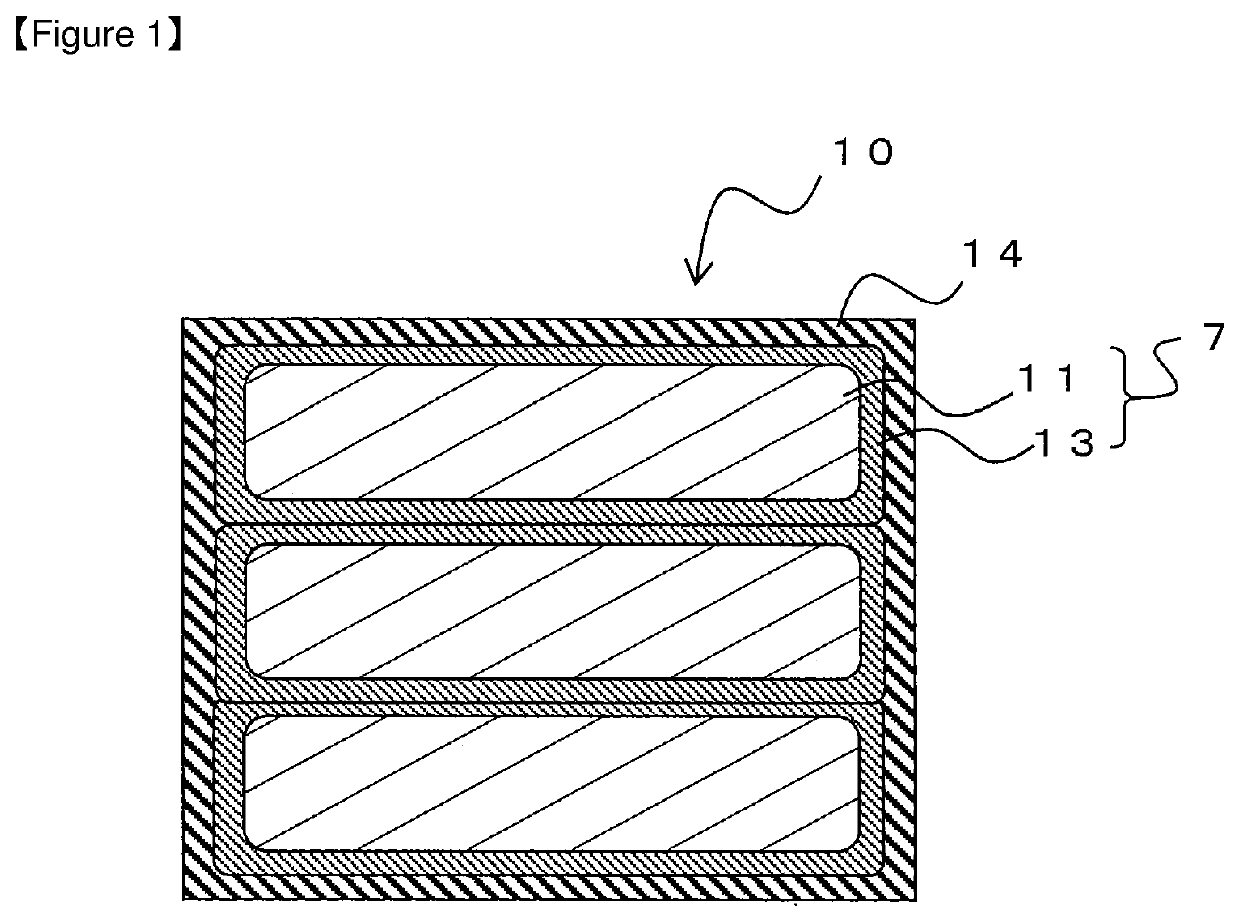
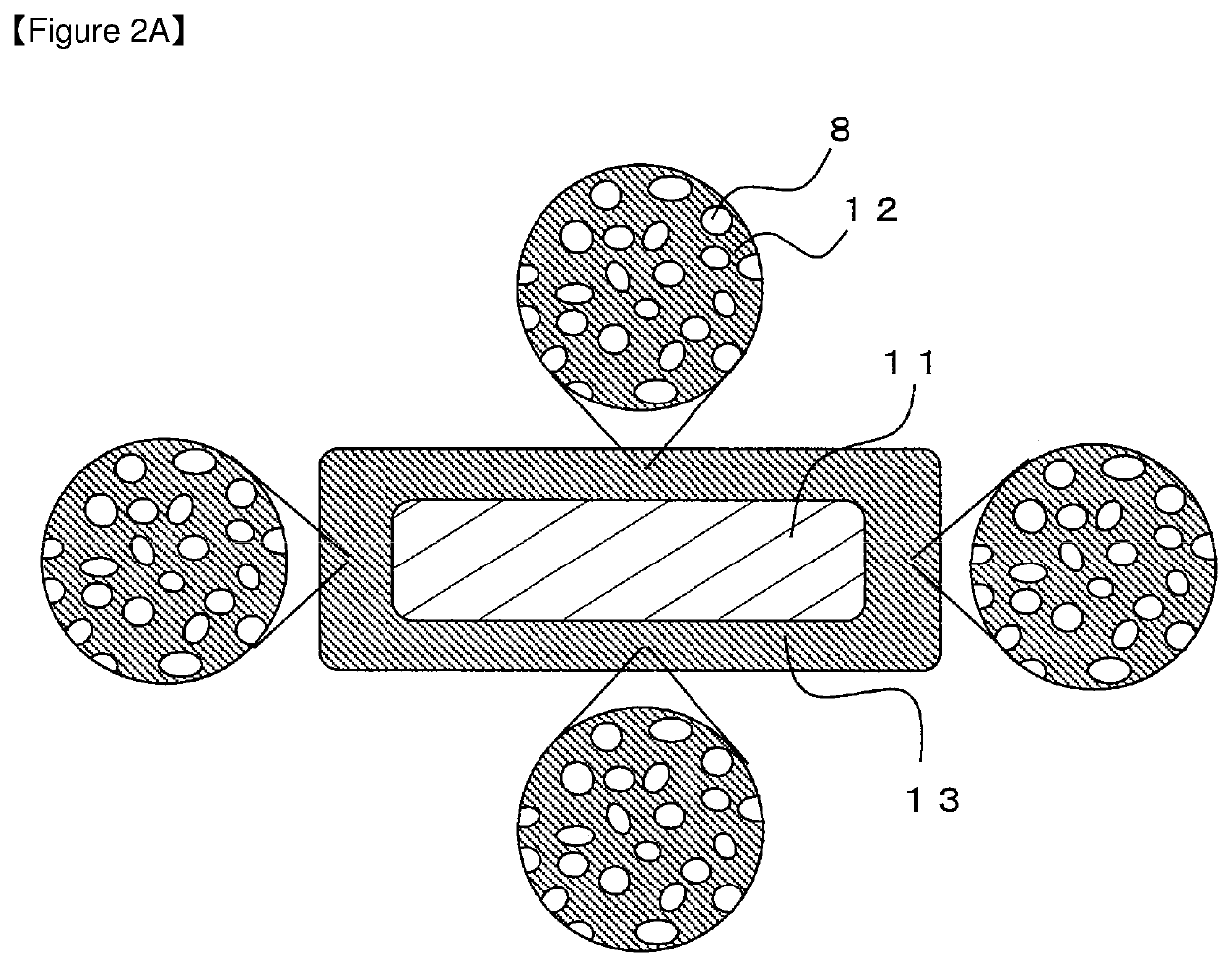
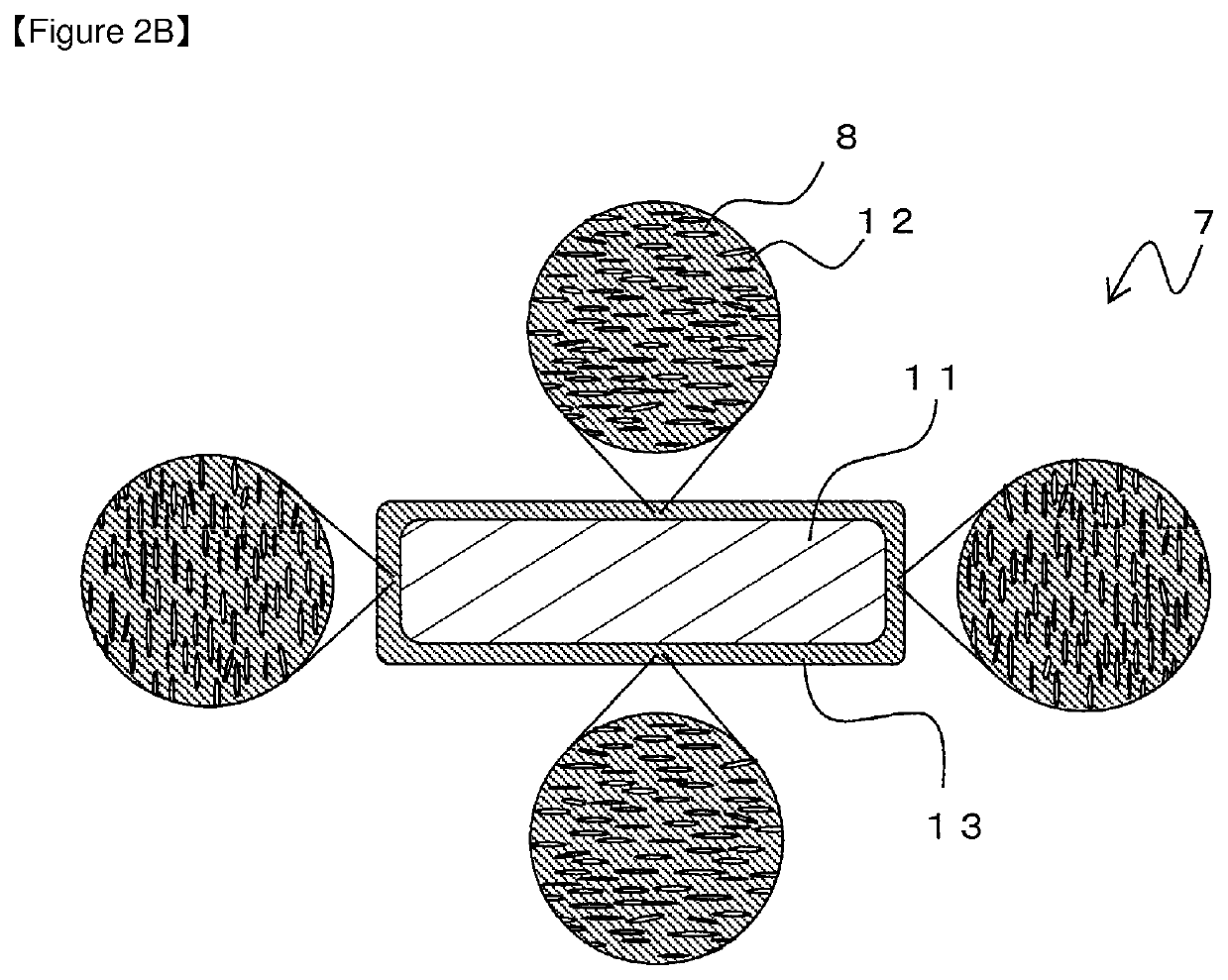
Patents
Literature
88results about "Single tube conductors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
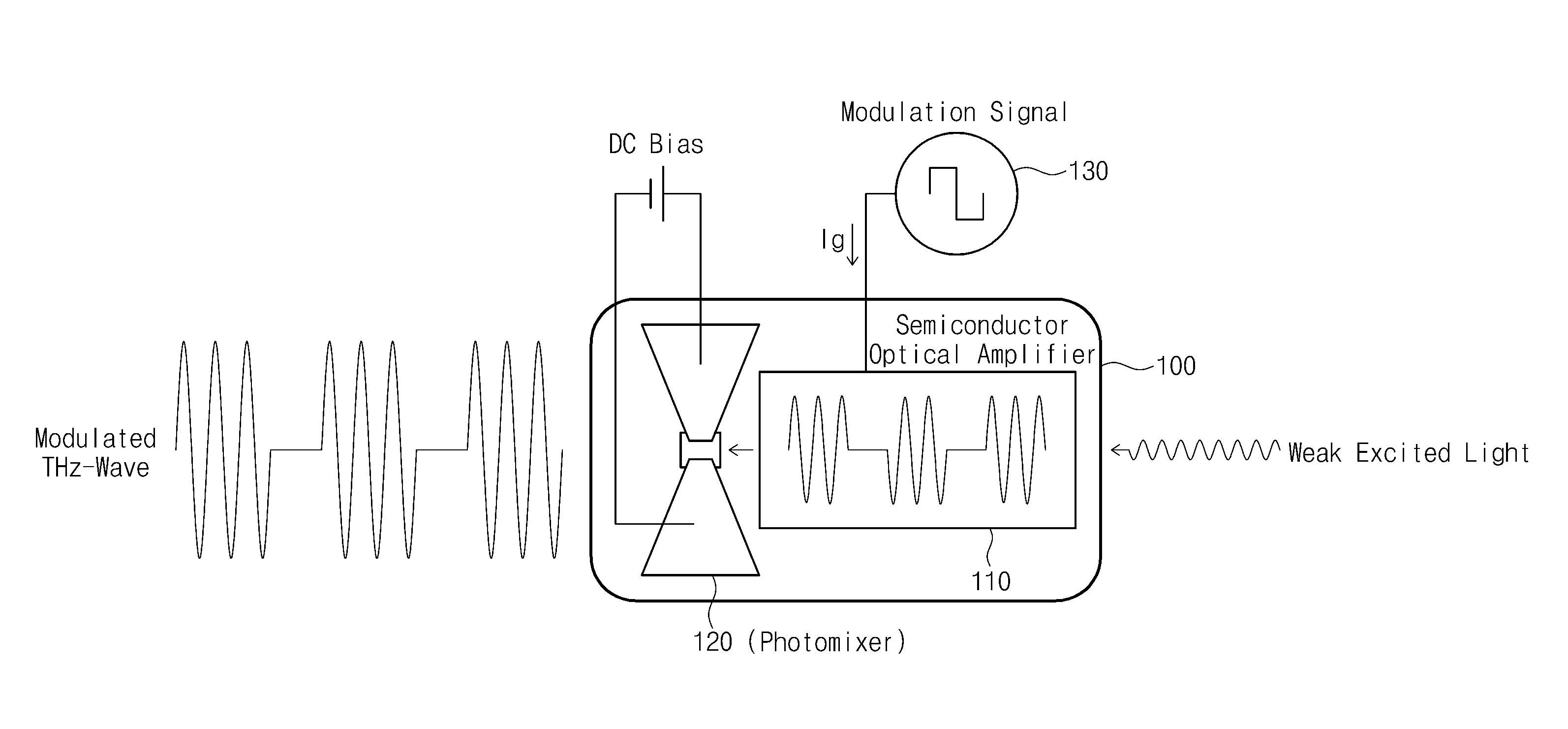
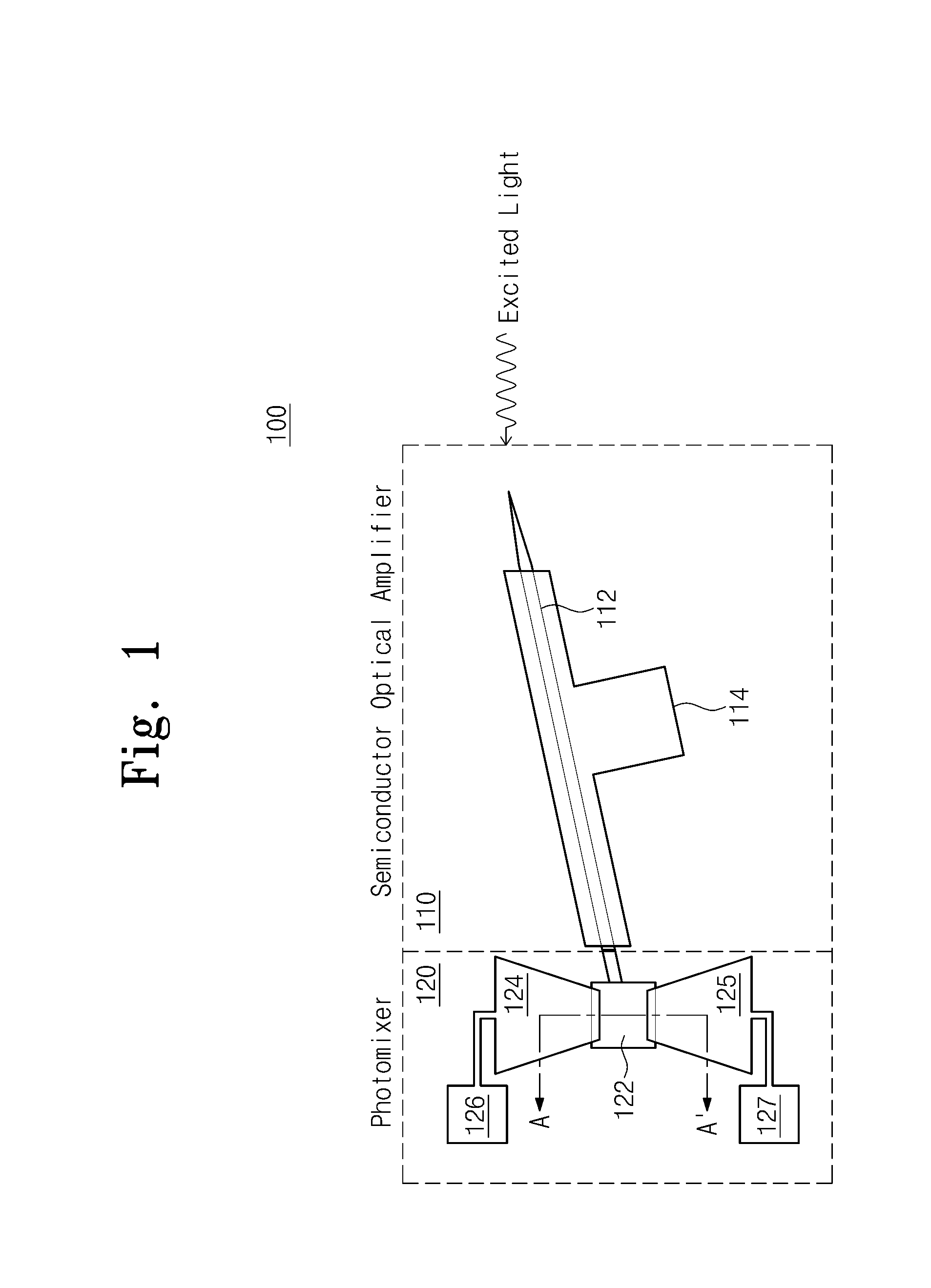
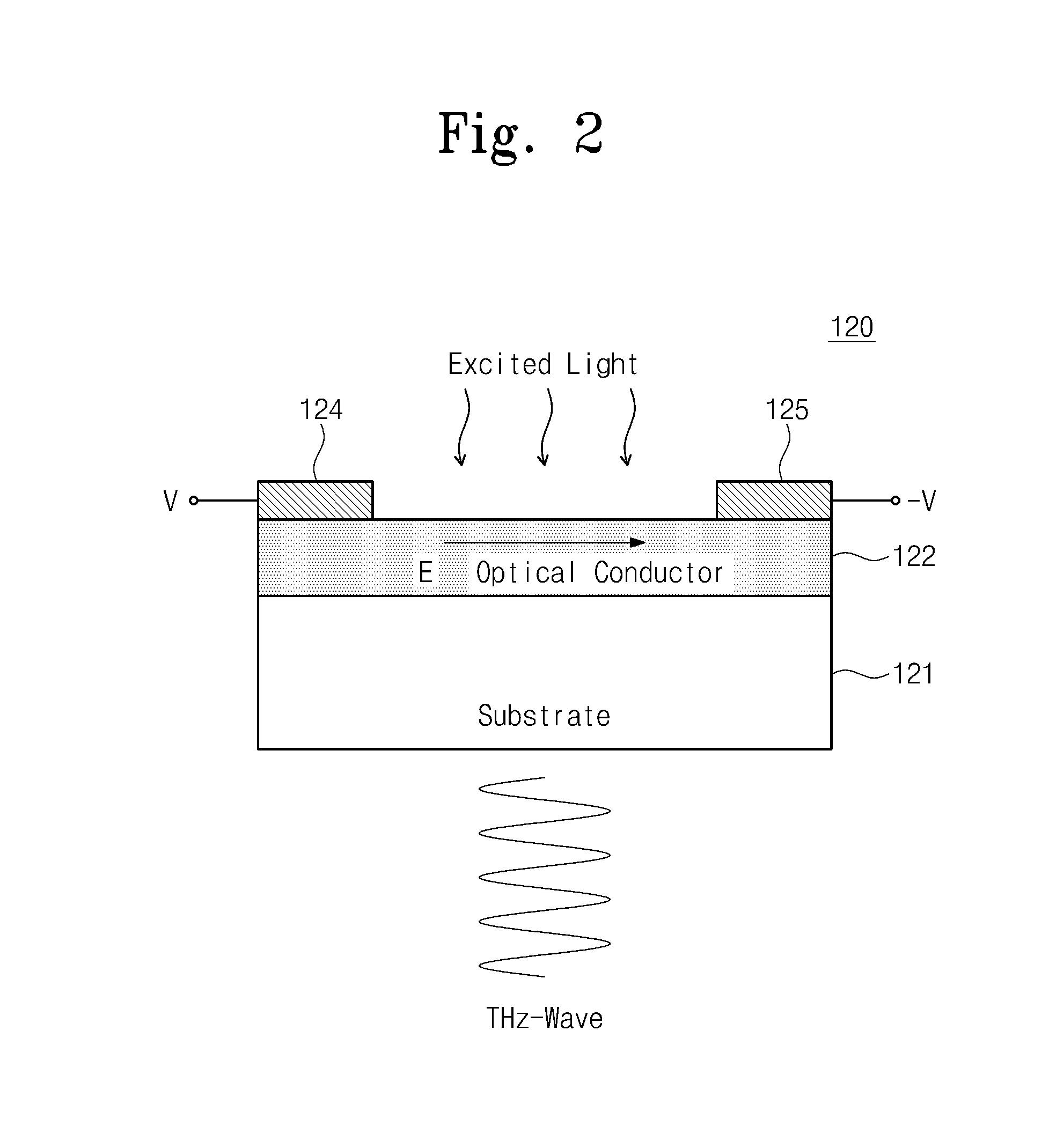
Photomixer module and terahertz wave generation method thereof
InactiveUS20110149368A1High strengthImprove stabilityLaser detailsSingle tube conductorsLaser lightSemiconductor
Provided are a photomixer module and a method of generating a terahertz wave. The photomixer module includes a semiconductor optical amplifier amplifying incident laser light and a photomixer that is excited by the amplified laser light to generate a continuous terahertz wave. The photomixer is formed as a single module together with the semiconductor optical amplifier.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
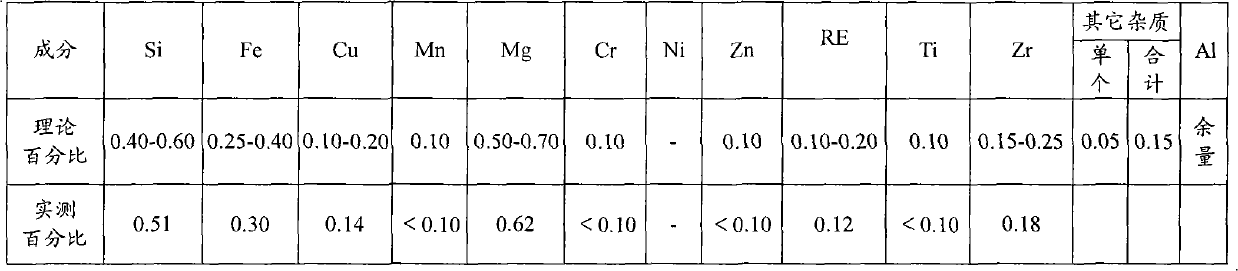
Aluminum alloy tubular conductor and production process thereof
InactiveCN101768688AHigh tensile strengthRaise the operating temperatureSingle tube conductorsMetal/alloy conductorsElectrical conductorHeat treated
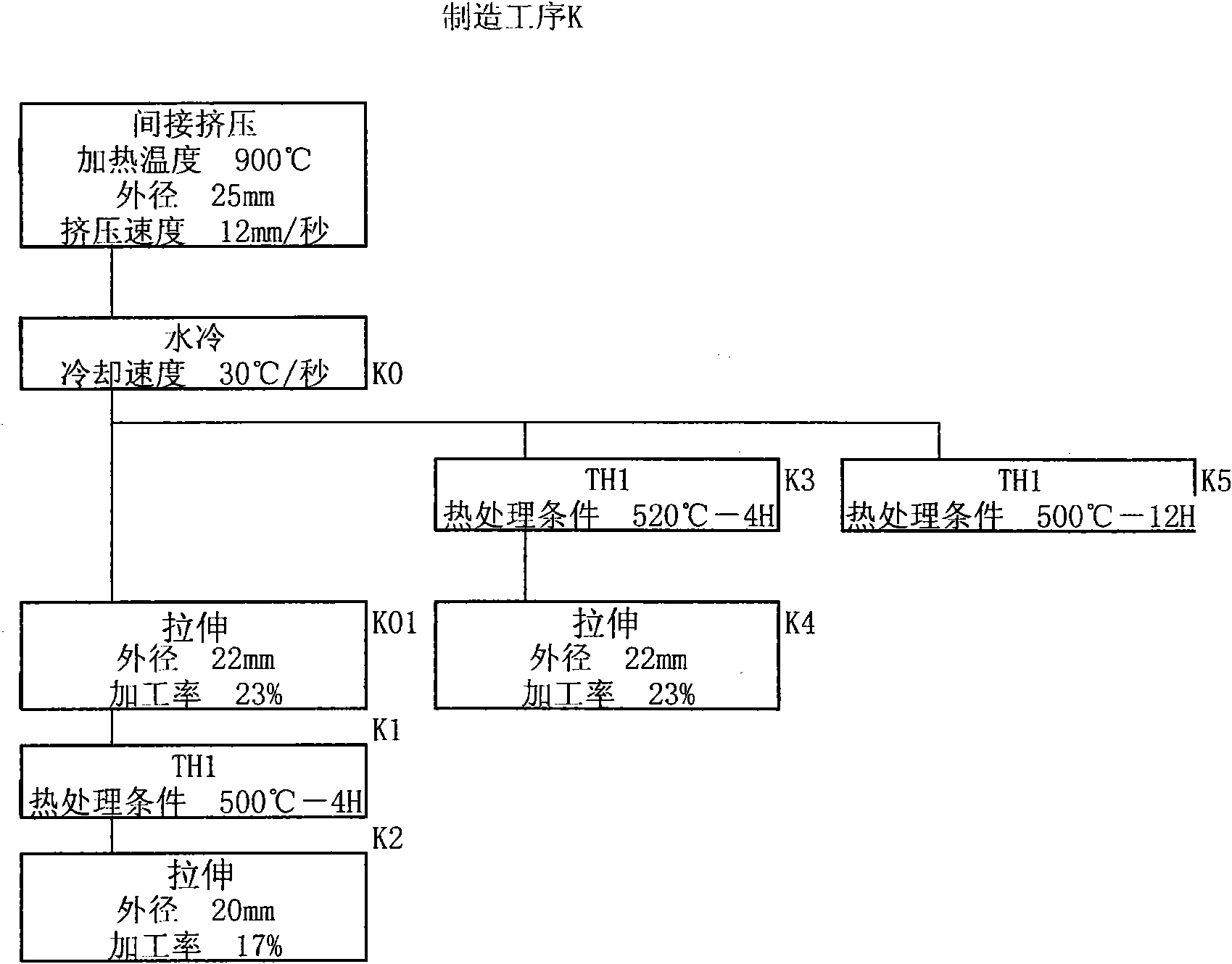
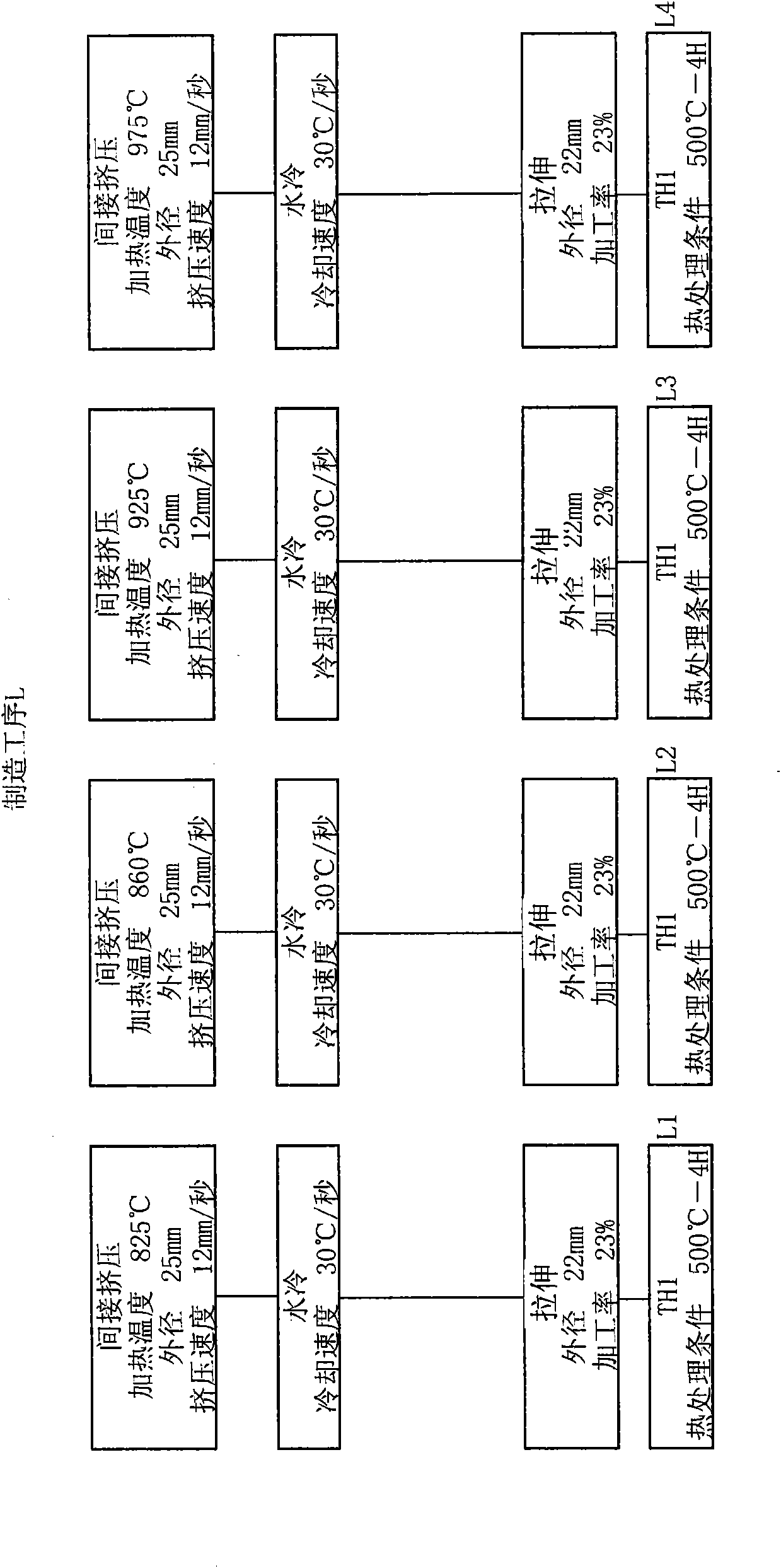
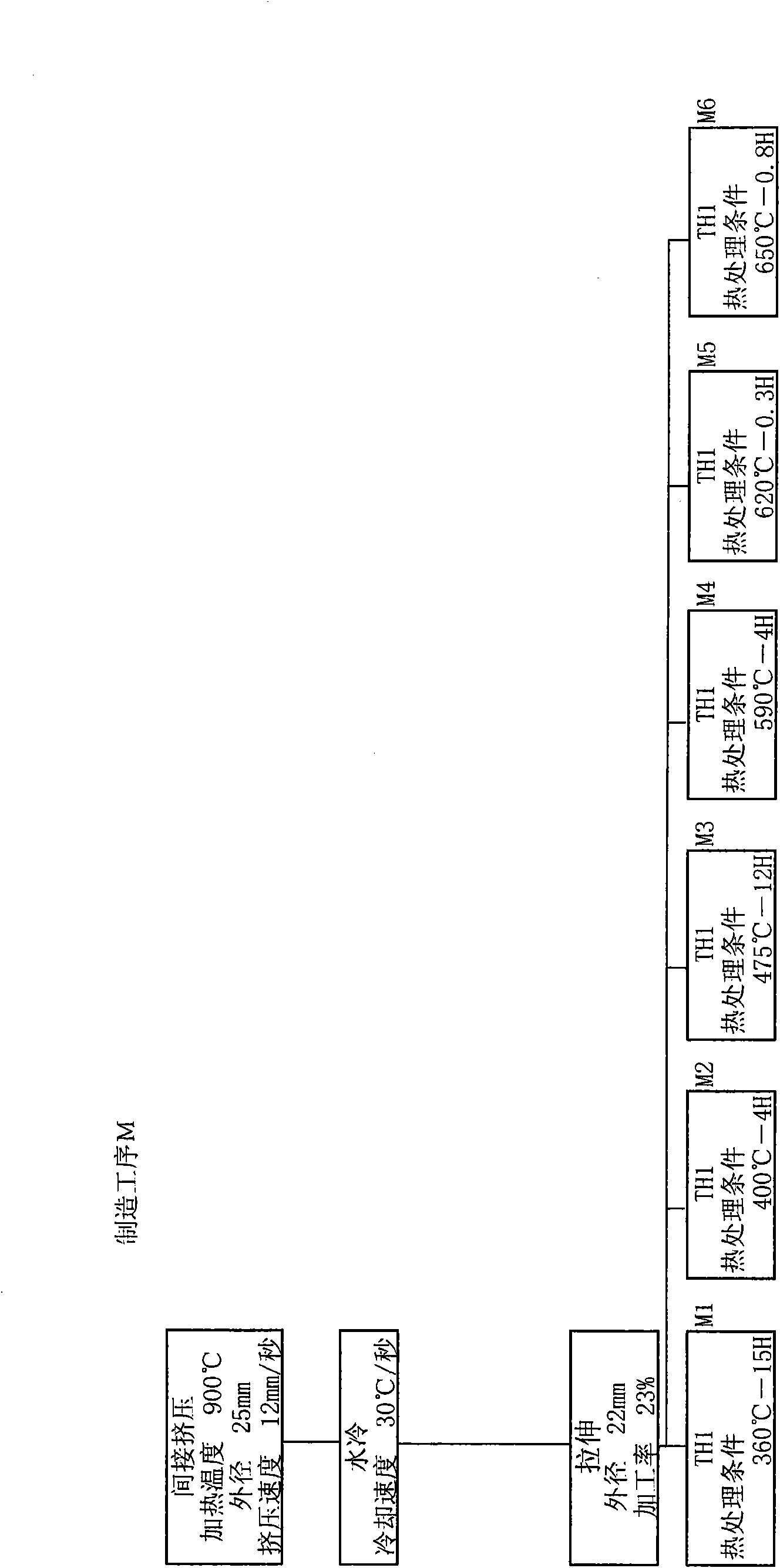
The invention provides an aluminum alloy tubular conductor and a production process thereof. The aluminum alloy tubular conductor is prepared with Al-Mg-Si-Fe-Cu-Zr-RE alloy. The aluminum alloy tubular conductor adopts the Al-Mg-Si-Fe-Cu-Zr-RE alloy, the tensile strength and the use temperature of the aluminum alloy after being added with Cu, Fe, Zr and RE are increased, thereby the performance of the aluminum alloy tubular conductor is greatly improved. The production process of the aluminum alloy tubular conductor adopts a thermomechanical processing process, controls the cold processing rate after quenching within a certain range, thereby not only greatly improving the tensile strength of the product, but also facilitating the improvement of the recrystallization temperature of the alloy, so as to improve the heat resistant performance of the alloy.
Owner:湖北兴和电力新材料股份有限公司
High-strength heat-resistant aluminium alloy pipe type generatrix
InactiveCN101174489AImprove heat resistanceIncrease ampacitySingle tube conductorsMetal/alloy conductorsElectrical conductorWorking temperature
Owner:HUBEI XINGHE ALUMINUM
Multilayer elastic tube having electric properties and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130037306A1Improve electrical performanceEasy to manufactureSingle tube conductorsLaminationClosed loopEngineering
A multilayer elastic tube having electric property, the multilayer elastic tube including: an elastic core having a tube shape; and an elastic rubber coating layer adhering to an inner surface of the core, the elastic rubber coating layer having at least one electric property of electric conductivity, piezoelectricity, and electric wave absorptiveness. The elastic rubber coating layer is formed by curing liquid elastic rubber having the electric property and adhering to the inner surface of the core, and has a closed loop shape to improve the electric property.
Owner:KIM SUN KI +1
High-strength and high-electroconductivity copper alloy pipe, bar, and wire rod
ActiveCN101960028AHigh strengthImprove conductivitySingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsSingle tube conductorsWire rodDissolution
Disclosed are high-strength and high-electroconductivity copper alloy pipe, bar, and wire rod. The high-strength and high-electroconductivity copper alloy pipe, bar, and wire rod are produced by a process comprising providing an alloy comprising 0.13 to 0.33% by mass of Co, 0.044 to 0.097% by mass of P, 0.005 to 0.80% by mass of Sn, and 0.00005 to 0.0050% by mass of O with the balance consisting of Cu and unavoidable impurities, Co and P satisfying a requirement of 2.9 <= ([Co] - 0.007) / ([P] - 0.008) <= 6.1, wherein [Co] represents the content of Co, mass%; and [P] represents the content of P, mass%, and hot extruding the alloy. Homogeneous precipitation of Co and P compounds and dissolution of Sn as a solid solution can improve the strength and electroconductivity of the high-strength and high-electroconductivity copper alloy pipe, bar, and wire rod. Further, since the high-strength and high-electroconductivity copper alloy pipe, bar, and wire rod are produced by hot extrusion, a reduction in cost can be realized.
Owner:MITSUBISHI SHINDOH CO LTD
Damping bus for suppressing VFTO
ActiveCN106486991AInhibition formationHigh working reliabilitySingle tube conductorsEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentSmart substationTransformer
The invention provides a damping bus for suppressing VFTO. A helical tube type damping bus capable of consuming electron flow energy is adopted, a conductive tube of the damping bus bar is made to be a spiral tube with a spiral groove structure. The damping bus is advantageous in that, VFTO formed in GIS can be suppressed, the amplitude and frequency are greatly introduced, starting from a primary device, work reliability of a secondary system of an electronic transformer and other state monitoring devices used for GIS is improved, accident rate is reduced, and establishment of an intelligent substation with the electronic transformer as the representative is promoted. Via the mode of changing the wave impedance of the bus, the bus power loss is increased, and the development of traveling waves is suppressed, thereby achieving the purposes of reducing the VFTO amplitude, and reducing the VFTO frequency. The technical scheme is suitable for reconstruction of a current GIS pipeline, and is suitable for a novel GIS pipeline.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Circular shielding insulating bus and machining method thereof
ActiveCN103366872AReduce skin effectReduce power lossSingle tube conductorsInsulated cablesElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention relates to a circular shielding insulating bus, which has the advantages of high carrying capacity, good heat dissipation, low temperature rise, strong electric insulation performance, no environmental disturbance and high reliability. The circular shielding insulating bus comprises a circular conductor and an outer layer sheath, wherein a plurality of insulating shielding layers are arranged between the circular conductor and the outer layer sheath and consist of insulating layers and shielding layers; each insulating layer comprises two polytetrafluoroethylene layers and a thermal shrinkage sheath from inside to outside; and silicone oil is uniformly brushed between the polytetrafluoroethylene and the thermal shrinkage sheath.
Owner:JIANGSU SHILIN ELECTRIC EQUIP
Method for producing improved radio-frequency cable inner conductor pipe
InactiveCN101139711AReduce weightLow costSingle tube conductorsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectrical conductorPyrophosphate
The invention provides a processing method for a conductor pipe in an improved radio frequency cable. The conductor pipe made by the method is of low dead weight, easy to construct and of low cost, can efficiently reduce the cost of the industry of cable and end users, and is of good communication effect. The invention is characterized in that, the method comprises the following procedures: de-oiling, cleaning, polishing by nitric acid, soaking zinc, de-zincing by nitric acid, soaking zinc, preparing pyrophosphate, plating copper, plating bright copper, passivating, cleaning with heated de-ionized water and drying.
Owner:肖立群
Equipment and process for manufacturing power transmission conductor with carbon fiber core
ActiveCN104538107AReduce gapEnsure safetySingle tube conductorsInsulated cablesFiberElectrical conductor
The invention relates to the technical field of overhead power transmission conductors, and in particular relates to equipment and a process for manufacturing a power transmission conductor with a carbon fiber core. The power transmission conductor with the carbon fiber core comprises a carbon fiber core rod and a metal conductive layer, wherein the metal conductive layer is arranged outside the carbon fiber core rod; the metal conductive layer is an overall metal tube which sleeves the carbon fiber core rod and is used for completely wrapping the carbon fiber core rod; the outer surface of the carbon fiber core rod and the inner surface of the metal conductive layer are integrally formed in an extrusion manner. In the process that an aluminum conductor layer is expanded or shrunk, the metal conductive layer is not expanded to two ends or shrunk due to limit of the carbon fiber core rod, so that the length of the metal conductive layer is not changed, the outer diameter of the metal conductive layer is changed at most, sag is not caused by change of the outer diameter, the metal conductive layer is free of force for pulling or pushing a support tower, and the use security of the power transmission conductor is ensured.
Owner:常州艾邦机械科技有限公司
Metal-ceramic built-up unit, a built-up framework for transfer of oxide ions, a built-up unit having a capability of sealing
InactiveCN1743056AImprove reliabilityPromote circulationSemi-permeable membranesSingle tube conductorsWide areaPartial oxidation
A sealing technique is established in which a seal can be easily formed and which is excellent in reliability and a heat cycle property in a high temperature region of 800 DEG C or higher, so as to provide a composite body preferably used for a device for producing pure oxygen, oxygen-rich air, and the like, a membrane reactor represented by that for partial oxidation of a hydrocarbon gas, a solid oxide fuel cell, an oxygen purification device, a heat exchanger, or the like. The present invention makes it possible to increase a possibility of practical use in a wide area which has been delayed in development owing to a bottleneck of improvement in a sealing property. Particularly, its application to the device for producing pure oxygen, oxygen-rich air, or the like, the membrane reactor represented by that for partial oxidation of the hydrocarbon gas, the solid oxide fuel cell, the oxygen purification device, the heat exchanger, or the like can greatly contribute to acceleration of the development.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Grid framework accessories
The present invention is directed to accessories which are attached to the support grid members of a grid framework system. The accessories insulate electrified conductors attached to the support grid members from other conductive items located proximate thereto, a management device for cables and wires, and a retention device for fixedly attaching a component to the grid framework system.
Owner:WORTHINGTON ARMSTRONG VENTURE
A connection pin, a converter assembly and a method for manufacturing a connection pin
InactiveUS20160278209A1Reliable handlingLessLine/current collector detailsElectrically conductive connectionsPrinted circuit board
A connection pin comprising a first contact part that is adapted for mounting in a hole in a printed circuit board (PCB), and a second contact part. The first contact part comprises a cavity surrounded by a wall, and the wall has at least one opening. At least one solder preform is located in the cavity. A converter assembly comprising a first PCB, and having at least one hole in which a connection pin is mounted. The first PCB with the connection pin is then mounted on a second PCB. Further is described a method for manufacturing a connection pin comprising: providing a connection pin with a cavity in a contact part of the pin, and providing at least one opening in a wall of the cavity, preparing at least one solder preform, and inserting at least one solder preform into the cavity.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
High frequency electric wire
InactiveCN102097169AIncrease surface areaDispersion and easeRail devicesCharging stationsYarnElectrical conductor
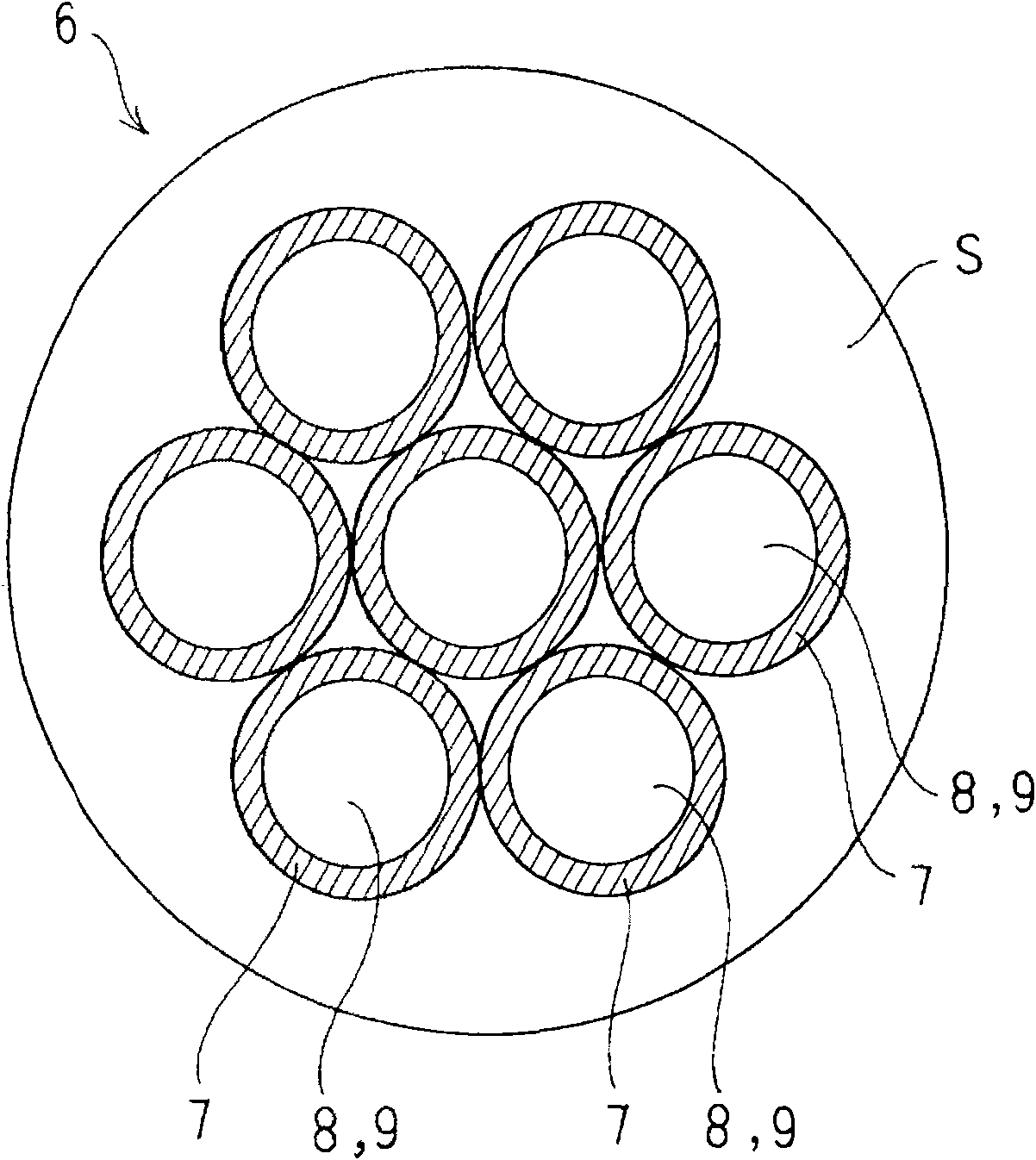
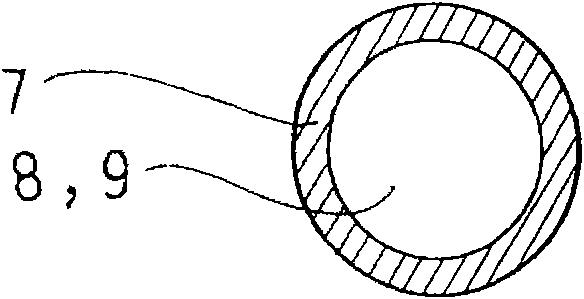
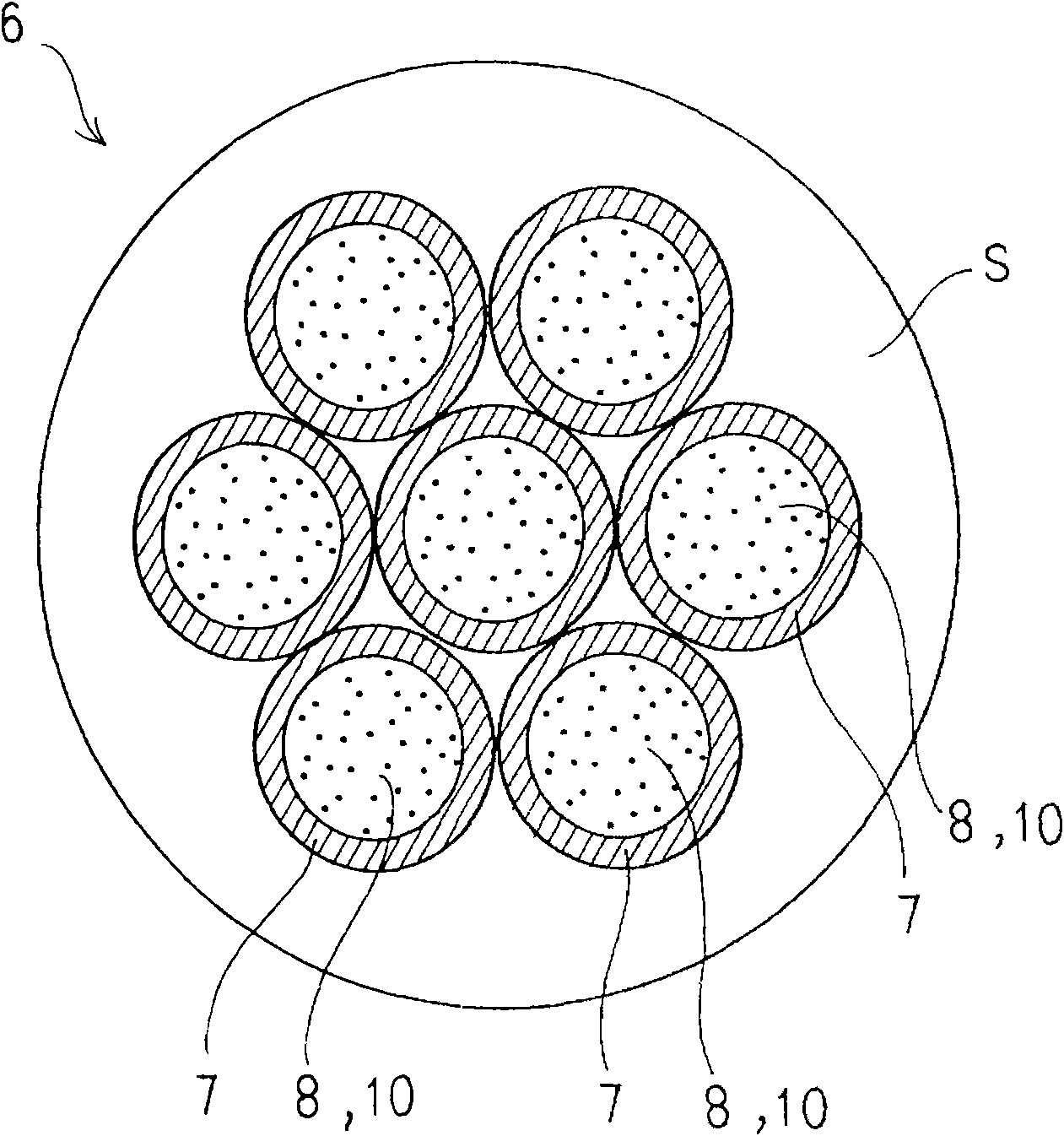
The present invention provides a high frequency electric wire in which, first, the high frequency alternating current resistance can be reduced to decrease a Joule heat loss, thereby improving the frequency characteristics, and, second, the first point can be excellently realized in terms of cost performance. A high frequency electric wire 6 is provided in such a manner that a large number of wires 7 are bundled, twisted and insulated with an outer sheath S. Each wire 7 has an extra-fine hollow pipe structure of a capillary shape. The wire 7 is provided to make its hollow section 8 with the extra-fine hollow pipe structure an air cavity 9 or to cause its hollow section 8 to house an insulating material 10. In the latter case, the wire 7 is provided to cause a metal conductor to adhere to the outer periphery of an extra-fine insulating yarn which serves as the insulating material 10 by plating or vapor- deposition. The electric wire 6 is used as a circuit cable or a coil in a non-contact power feeding device which supplies power based on a mutual induction action of the electromagnetic induction. In this manner, the electric wire 6 fulfills its function to suppress and reduce an increase of the alternating current resistance due to a high frequency alternating current.
Owner:SHOWA AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY
Conductive corrugated tube
InactiveCN101458974AWill not deform and breakPrevent crushingSingle tube conductorsRigid-tube cablesElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention provides a conductive corrugated pipe of corrugated pipe structure, which has the advantages of wires and cables as flexibility, and can be freely bended and released as wires and cables, has the advantages of hollow conductors as high current carrier amount, and is a multilayer conductive corrugated pipe capable of improving the effective section area of transmission current. The corrugated pipe should be added with a cable core before being applied in overhead lines, the corrugated pipe is made from copper or aluminum, the adjacent corrugated pipes are provided with an insulation layer therebetween. Additionally, the ratio current will not change when the temperature is lower than 4DEG C, the conductors of the corrugated pipe reduces some section area, the current is transmitted by the corrugated pipe, the temperature increase of the whole corrugated pipe conductor will be higher than former temperature increase, to fuse ice and snow.
Owner:罗志昭
Insulated tubular busbar having composite insulation layer and in voltage class of 1kV and below and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105931700AAvoid enteringLong aging lifeSingle tube conductorsPower cables with screens/conductive layersPolyolefinElectrical conductor
The invention discloses an insulated tubular busbar having a cold-hot shrinkage composite insulation layer and in a voltage class of 1kV and below and a preparation method thereof. The cross section structure of a tubular busbar is a four-layer structure, which is formed by a metal tube conductor layer, a cold-hot shrinkage composite insulation layer (the inner layer is an ethylene propylene diene monomer cold shrinkage layer, and the outer layer is a polyolefin hot shrinkage layer), a metal grounding shielding layer and an outer protection cover layer from the inside out in sequence. The provided insulated tubular busbar product suitable for the voltage class of 1kV and below is characterized in that a shrinkage tube co-extruded by the cold-hot shrinkage composite insulation layer can be fit to a metal conductor pipe very well without leaving a gap inbetween after heating shrinkage, and the phenomenon of heat expansion and cold contraction does not appear due to the influence of hot and cold environment. The preparation method is simple and feasible; works and labor intensity are reduced; product quality is not influenced by human factors; production efficiency and finished product ratio are improved greatly; cost is reduced; and comprehensive competitiveness of an enterprise is improved.
Owner:深圳市智豪特材科技有限公司
Conductor of high voltage electrical apparatus
InactiveUS20110284264A1Low costImprove reliabilityCoupling device connectionsSwitchgear arrangementsElectrical conductorEngineering
In a conductor of a high voltage electrical apparatus, the conductor being placed in a vessel filled with insulating gas together with an electrical apparatus, the conductor is configured by a polygonal tubular conductor, and an opening portion which makes the insulating gas flowing in from an end portion of the polygonal tubular conductor flow out is formed in at least one surface of the polygonal tubular conductor. This aims to obtain the conductor of the high voltage electrical apparatus, the conductor being capable of achieving reduction in cost and high reliability.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Sheathed nanotube fiber and method of forming same
Embodiments of the invention provide a cellulose-sheathed carbon nanotube fiber. One aspect of the invention provides a sheathed nanotube fiber comprising: a carbon nanotube fiber; and a cellulose sheath extending co-axially along at least a first portion of a length of the carbon nanotube fiber. Another aspect of the invention provides a method of forming a sheathed carbon nanotube fiber, the method comprising: co-electrospinning a carbon nanotube fiber gel core within a cellulose solution sheath.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Full closed pipe type fire resistant flame retardant bus
InactiveCN101859611AReduce temperature riseImprove the insulation levelSingle tube conductorsPower cablesSynthetic resinUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a full closed pipe type fire resistant flame retardant bus, comprising conductors, insulating layers and insulating jackets. The conductor is a hollow metal pipe; the conductors are coated with mica tapes; the insulating layers are filled between adjacent conductors; all the conductors and the insulating layers are covered by the insulating jackets; the insulating layer or the insulating jacket can be made from synthetic resin insulating materials; and the insulating layers and the insulating jackets can be integrally poured to be formed. The invention has good heat radiation condition and low temperature rising when in operation. Interphase of the bus and whole ground insulating layers are integrally poured to be formed by adopting the synthetic resins, thereby improving insulating level of the bus; fire resistant and flame retardant effects can be achieved by coating the mica tapes outside the conductors; and the insulating parts have integrally poured structures and the allowable stress is big, thereby improving mechanic strength of the bus. Due to the structure advantages of the invention, current-carrying capacity of the bus can be greatly improved and the requirement of system operation is well satisfied.
Owner:李永勤
Tubular conductive piece and conductive device by employing the same
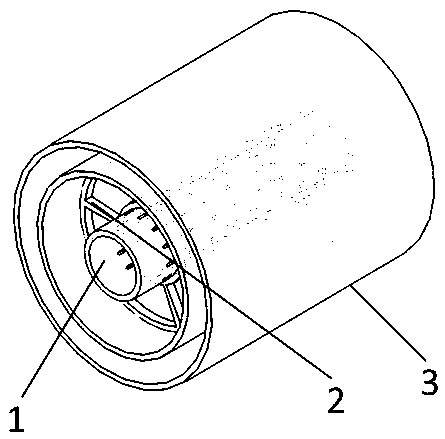
The present invention relates to a tubular conductive piece and a conductive device by employing the same. The tubular conductive piece comprises a tube body, and two ends of the tube body is provided with blocking boards to block up inner holes of the tube body to separate the inner holes of the tube body from the internal air chamber of the tubular conductive piece assembly device. The blocking boards are configured to block up the inner hole ports at two ends of the tube body to allow the inner holes of the tube body to form an independent sealing space and separate the inner holes from the internal air chamber of the tubular conductive piece assembly device so as to prevent the non-cleaning residual metal foreign matters and moisture in the tubular conductive piece and the metal foreign matters in the manufacturing process from being mixed into the insulation medium of the air chamber to cause discharge, omit the process of cleaning the inner wall of the tubular conductive piece, reduce the labor intensity, shorten the product assembling period and greatly improve the work efficiency.
Owner:HENAN PINGGAO ELECTRIC +2
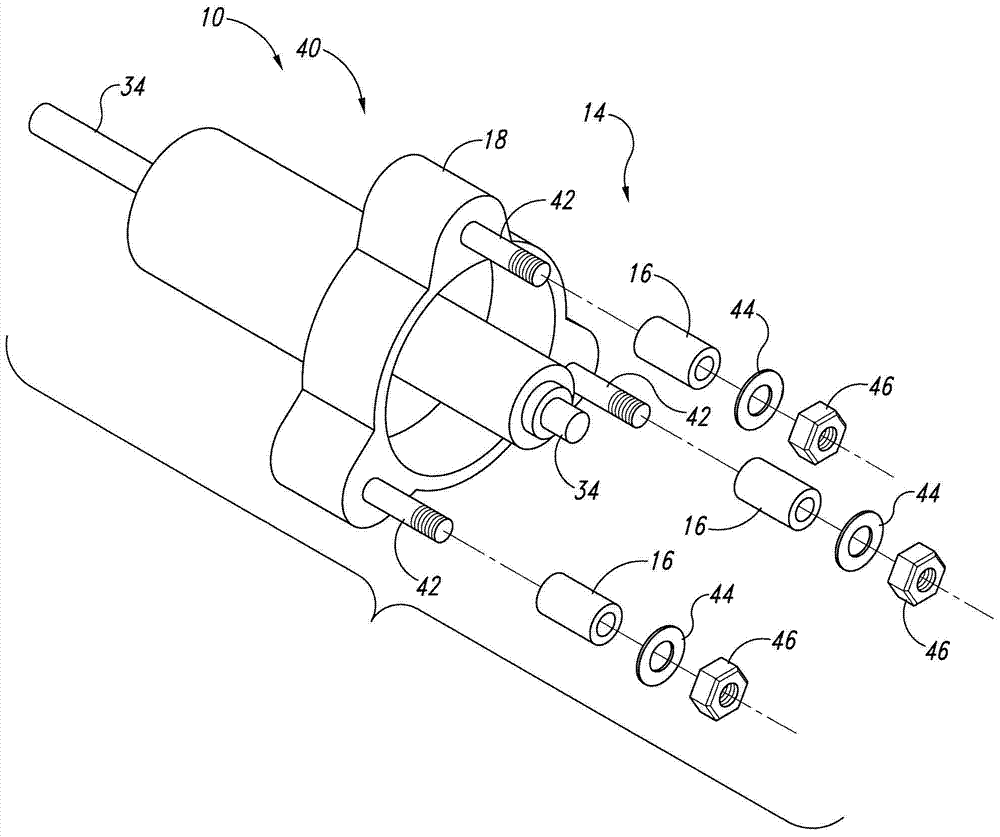
Bushing assembly, bushing assembly kit, apparatus including bushing assembly, and associated method
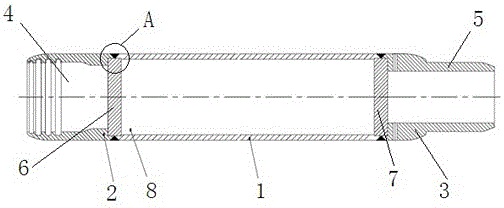
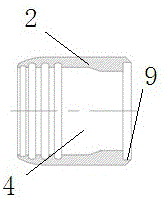
ActiveCN103807298ASingle tube conductorsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringCompressive strength
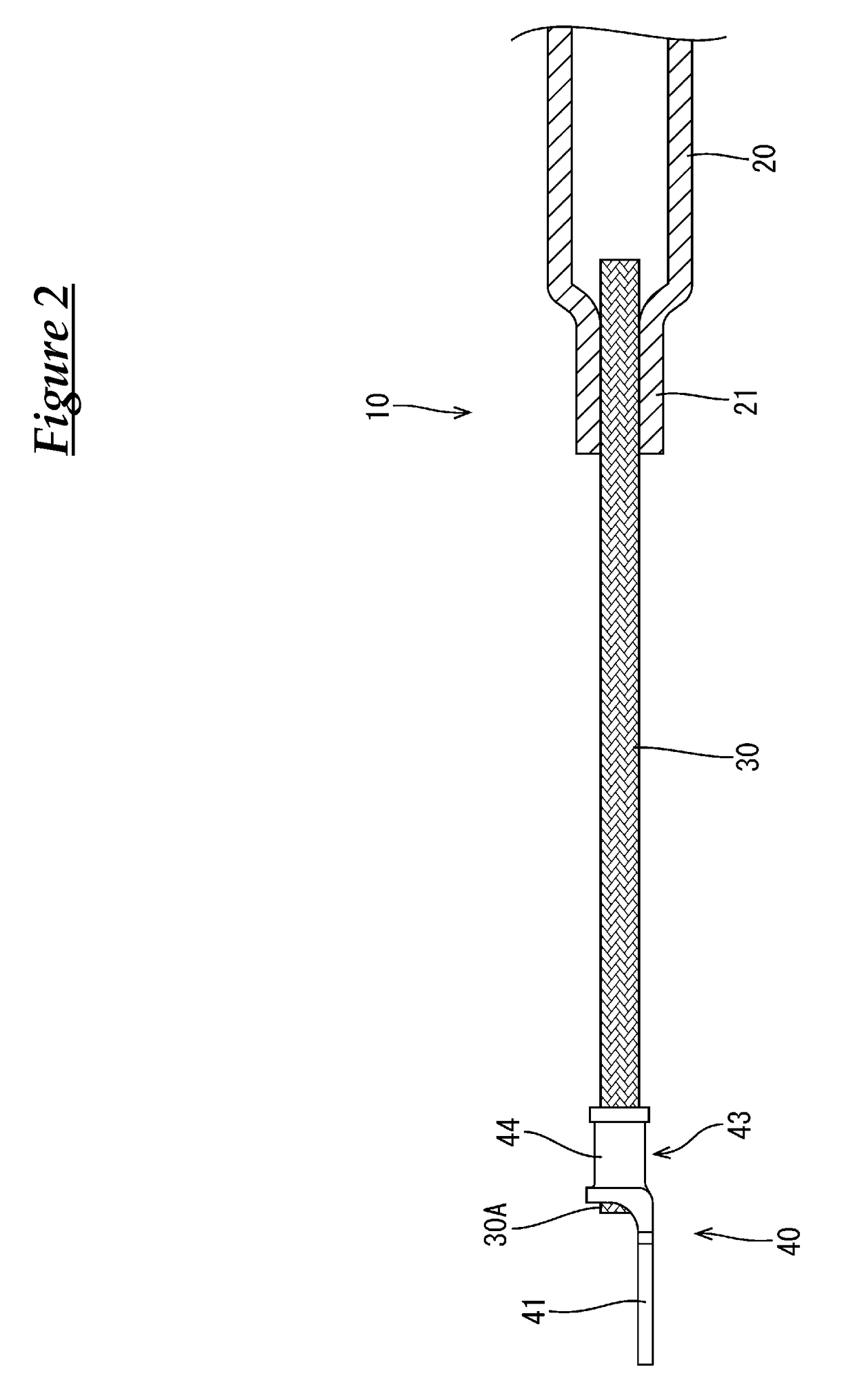
The invention provides a bushing assembly, a bushing assembly kit, an apparatus including the bushing assembly, and an associated method. The bushing assembly comprises a first tubular end portion, a second tubular end portion and a middle tubular portion. The middle tubular portion has a longitudinal compressive strength that is less than that of the end portions. In some embodiments, the middle tubular portion is constructed of braided sleeving. Also disclosed is a bushing assembly kit, an apparatus that includes the bushing assembly, such as aircraft, and an associated method of utilizing the bushing assembly.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Power cable
InactiveCN106024106AImprove heat resistanceReduce heat shrinkageSingle tube conductorsClimate change adaptationWrinkle skinPower cable
The invention discloses a power cable. The power cable comprises a supporting core, single-core bodies and an insulating layer, wherein the supporting core and the single-core bodies are located in the insulating layer, the supporting core is located in the center of the insulating layer, the number of the single-core bodies is larger than one, and the single-core bodies are circumferentially distributed in layers in an annular cavity formed by the supporting core and the insulating layer; each single-core body comprises a hollow conducting layer, insulating medium filler and an insulating medium protective sleeve, the insulating medium filler is arranged in the hollow conducting layer, wrinkle-shaped texture is arranged on the periphery of the insulating medium protective sleeve, an inner sheath is arranged outside the insulating layer, a refractory layer is arranged outside the inner sheath, a steel wire armoring layer is arranged outside the refractory layer in a single-strand spirally twisted mode and is made of round galvanized steel wires, and an outer sheath is arranged outside the steel wire armoring layer. According to the power cable, the thermal shrinkage problem of the cable can be effectively solved, and meanwhile mechanical damage during underground construction and damage of underground animals can be prevented.
Owner:江苏瑞扬线缆有限公司
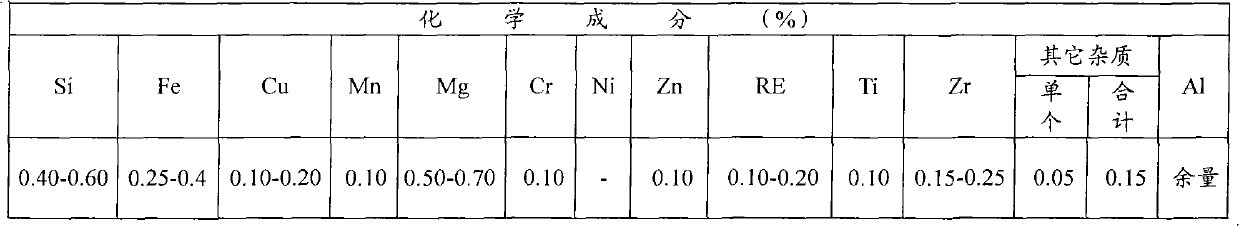
Low-resistivity high-strength aluminum alloy conductive tube and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN111549262AReduce contentImprove conductivitySingle tube conductorsConductive materialElectric resistivitySilicon
The invention discloses a low-resistivity high-strength aluminum alloy conductive tube. The low-resistivity high-strength aluminum alloy conductive tube comprises, by mass, 0.50% -0.55% of Si, 0.15% of Fe, 0.01% of Cu, 0.01% of Mn, 0.52%-0.58% of Mg, 0.01% of Cr, 0.01% of Zn, 0.02% of Ti, not greater than 0.05% of Zr, not greater than 0.05% of mixed rare earth Re, less than 0.01% of Pb, not greater than 0.05% of B, not greater than 0.05% of V and the balance Al, wherein the total content of Zr, Re, Pb, B and V is less than or equal to 0.15%; and when the total content of Mn, V, Cr and Ti is lower than 0.012%, the addition amount of B is 0; and when the total content of Mn, V, Cr and Ti exceeds 0.012%, the addition amount of B is 1.25-1.5 times the stoichiometric number of B needed by a boron compound formed by Mn, V, Cr, Ti and B. According to the low-resistivity high-strength aluminum alloy conductive tube, the content of magnesium and silicon is strictly controlled, the content of other impurity elements is reduced, and the conductivity and performance of the tube are improved through standard limitation of the subsequent extrusion, quenching, stretching, aging and other processes.
Owner:郑州明泰交通新材料有限公司
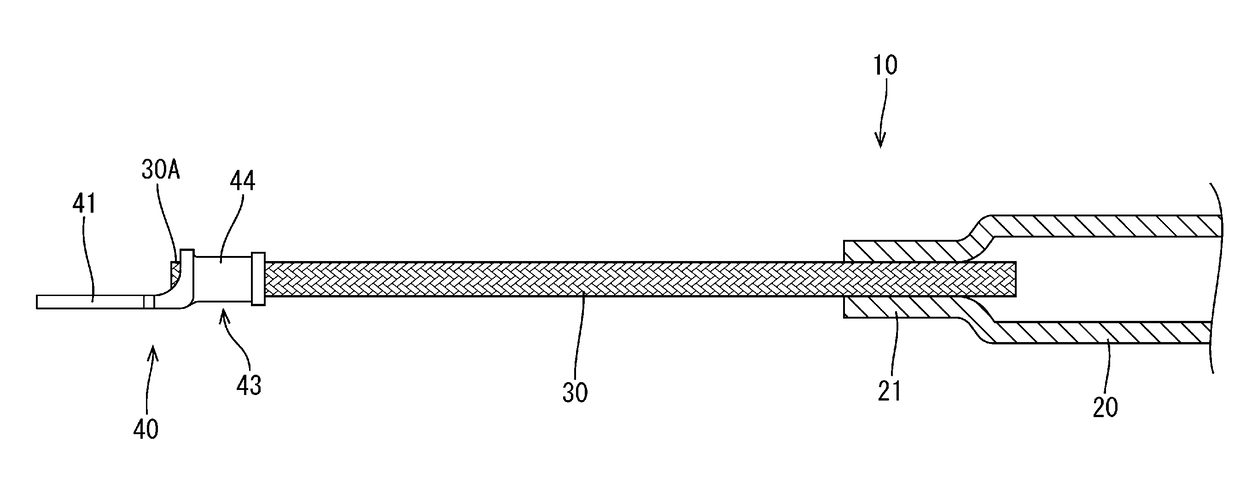
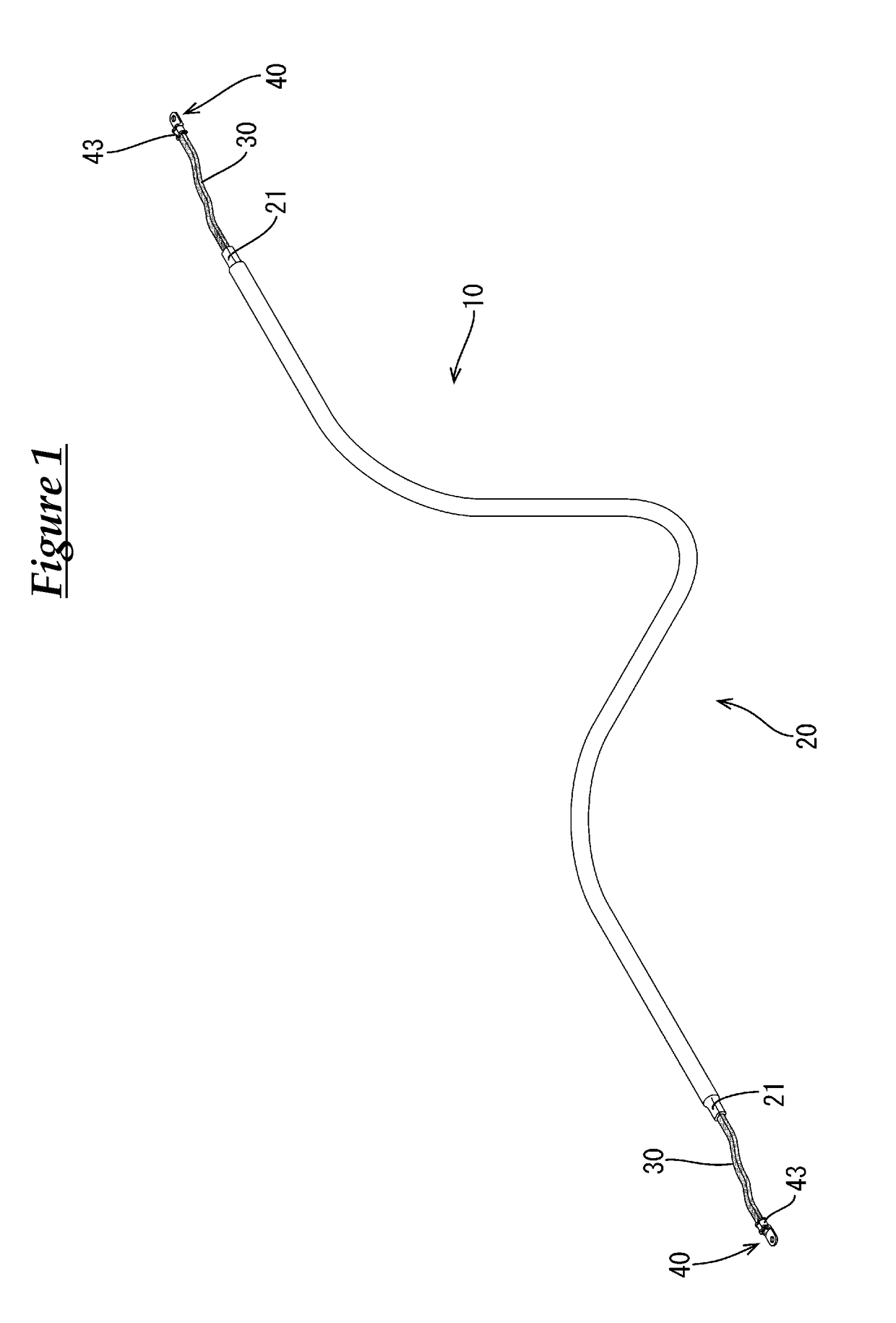
Conductive member
InactiveUS20180122532A1Braided wire conductorsSingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsEngineeringFront and back ends
A conductive member disclosed herein is a conductive member that is routed from the front to the rear of a vehicle, and includes: a shape-retaining tubular pipe member made of a metal having excellent conductivity; a braided wire having flexibility and configured to be crimped to be connected to a crimped connection portion provided at front and rear ends of the pipe member; a round terminal configured to be crimped and connected to the braided wire; and a heat-shrinkable tube that covers from a crimped portion of the round terminal at the front end to a crimped portion of the round terminal at the rear end.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Dry overall shield insulating tubular bus
ActiveCN103680685ALarge capacityReduce volumeRubber insulatorsSingle tube conductorsElectric power systemEngineering
The invention relates to the field of power generation, transmission, transformation and distribution devices of power systems, in particular to a dry overall shield insulating tubular bus which comprises a tubular conductive core. A first semi-conductive shield layer, an insulating layer, a second semi-conductive shield layer, a grounding shield layer and an outer protection layer sequentially wrap the outside of the conductive core from inside to outside, wherein the insulating layer is made of organic silicone rubber. The tubular conductive core is high in capacity and small in size, the insulating layer made of the organic silicone rubber has a fine electrical insulating property, dielectric loss, voltage resistance, arc resistance, corona resistance, volume resistivity, surface resistivity and the like of the insulating layer are among the best in insulating materials, the electrical performance of the insulating layer is less affected by temperature and frequency, and the organic silicone rubber insulating layer has excellent heat resistance and water repellency, has a certain flexibility after curing, can be bent and can meet use requirements under different conditions.
Owner:南网电气有限公司 +1
Cryogenic-liquid forced cooling cable structure
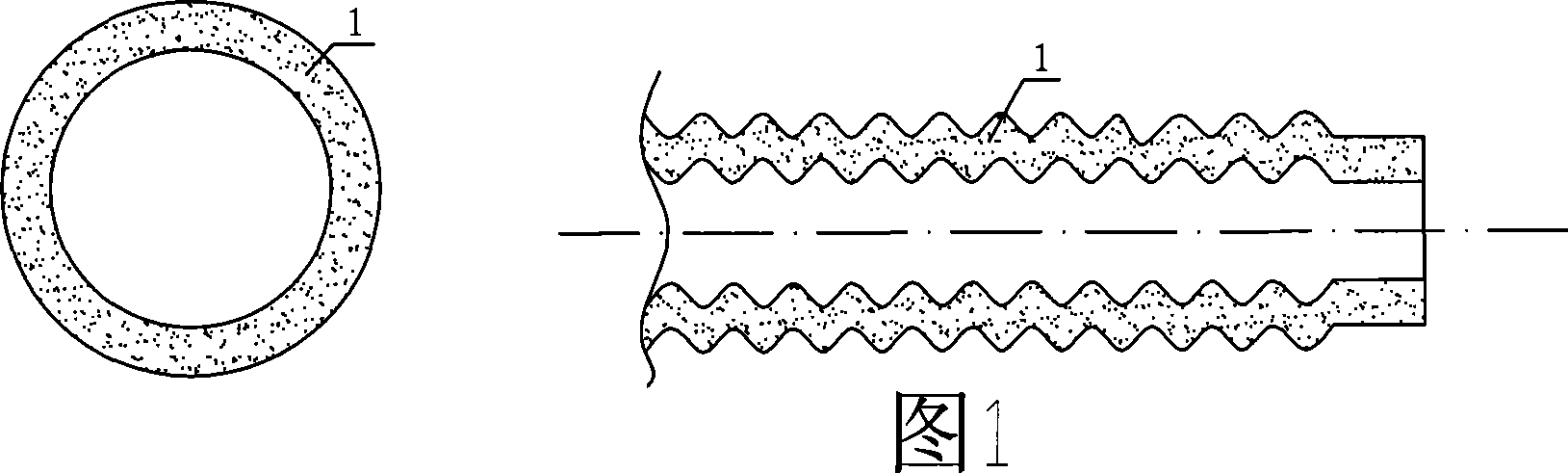
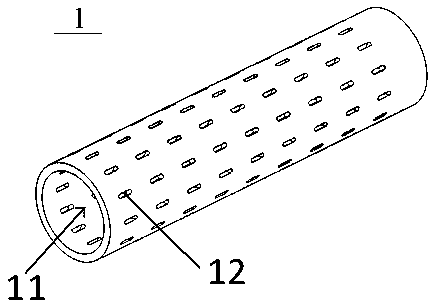
PendingCN109390078AIncreased disorderAvoid affecting heat transfer efficiencySingle tube conductorsInsulated cablesElectrical conductorThermal insulation
The embodiment of the invention discloses a cryogenic-liquid forced cooling cable structure, and the structure comprises a conductor (1), a plurality of supports (2) and a thermal insulation tube (3),wherein the conductor (1), the plurality of supports (2) and the thermal insulation tube (3) are sequentially from the inside to the outside. The conductor (1) is a hollow metal tube, and a side wallof the metal tube is provided with through holes (12) at intervals. The interior of the conductor forms a cryogenic-liquid channel (11), and the supports (2) are each of a hollow-out structure formedby the processing of a non-metal material, and sleeve the conductor (1) at certain intervals. The thermal insulation tube (3) is a high-vacuum thermal insulation tube, and the conductor (1) is disposed in the thermal insulation tube (3) in a coaxially sleeved manner through the supports (2). According to the embodiment of the invention, the structure can improve the thermal conduction efficiencyand avoid the skin effect during the transmission of a large current.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
Conductive member
InactiveUS10217542B2Braided wire conductorsSingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsEngineeringFront and back ends
A conductive member disclosed herein is a conductive member that is routed from the front to the rear of a vehicle, and includes: a shape-retaining tubular pipe member made of a metal having excellent conductivity; a braided wire having flexibility and configured to be crimped to be connected to a crimped connection portion provided at front and rear ends of the pipe member; a round terminal configured to be crimped and connected to the braided wire; and a heat-shrinkable tube that covers from a crimped portion of the round terminal at the front end to a crimped portion of the round terminal at the rear end.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Generatrix conductor
ActiveCN103106957AImproved current density distributionLarge carrying capacitySingle tube conductorsInsulated cablesElectrochemical responseElectrical conductor
The invention provides a generatrix conductor. The generatrix conductor is characterized in that a body oxide layer of copper and an aluminum alloy (the oxide layer is thin, and resistance is small) is retained as an isolation protective layer. Electrochemical reaction can be prevented. The copper and the aluminum alloy (such as aluminum magnesium alloy and rare earth aluminum alloy) are matched in a lap joint mode. By splitting of the isolation protective layer, the copper and the aluminum alloy form two conductors which are relatively independent but equal in electric potential. Electromagnetic interference is not generated between the two conductors. Current density distribution uniformity effect is greatly improved. The generatrix conductor is suitable for utilizing in generatrixes of various voltage classes and the conductor of a sleeve tube.
Owner:广东日昭新技术应用有限公司
Copper aluminum interface alloy composite conductor internal wave tube used in tubular bus duct
InactiveCN106655035AEfficient auxiliary cross-section and large current carryingGood load cooling performanceSingle tube conductorsConductive materialCarrying capacityPower flow
The invention discloses a tubular busbar, especially a copper aluminum interface alloy composite conductor internal wave tube used in a tubular bus duct, and belongs to the technical field of power distribution equipment. The copper aluminum interface alloy composite conductor internal wave tube comprises a main conductor aluminum pipe and a copper pipe sleeved at the outer wall of the aluminum pipe; and the inner wall of the aluminum pipe is provided with a plurality of convex-concave wavelike convex strips. The copper aluminum interface alloy composite conductor internal wave tube used in the tubular bus duct provided by the invention greatly increases the conductivity of the inner surface of the conductor, reduces the temperature rise during current carrying capacity, and has a good heat dissipation and convection function, thereby ensuring the long load operation of the safety production of a large current tubular busbar.
Owner:四川瀚舟铜铝复合材料有限公司
Hollow conductor with reinforcing ribs
InactiveCN104464896AGuaranteed cooling effectAvoid section reductionSingle tube conductorsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsWater channelTransformer
The invention relates to a hollow conductor with reinforcing ribs for a water-cooled transformer and a water-cooled electric reactor. The conductor comprises a conductor wall and at least one reinforcing rib arranged in the conductor wall, and a hollow cavity defined by the conductor wall is divided into a plurality of flow water channels by the reinforcing ribs. The hollow conductor with the reinforcing ribs can effectively avoid the phenomenon that the sections of the hollow-out channels are reduced due to inwards recessing of the hollow conductor caused by bending deformation in the process that the hollow conductor is wound into a coil, and ensure the sectional area of the water flow channels and the cooling effect of the water-cooled transformer and the water-cooled electric reactor.
Owner:JINPAN ELECTRIC GRP SHANGHAI
Assembled wire, method of manufacturing assembled wire and segment coil
ActiveUS20200126688A1Reduce distortionImprove heat resistanceWindings insulation materialWindings insulation shape/form/constructionWire rodElectrical conductor
Owner:ESSEX FURUKAWA MAGNET WIRE JAPAN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com