinks, the length of the aluminum conductor layer will become shorter and the diameter will become smaller, which will generate a force that pulls the supporting tower to tilt inward, and also promotes the tilting of the supporting tower; The conductor layer only plays the role of hanging in mid-air, and does not restrain the aluminum conductor layer
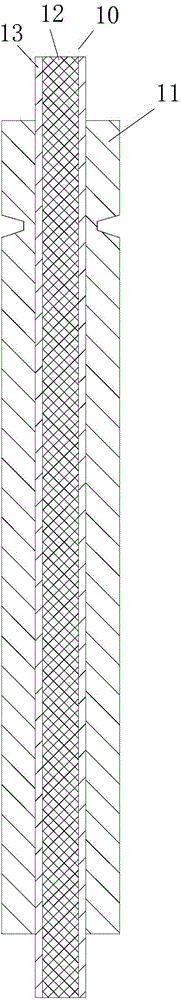
[0006] 2. The aluminum conductor layer is a plurality of aluminum conductors wound outside the wire core and arranged in a spiral counterclockwise direction along the wire core to form an aluminum conductor layer; since the aluminum conductor layer is formed by spirally winding multiple aluminum conductors, the adjacent aluminum conductors There will inevitably be gaps between them. During use, impurities and water will enter the gaps to form barriers and corrode, which will affect the
conductivity of the wires and cause a large
power loss. In order to meet the
conductivity of the wires, it is necessary to increase the aluminum conductor layer. Cross-sectional area, which undoubtedly greatly increases the input cost of the wire
[0008] 4. Since the aluminum conductor layer is formed by winding the inner layer of the aluminum conductor and the outer layer of the aluminum conductor, the thickness of the aluminum conductor layer composed of double aluminum conductors is thicker, the cost is high, and the production is difficult. At the same time, the weight of the entire
transmission line is increased, thereby further Sag Phenomenon During the Use of Earth-weighted Transmission Lines
[0009] 5. Since the existing aluminum conductor layer is spirally wound by multiple aluminum conductors, gaps will inevitably be formed between adjacent aluminum conductors; in this way, when the overhead
transmission line is blown by the wind, the wind will enter the interior of the transmission line through the gap, The gas vortex is generated inside the transmission line, so that the gas stays in the transmission line for a long time, which will increase the swaying amplitude and frequency of the transmission line; because the transmission line needs to use the clamp 3 to prevent the loosening of the transmission line, the swaying of the transmission line During the process, the transmission line at the clamp is repeatedly bent, causing
material fatigue, and finally leads to broken strands and disconnection accidents of the transmission line, which is harmful to the normal and
safe operation of the
transmission system, and the service life of the transmission line and the
transmission system is relatively short
[0010] 6. Since there is no firm connection between the wire core and the aluminum conductor layer in the transmission line, and due to the
long span and
heavy weight of the overhead transmission line, the aluminum conductor layer takes the wire core to produce arc sag. When the aluminum conductor layer is bent and deformed, its cross-section The
centroid produces
linear displacement along the direction perpendicular to the axis, that is, deflection. Therefore, in the design of the pre-
transmission system, the length of the transmission line after the sag needs to be considered; for example, an overhead transmission
system of one kilometer needs at least 10 meters more Left and right transmission lines to overcome the problem of sag. If the total length of transmission lines used in a
regional power grid is 1,000 kilometers, an additional 10 kilometers of transmission lines are required. If a meter of transmission lines is worth 100 yuan, an additional 1 million yuan is required. Increased input costs for the transmission grid
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More