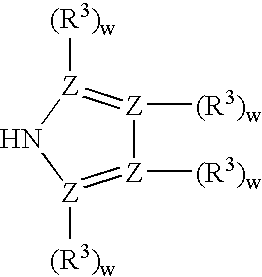
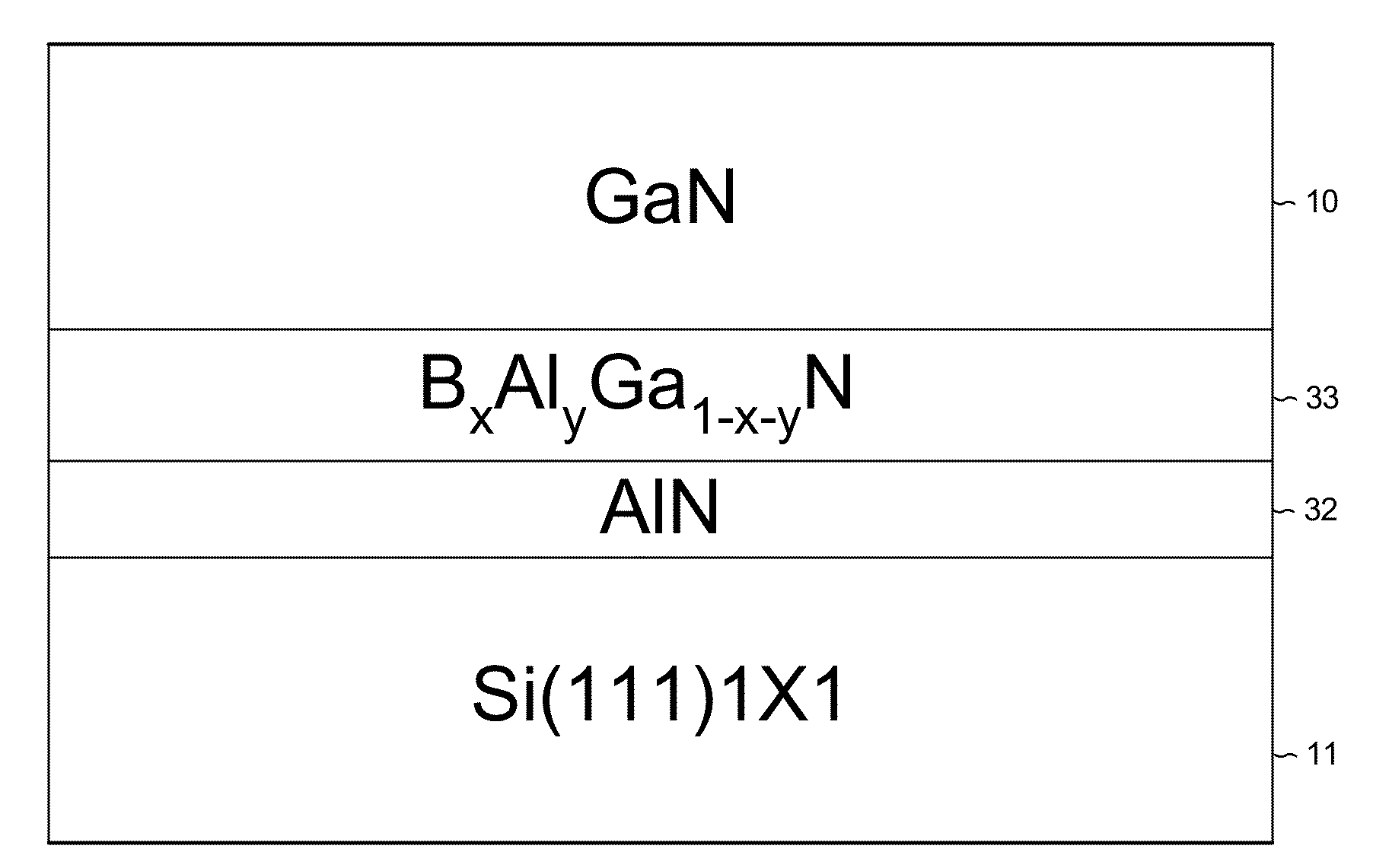Patents
Literature
407 results about "Boron atom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Boron is the first element in the thirteenth column of the periodic table. It is classified as a metalloid which means that its properties are in between that of a metal and a nonmetal. The boron atom has five electrons and five protons. Amorphous boron (meaning the atoms are bonded together in a random order) comes in the form of a brown powder.
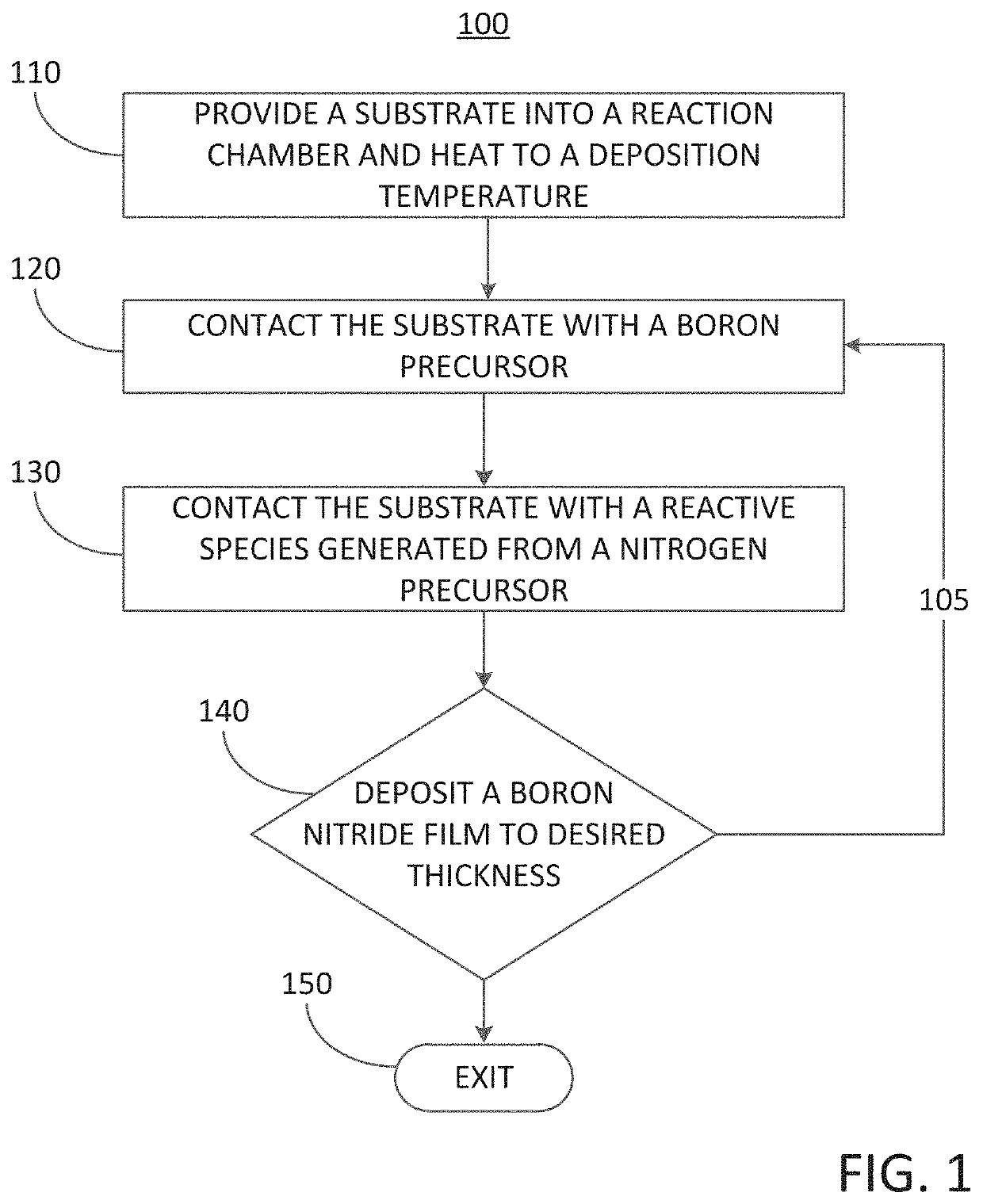
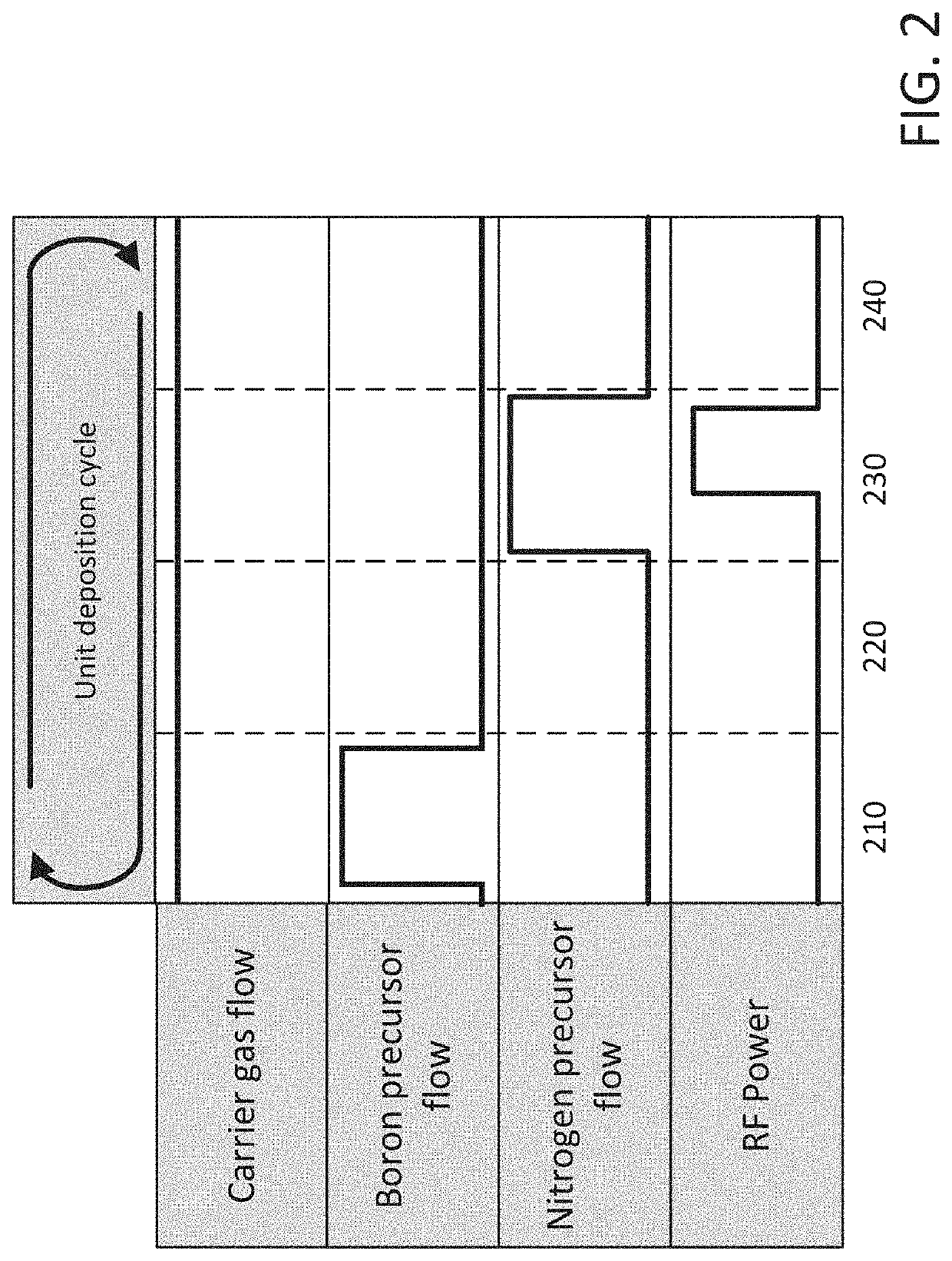
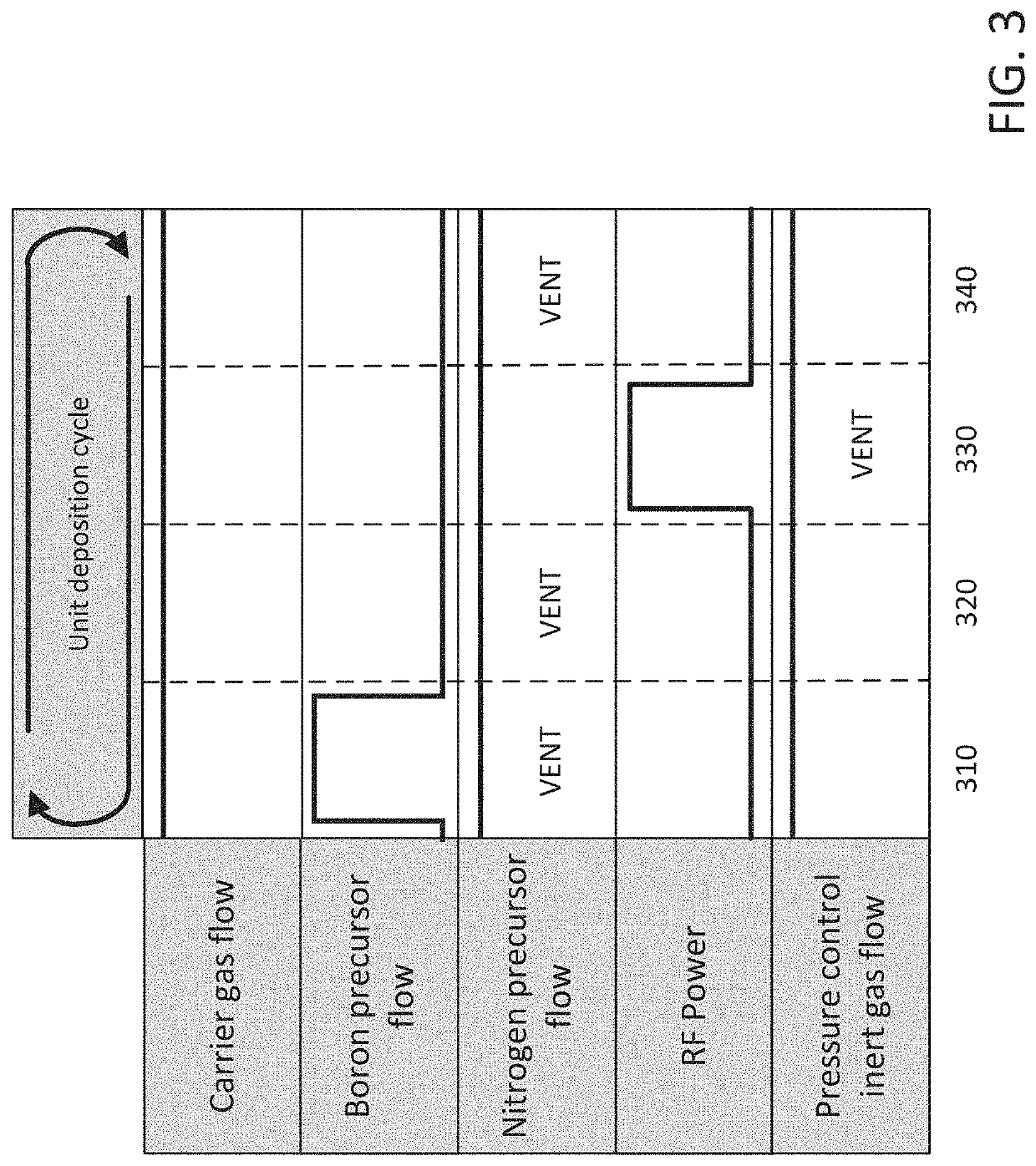
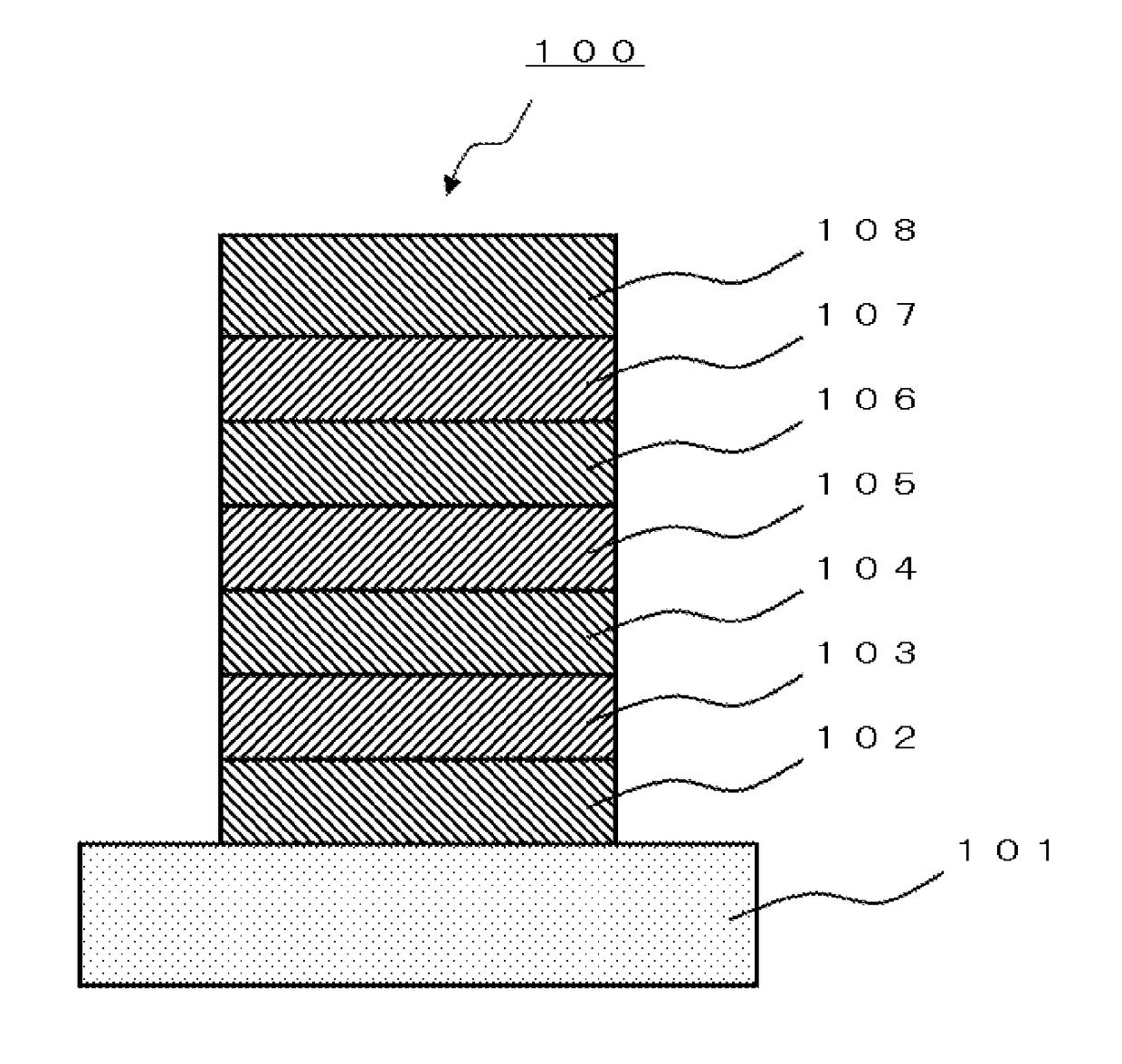
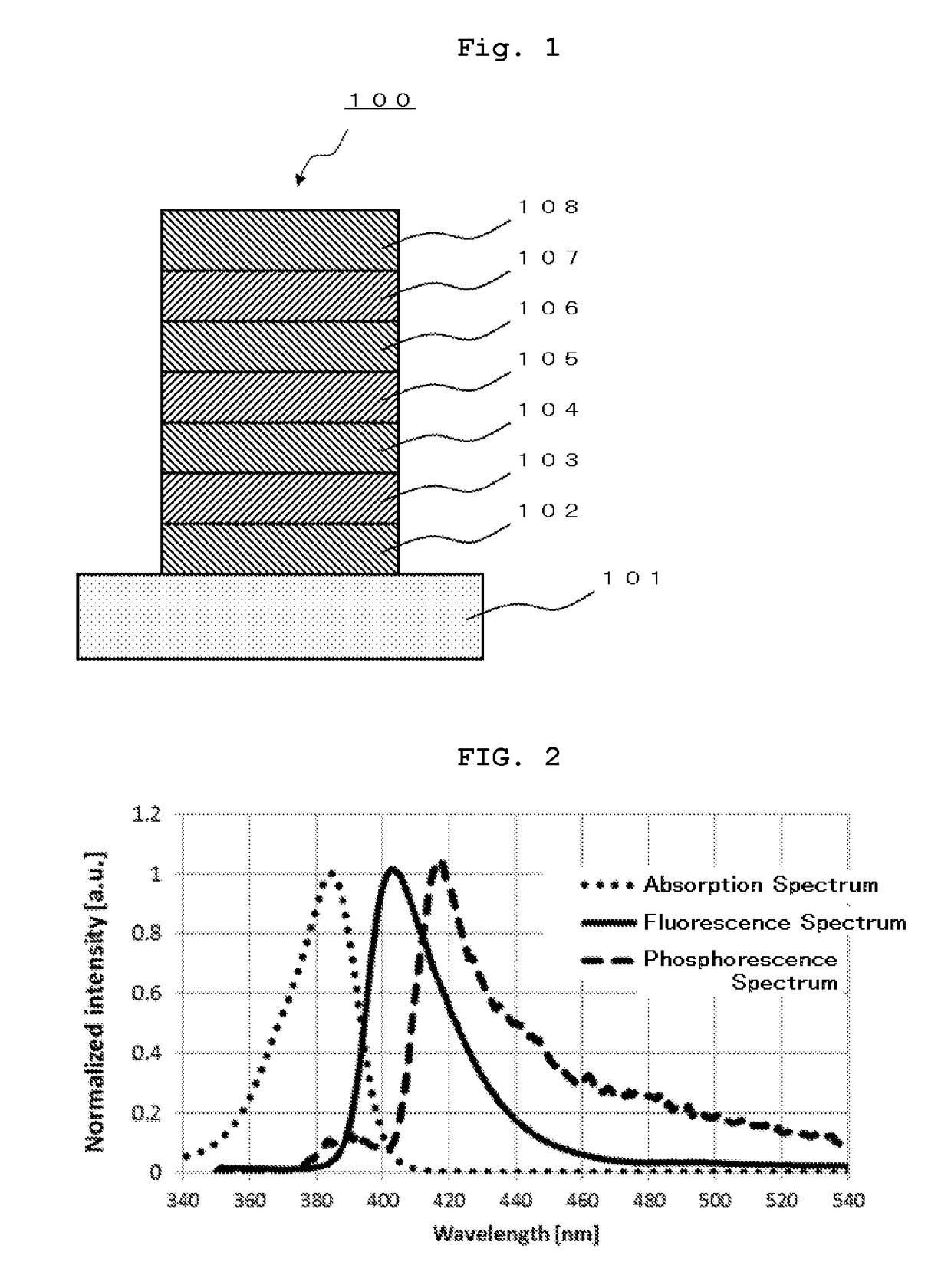
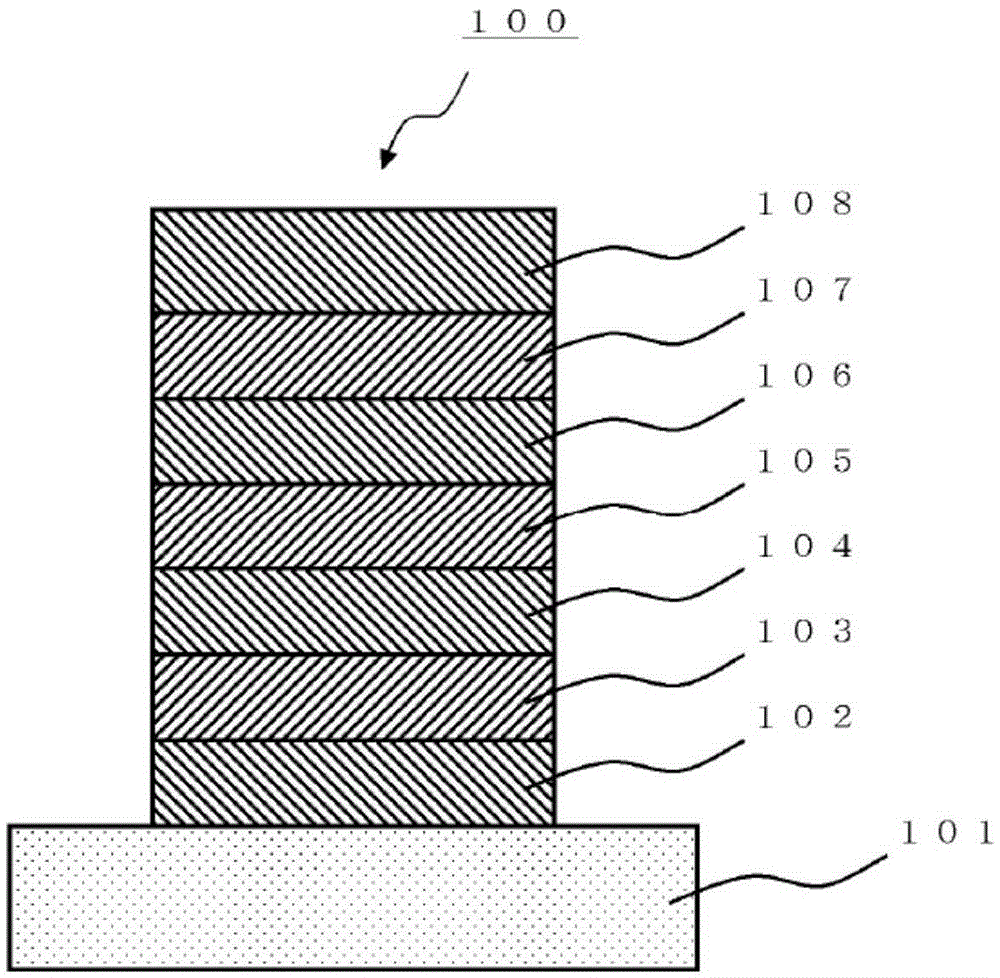
Methods for forming a boron nitride film by a plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition process
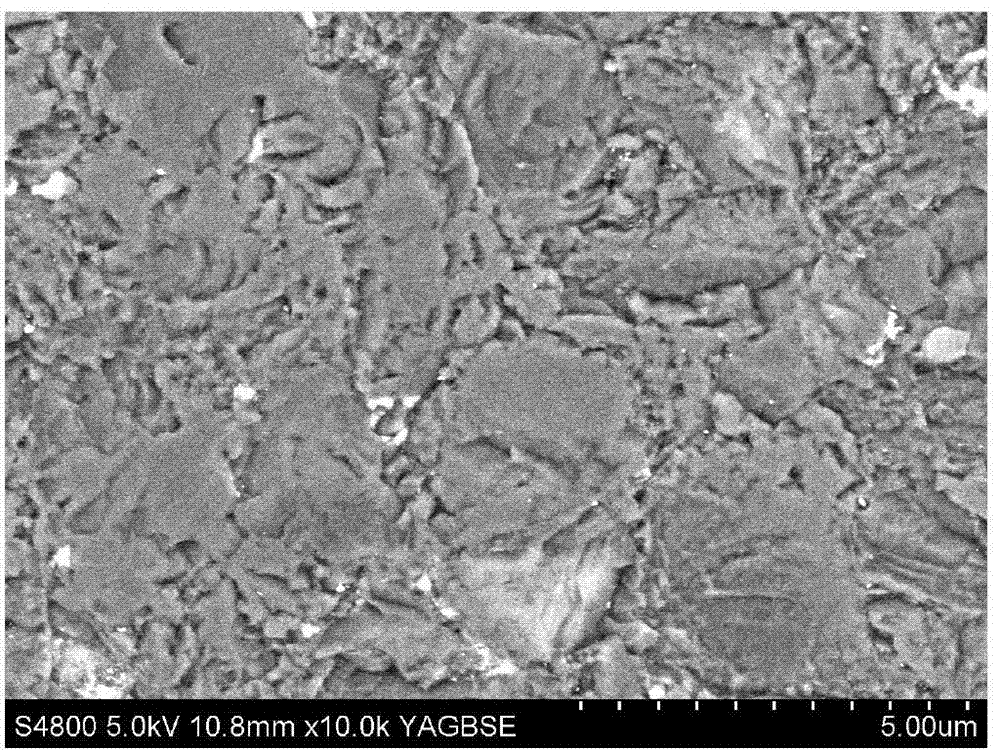
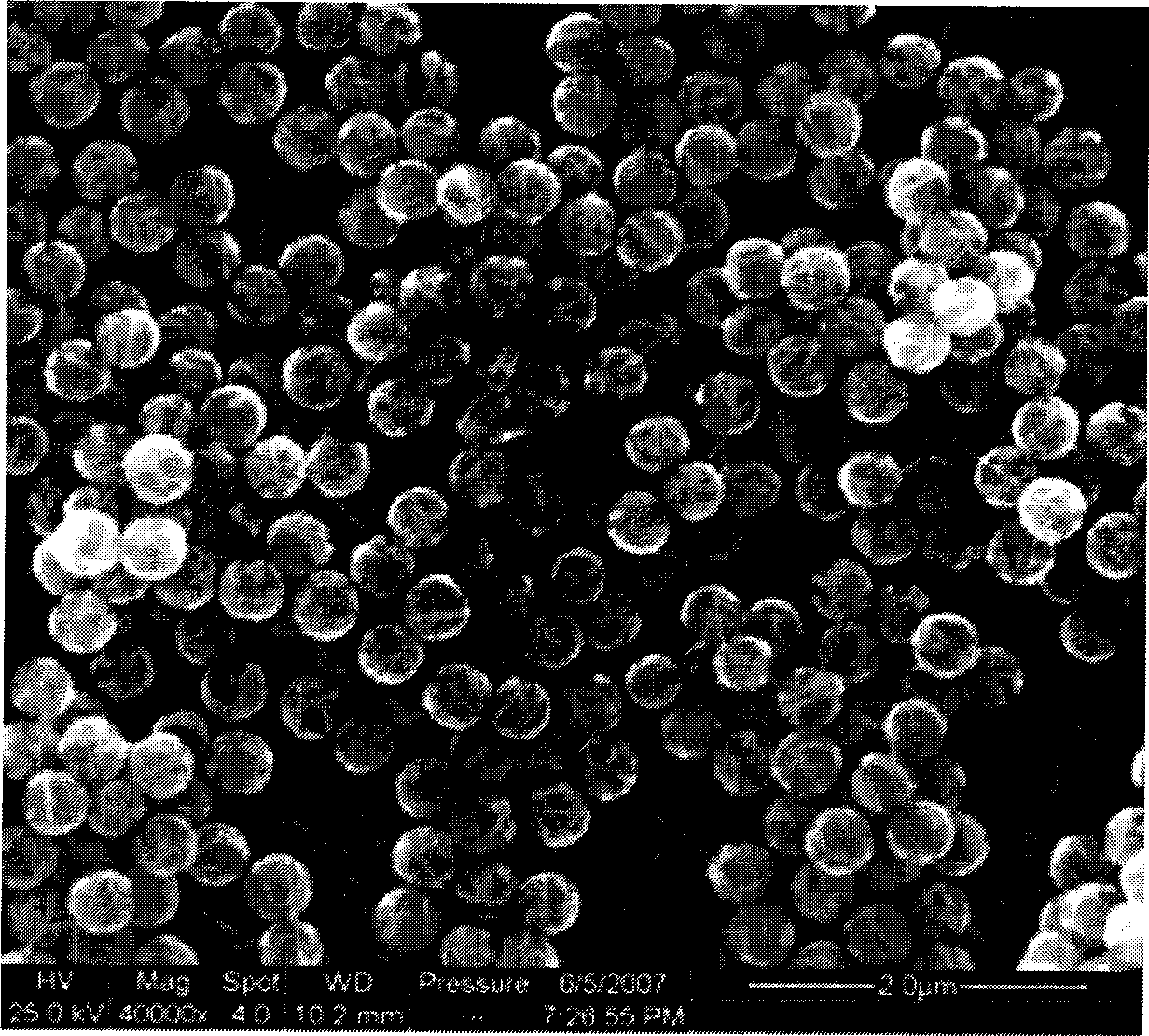
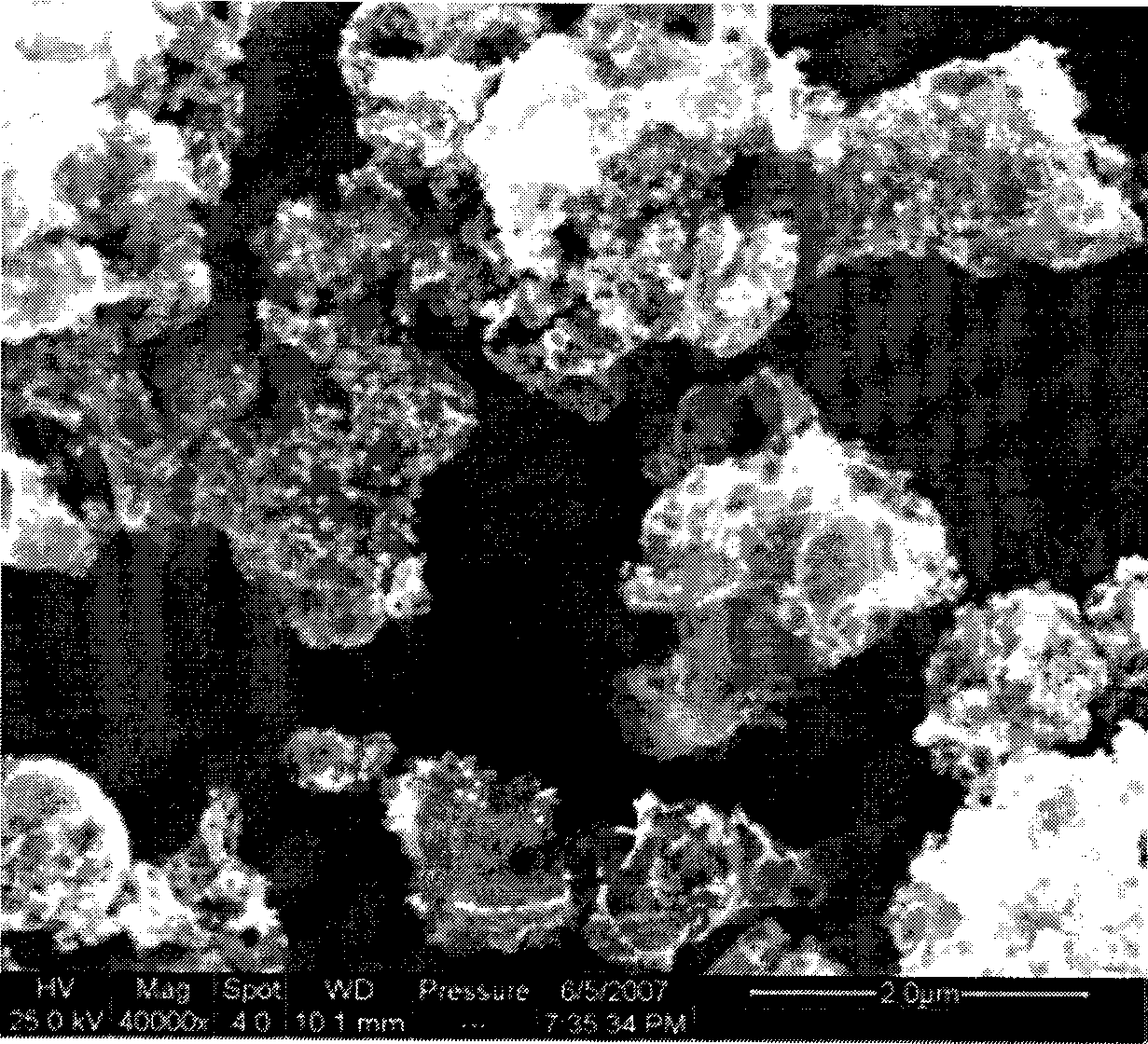
Methods for forming a boron nitride film by a plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) process are provided. The methods may include: providing a substrate into a reaction chamber; and performing at least one unit deposition cycle of a PEALD process, wherein a unit cycle comprises, contacting the substrate with a vapor phase reactant comprising a boron precursor, wherein the boron precursor comprises less than or equal to two halide atoms per boron atom; and contacting the substrate with a reactive species generated from a gas comprising a nitrogen precursor.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Polycyclic aromatic compound
ActiveUS20180069182A1Easy to optimizeHigh triplet excitation energyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesPolycyclic compoundBoron atom
By providing a novel polycyclic aromatic compound in which a plurality of aromatic rings are linked via a boron atom, a nitrogen atom, or the like, options of a material for an organic EL element are increased. In addition, by using the novel polycyclic aromatic compound as a material for an organic electroluminescent element, an excellent organic EL element is provided.
Owner:SK MATERIALS JNC CO LTD +1
Polycyclic aromatic compound
ActiveCN105431439AReduced exchange interactionsHigh affinityTransistorGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPolycyclic compoundBoron atom
The present invention addresses the problem of providing a novel polycyclic aromatic compound and an organic electroluminescent element using the same. The above problem is solved by providing a novel polycyclic aromatic compound in which a plurality of aromatic rings are connected by boron atoms, oxygen atoms, or the like, thereby increasing the number of options for organic EL element materials, and also solved by providing a superior organic EL element using said novel polycyclic aromatic compound as an organic EL element material.
Owner:KWANSEI GAKUIN EDUCTIONAL FOUND +1
Organic electroluminescent element
InactiveUS20180301629A1Improve quantum efficiencyShine wellSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnthraceneAryl
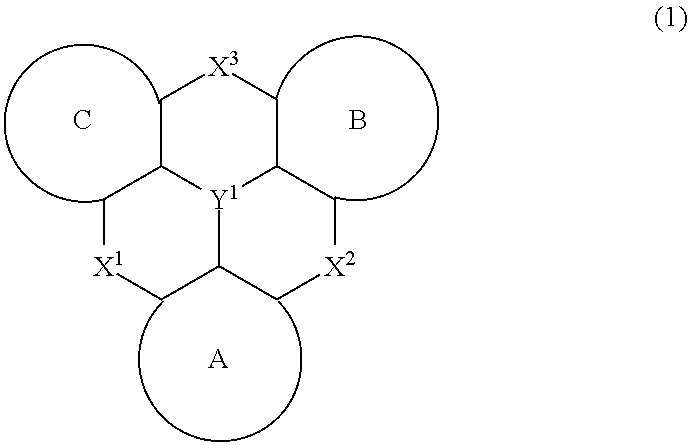
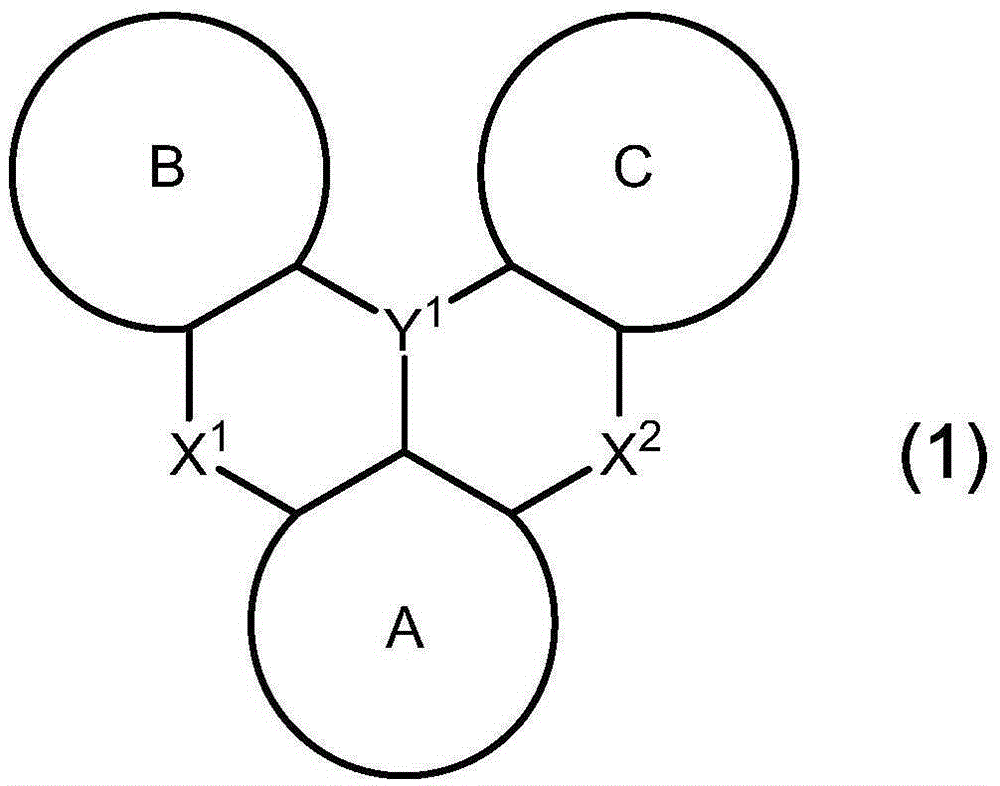
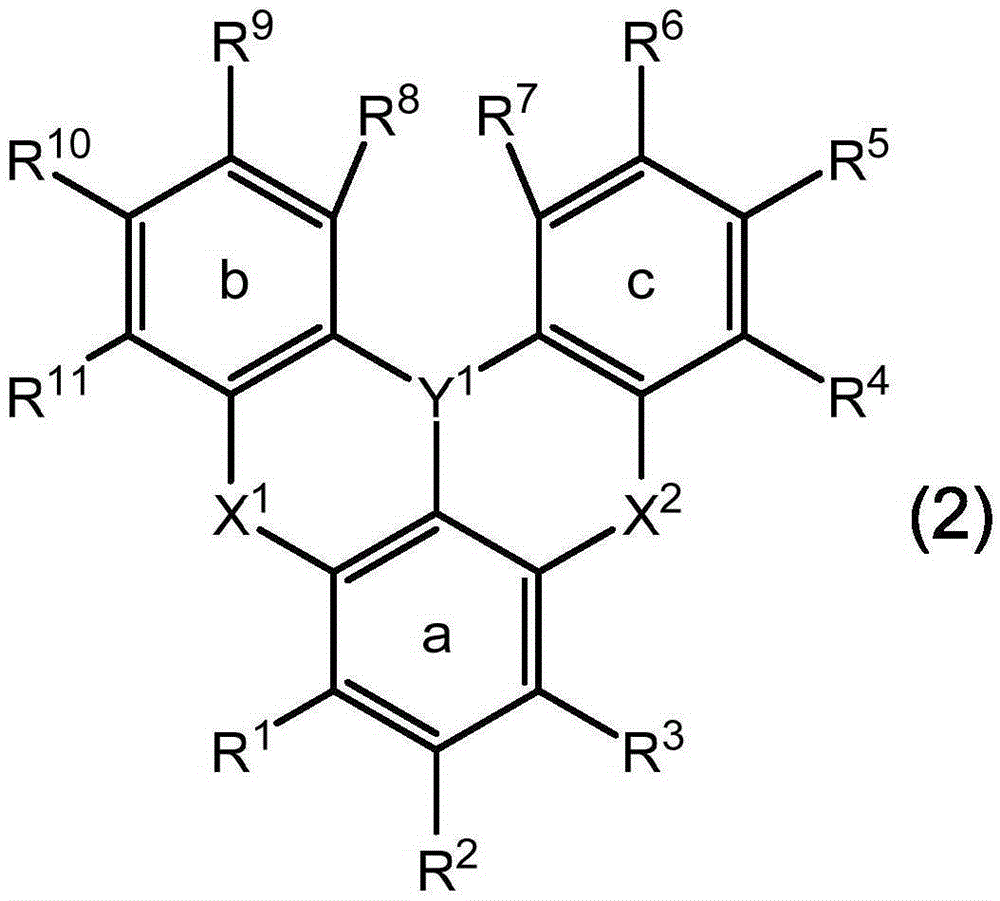
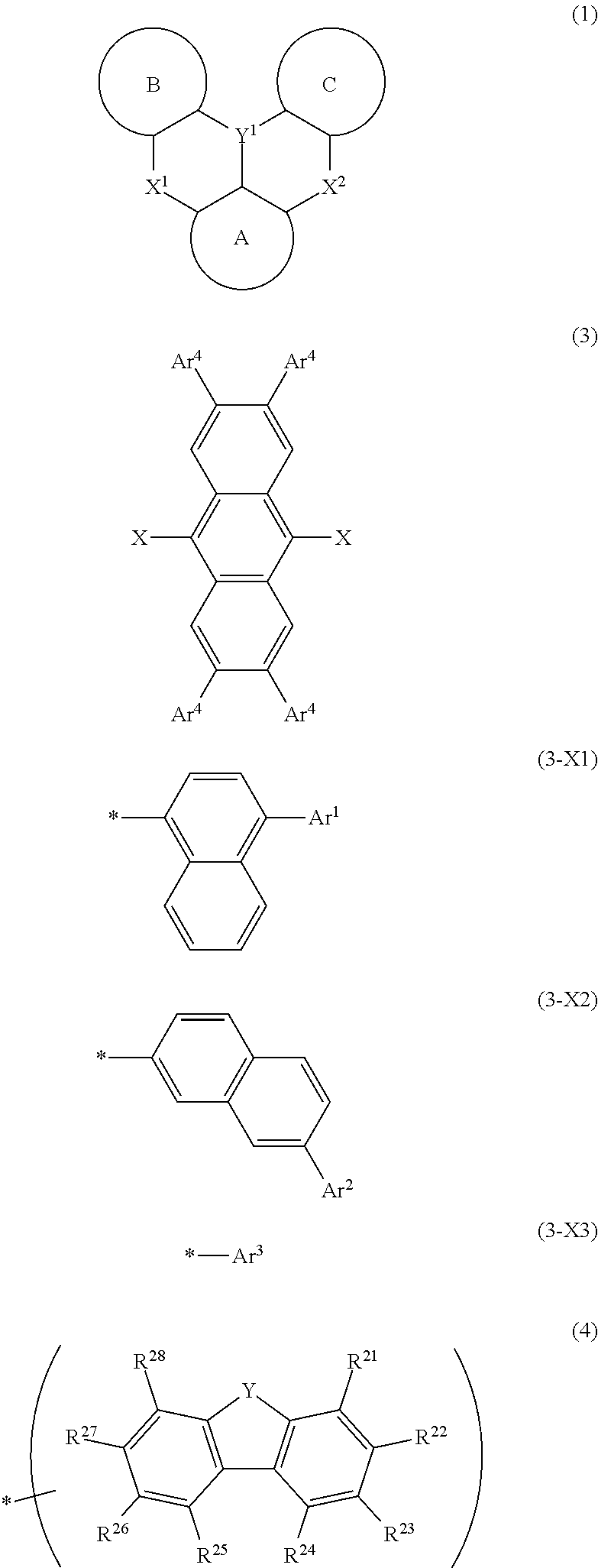
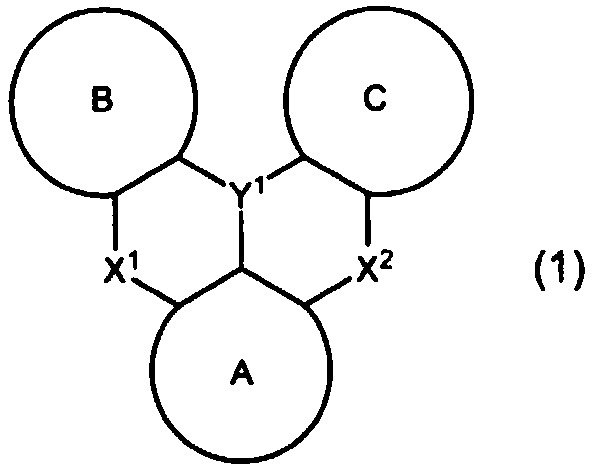
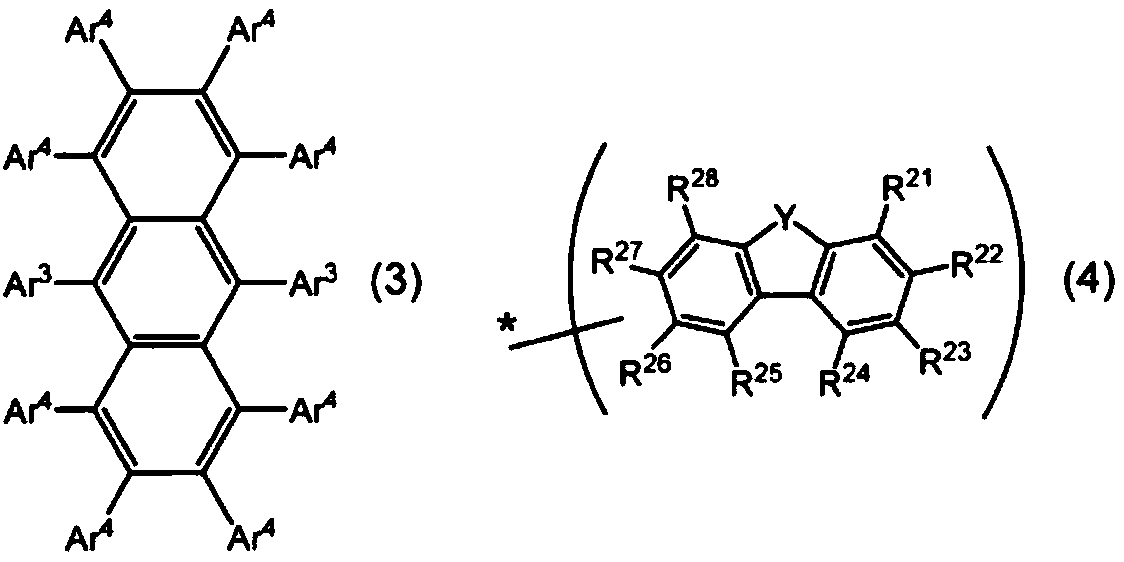
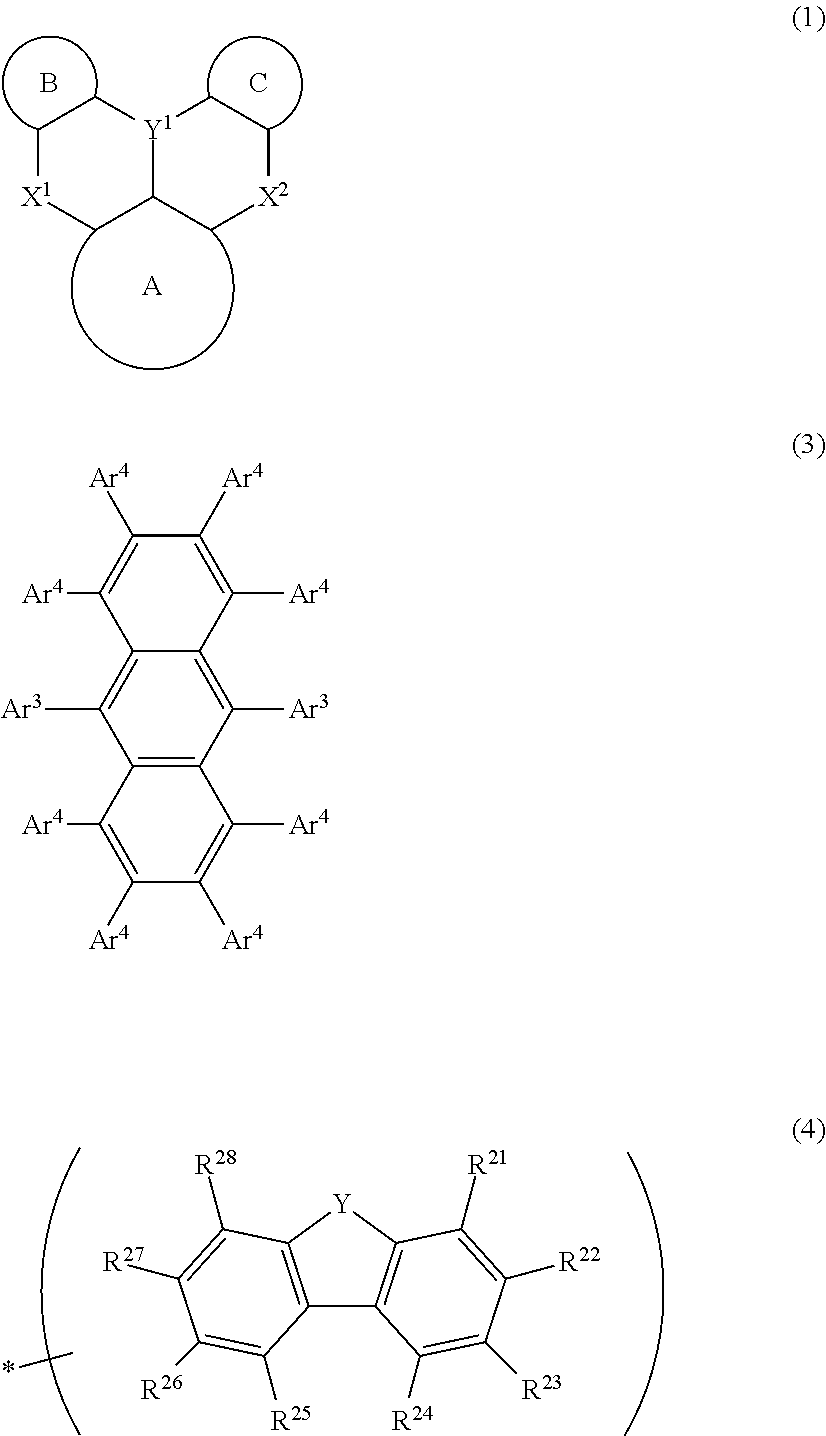
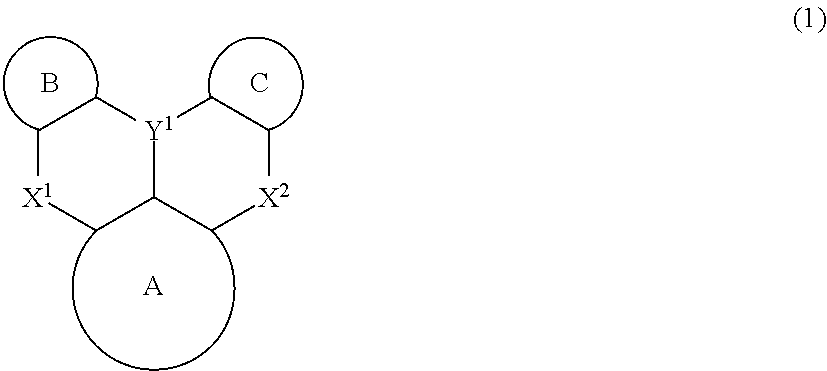
The present invention relates to a light-emission-layer material comprising: a novel polycyclic aromatic compound (1) in which a plurality of aromatic rings are linked by a boron atom and a nitrogen atom; and a specific anthracene-based compound (3) that achieves optimum light-emission characteristics in combination with said polycyclic aromatic compound. With this light-emission-layer material having optimum light-emission characteristics, it is possible to provide an excellent organic EL element.Ring A to ring C are an aryl ring or the like, X is a group represented by formula (3-X1), formula (3-X2), or formula (3-X3), and Ar1 to Ar4 are phenyl, a group represented by formula (4), or the like.
Owner:KWANSEI GAKUIN EDUCATIONAL FOUND +1
Graphene substituted with boron and nitrogen , method of fabricating the same, and transistor having the same
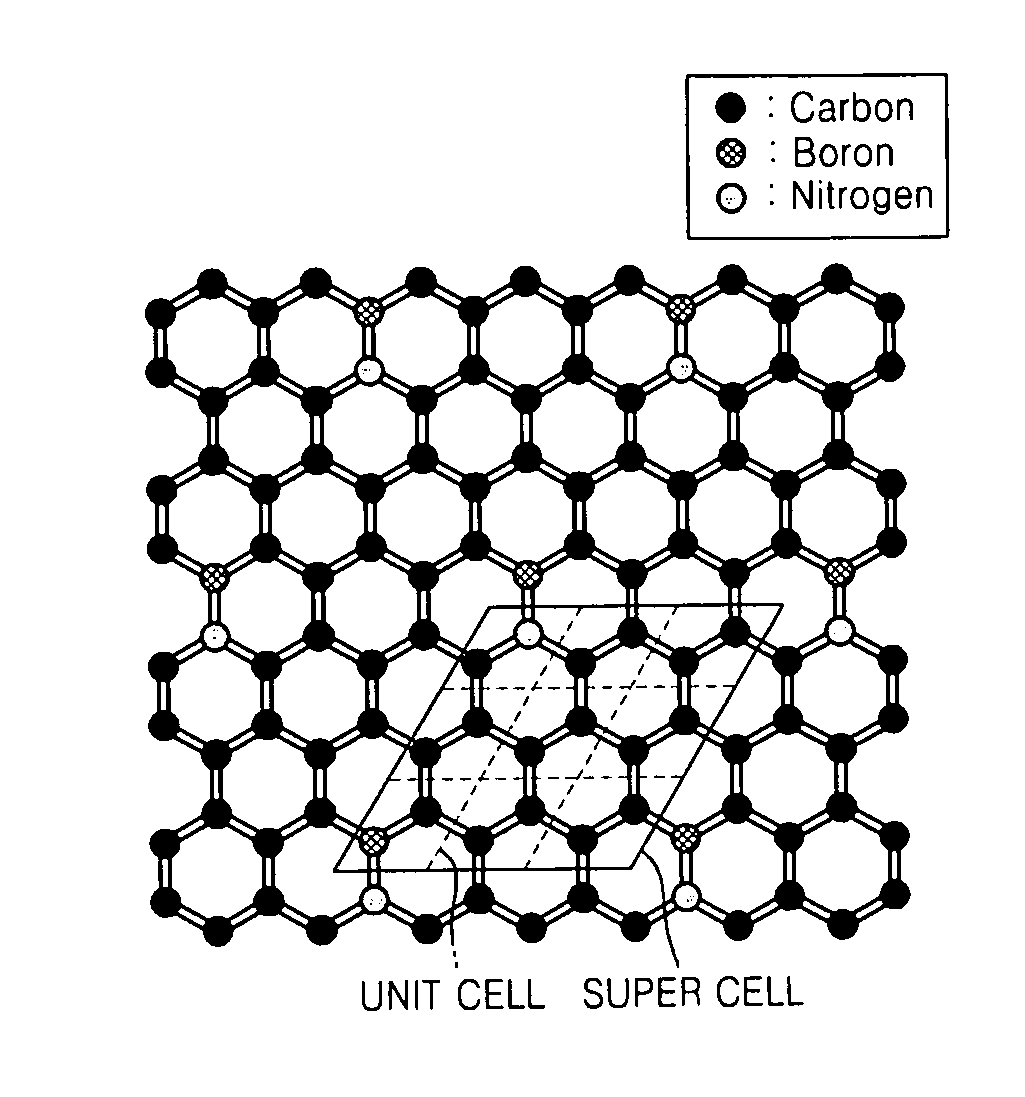
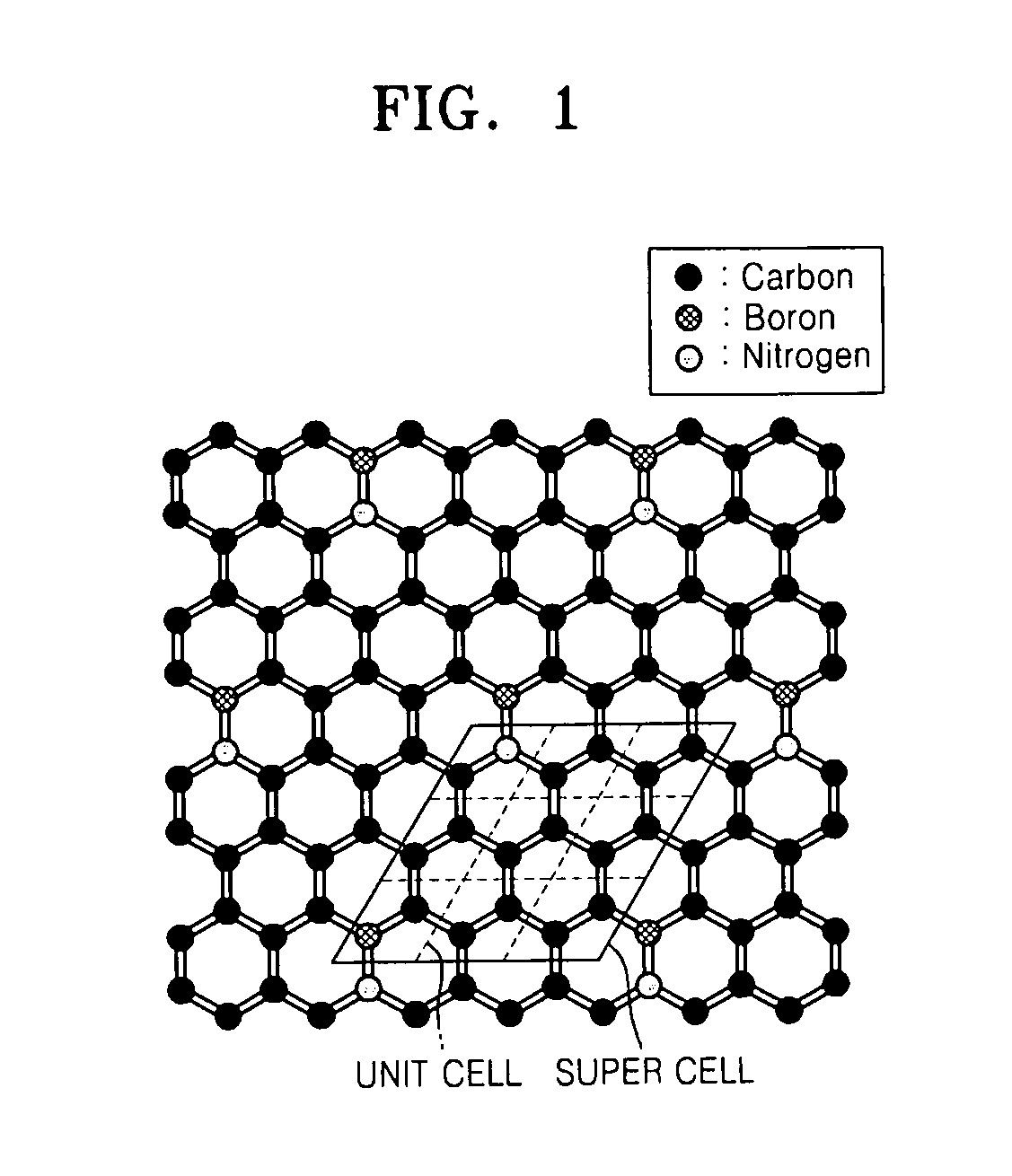
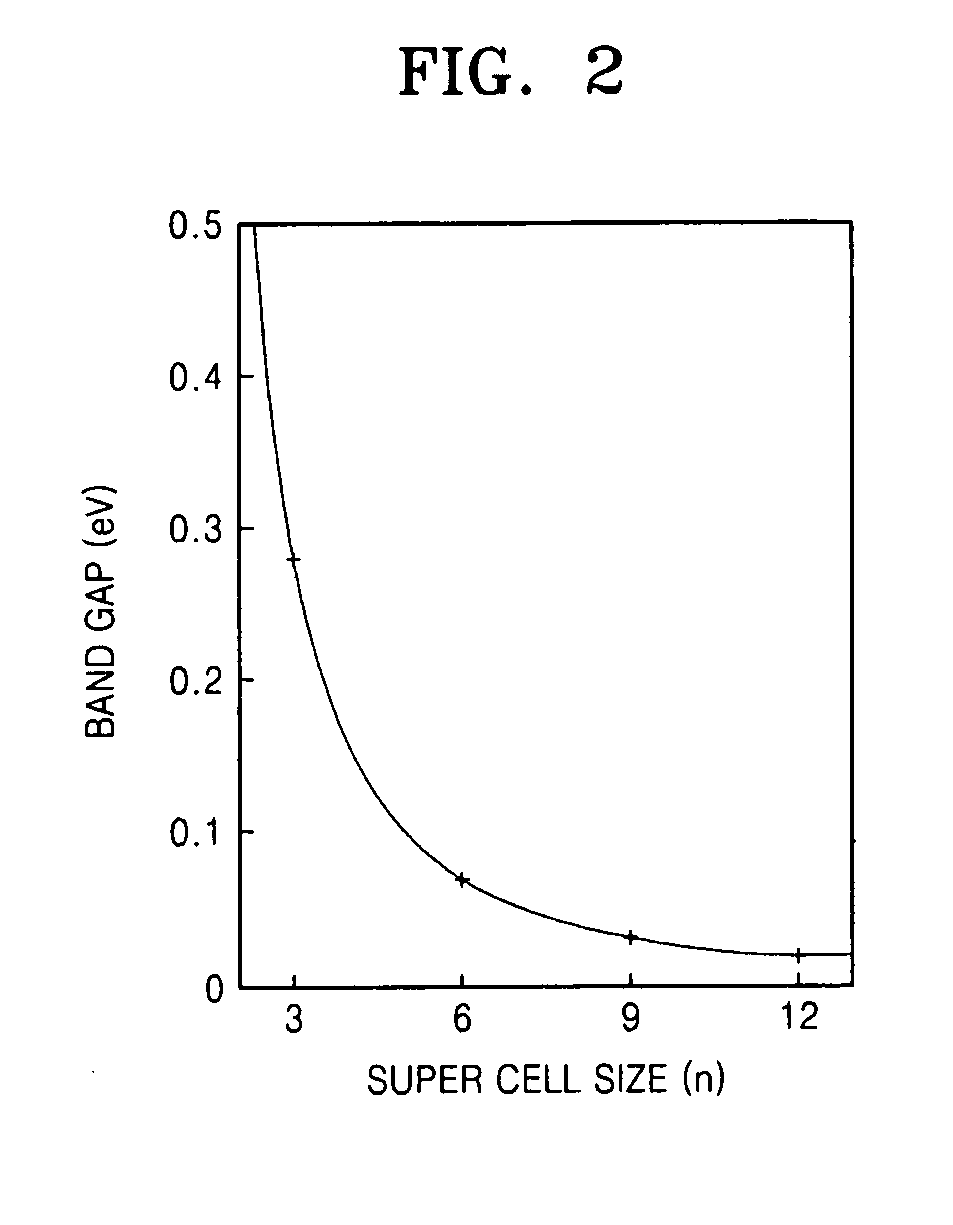
Graphene, a method of fabricating the same, and a transistor having the graphene are provided, the graphene includes a structure of carbon (C) atoms partially substituted with boron (B) atoms and nitrogen (N) atoms. The graphene has a band gap. The graphene substituted with boron and nitrogen may be used as a channel of a field effect transistor. The graphene may be formed by performing chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method using borazine or ammonia borane as a boron nitride (B—N) precursor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Boron-Containing Buffer Layer for Growing Gallium Nitride on Silicon
InactiveUS20130026482A1Small sizeMore stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitrogenBoron containing
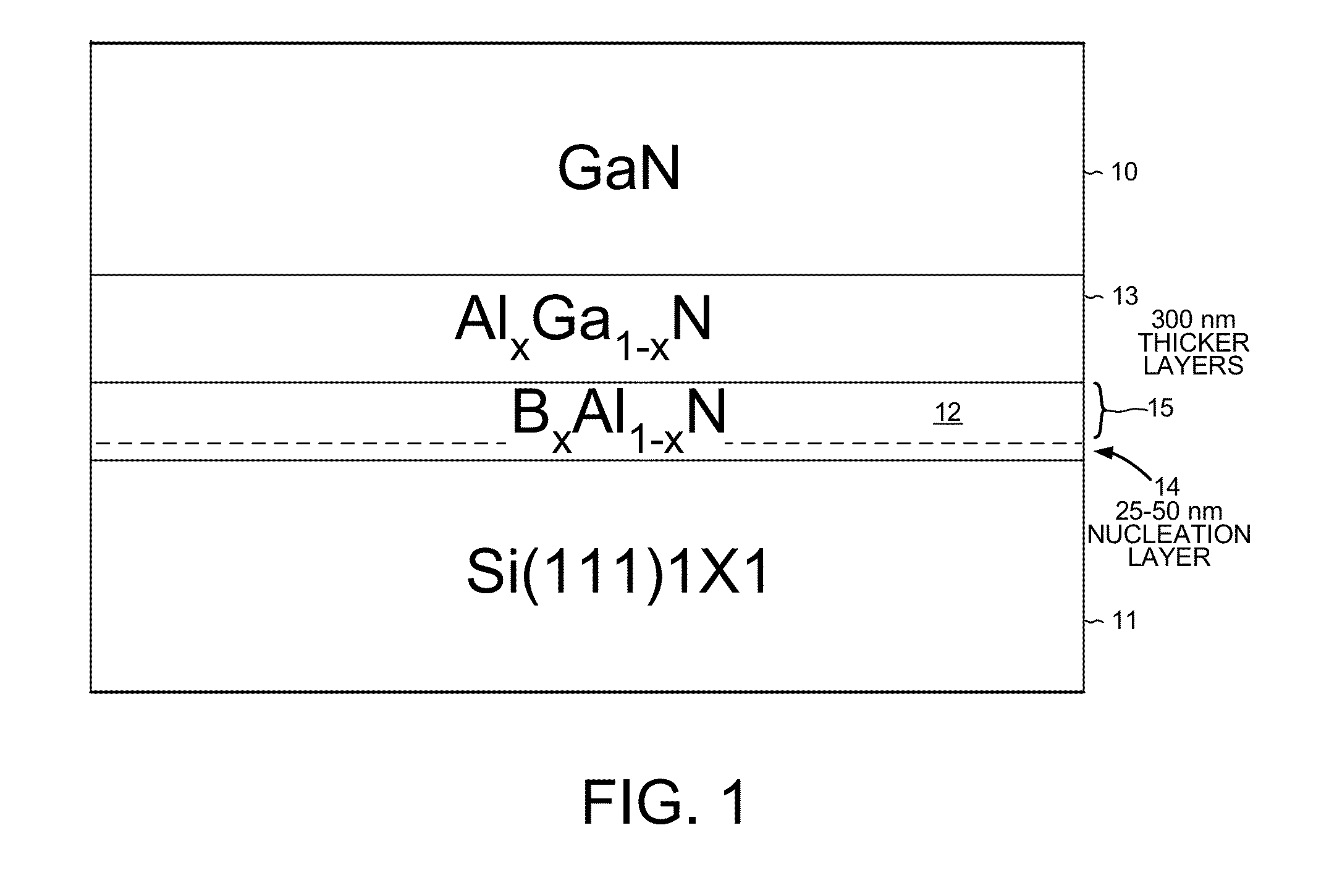
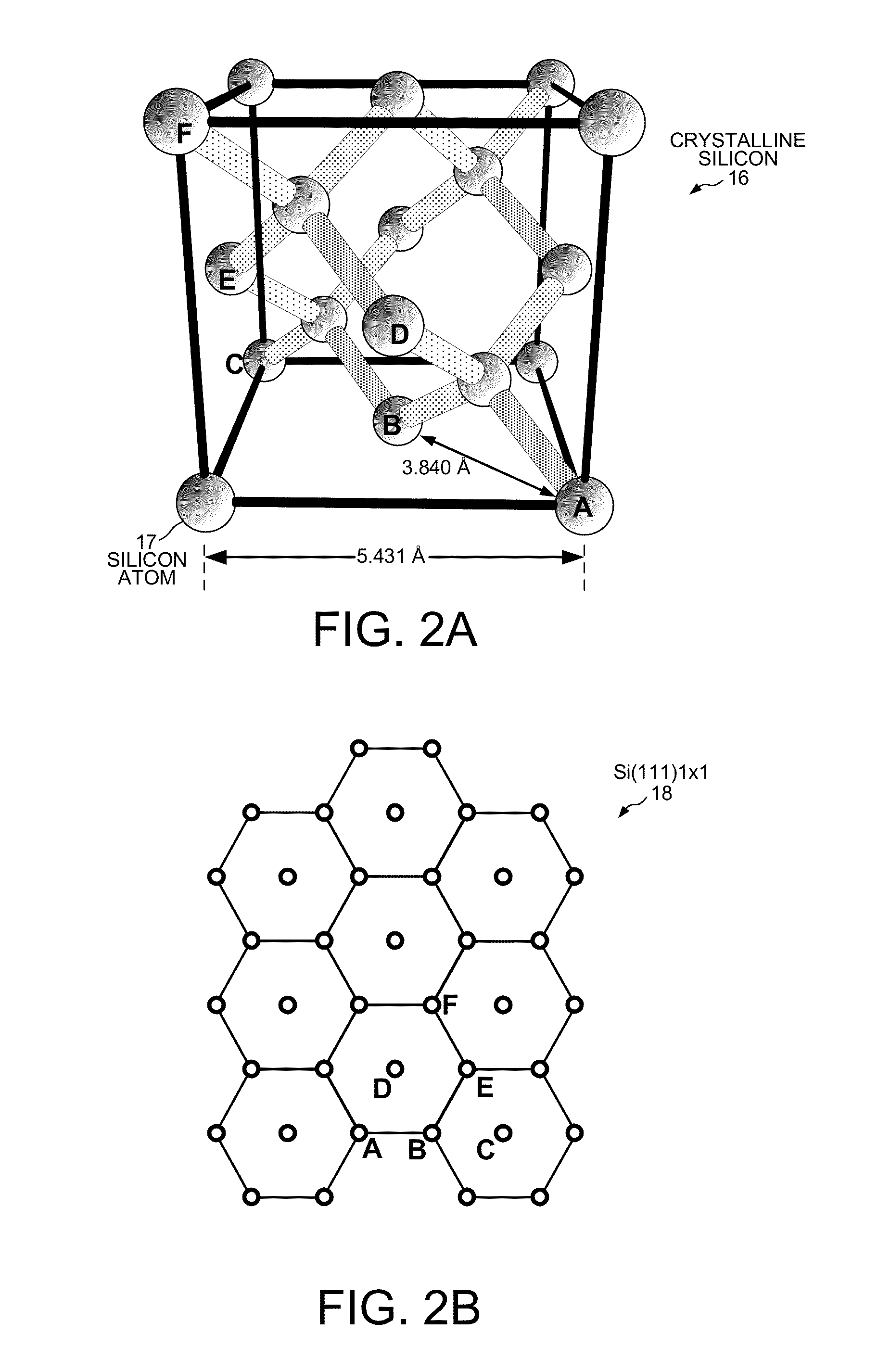
A silicon wafer used in manufacturing GaN for LEDs includes a silicon substrate, a buffer layer of boron aluminum nitride (BxAl1-xN) and an upper layer of GaN, for which 0.35≦x≦0.45. The BAlN forms a wurtzite-type crystal with a cell unit length about two-thirds of a silicon cell unit length on a Si(111) surface. The C-plane of the BAlN crystal has approximately one atom of boron for each two atoms of aluminum. Across the entire wafer substantially only nitrogen atoms of BAlN form bonds to the Si(111) surface, and substantially no aluminum or boron atoms of the BAlN are present in a bottom-most plane of atoms of the BAlN. A method of making the BAlN buffer layer includes preflowing a first amount of ammonia equaling less than 0.01% by volume of hydrogen flowing through a chamber before flowing trimethylaluminum and triethylboron and then a subsequent amount of ammonia through the chamber.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
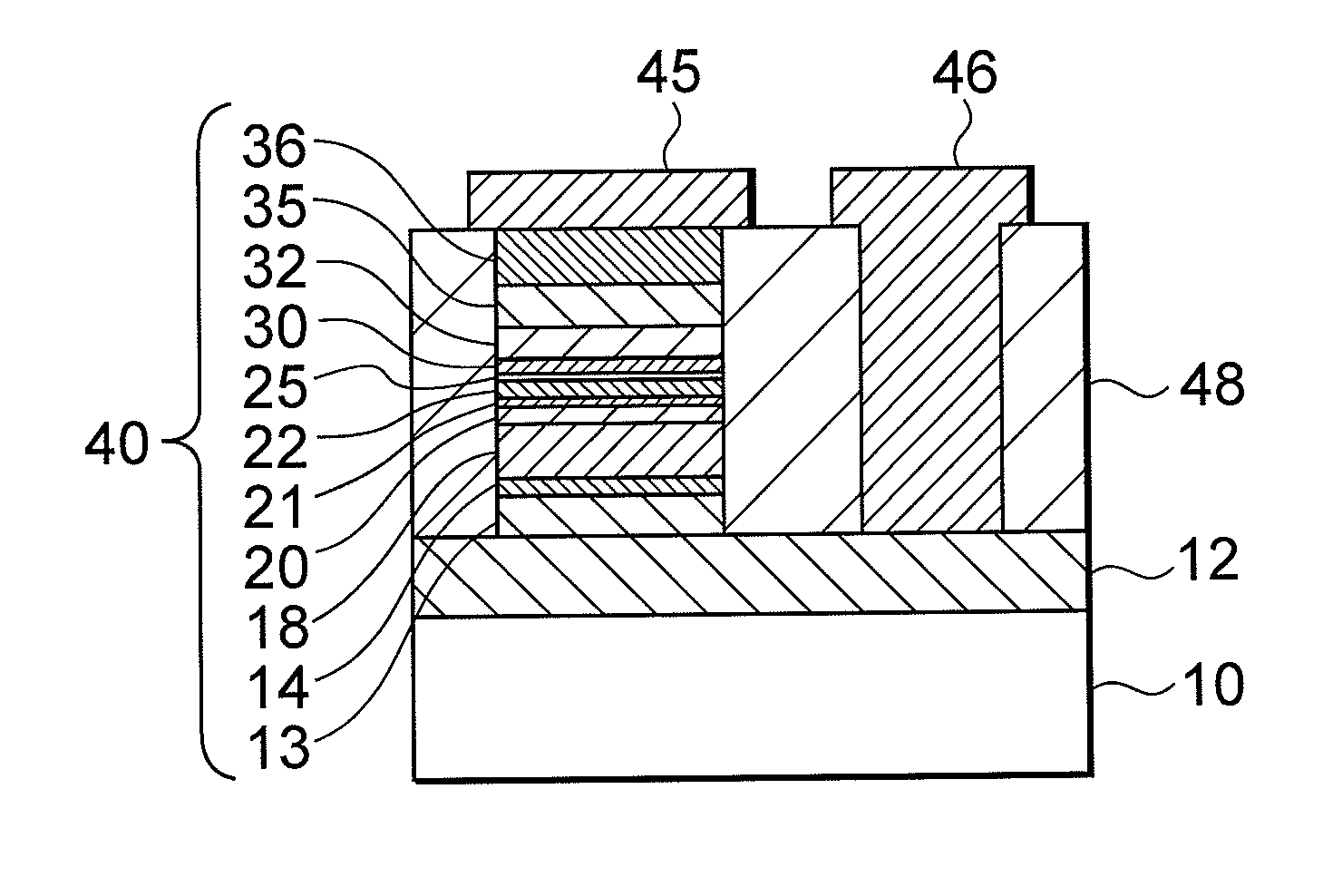
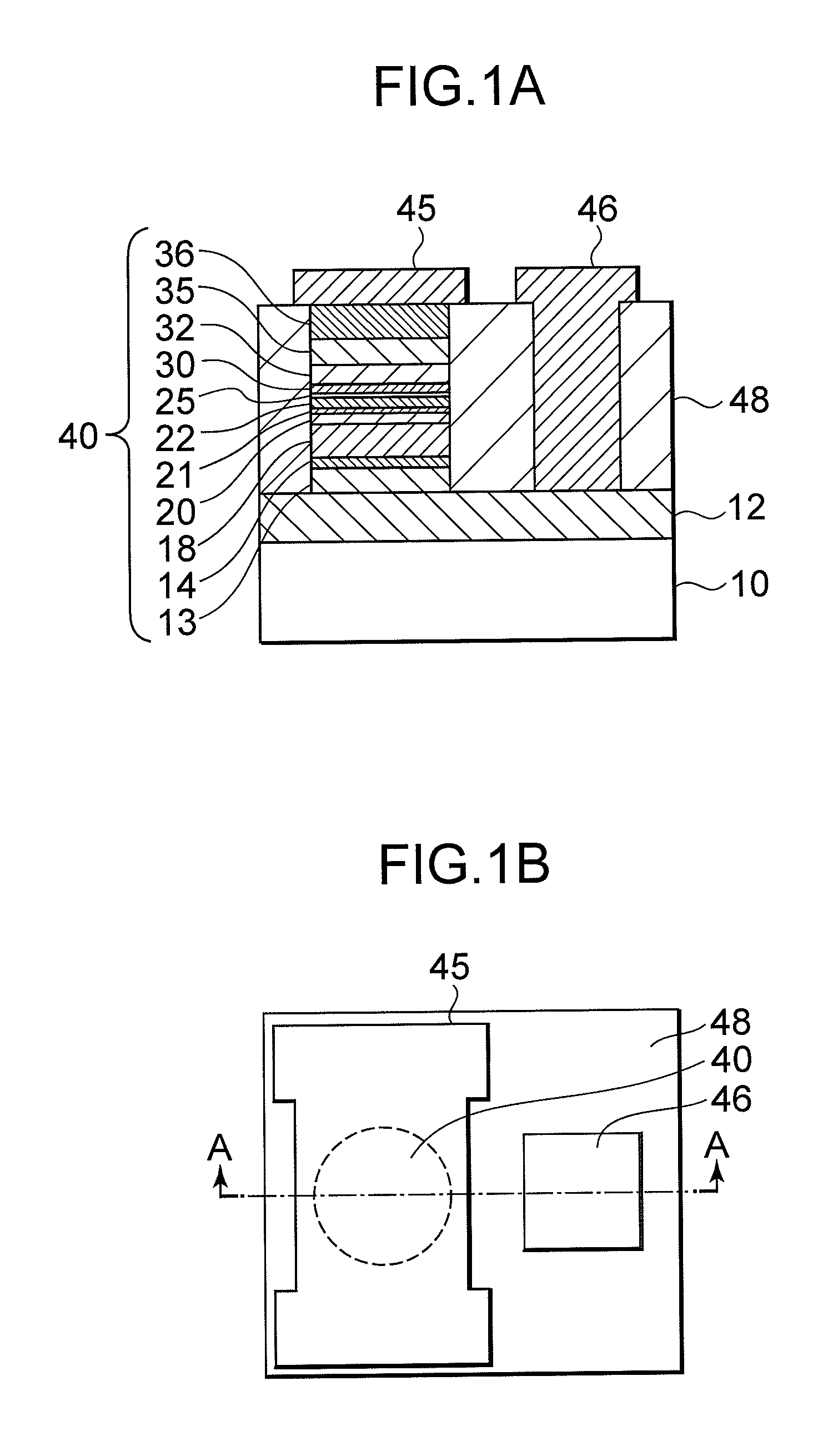
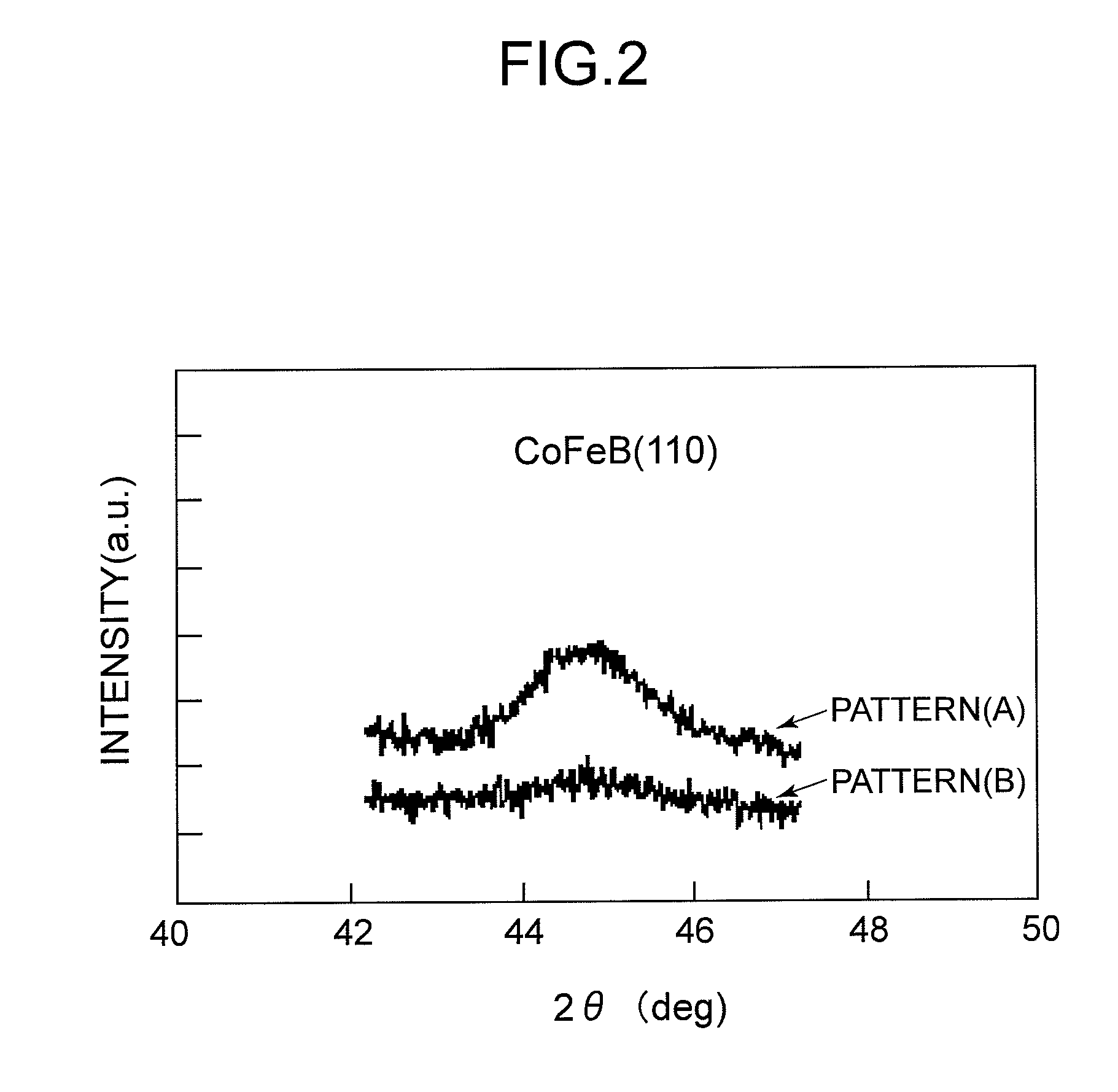
Ferromagnetic tunnel junction device, magnetic head, and magnetic storage device
According to an aspect of an embodiment, a ferromagnetic tunnel junction device includes: a first pinned magnetic member including a ferromagnetic material having a boron atom; a second pinned magnetic member including a ferromagnetic material on the first pinned magnetic member, the content of the boron atom in the second pinned member being smaller than that in the first pinned member; and a first free magnetic member superposed with respect to the second pinned layer, including a ferromagnetic material. The ferromagnetic tunnel junction device further includes: an insulating layer between the second pinned magnetic layer and the first free magnetic layer; and a second free magnetic member including a ferromagnetic material having a boron atom on the first free magnetic member, the content of the boron atom in the second free member being smaller than that in the first free member.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Organic electroluminescent element
ActiveCN109155368AReduce power consumptionImprove quantum efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingArylBoron atom
Provided is an organic EL element having optimum light emission characteristics using a light-emitting layer material comprising a novel polycyclic aromatic compound (1) in which a plurality of aromatic rings are linked by a boron atom and a nitrogen atom or a multimer thereof, and a specific anthracene compound (3) that is combined with the novel polycyclic aromatic compound (1) or the multimer thereof to exhibit optimum light emission characteristics. Rings A-C are an aryl ring, etc., Y1 is B, X1 and X2 are N-R, the R in the N-R is an aryl, etc., and Ar3 and Ar4 are hydrogen, a phenyl, or agroup represented by formula (4), etc.
Owner:KWANSEI GAKUIN EDUCTIONAL FOUND +1
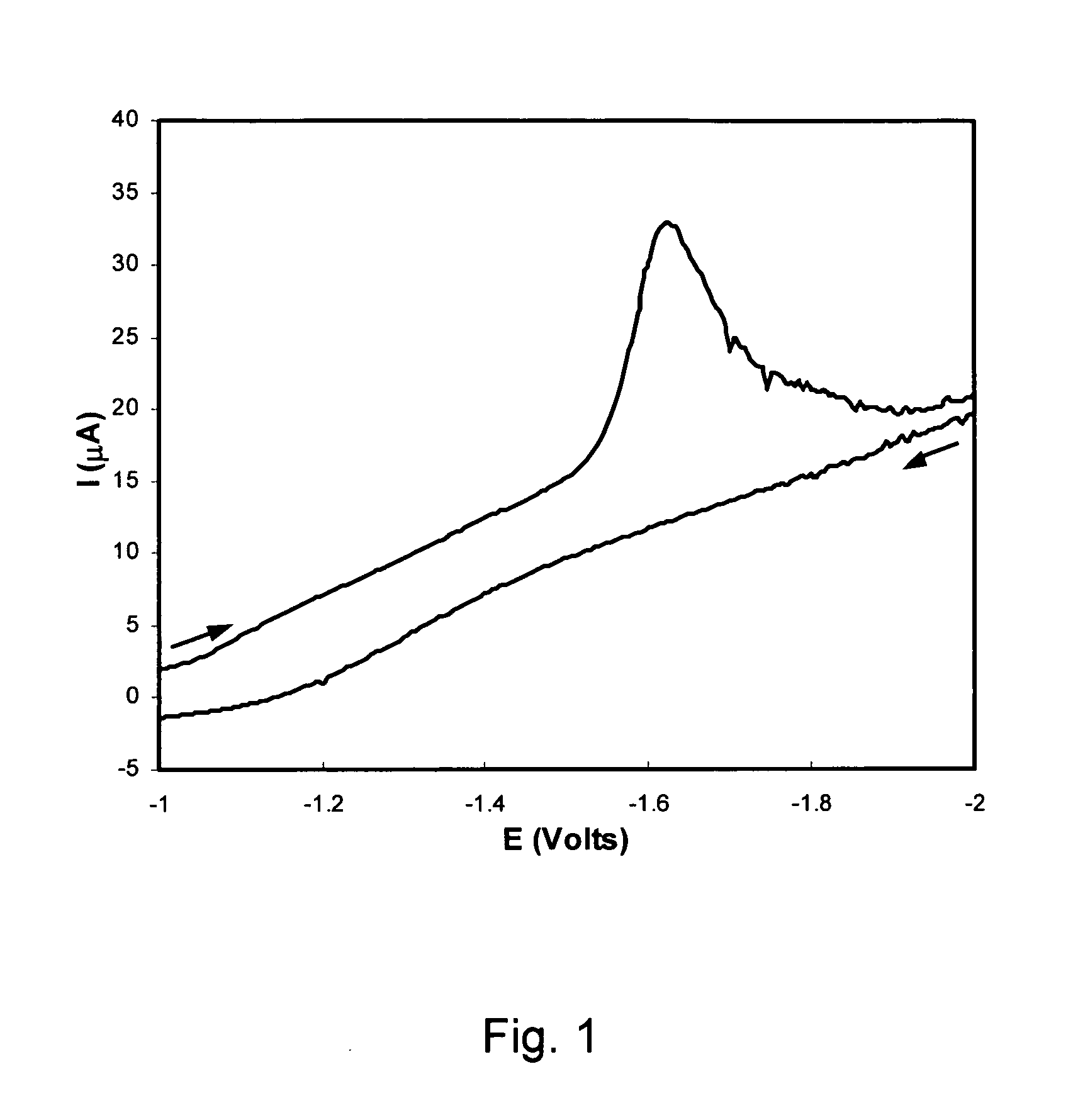
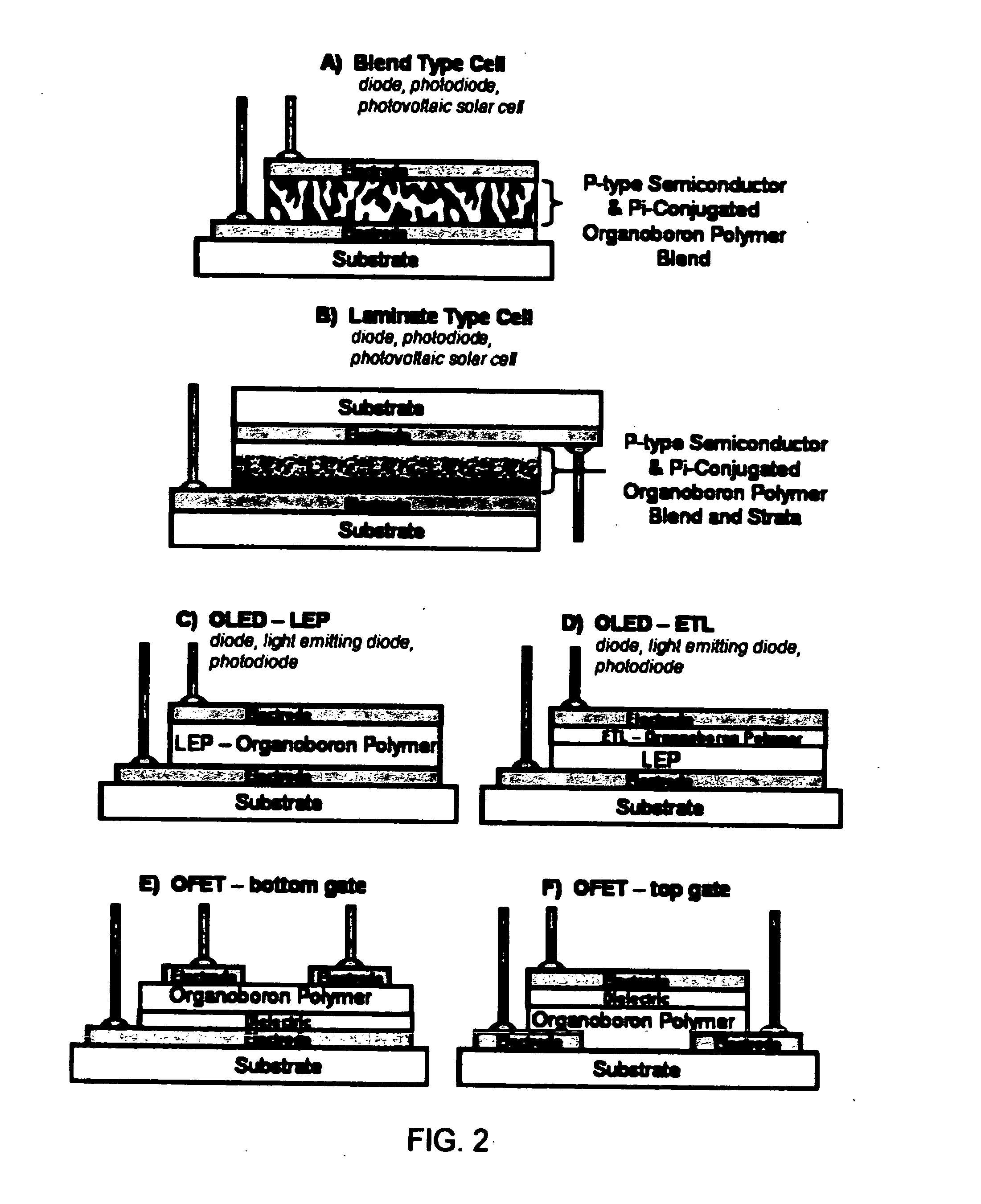
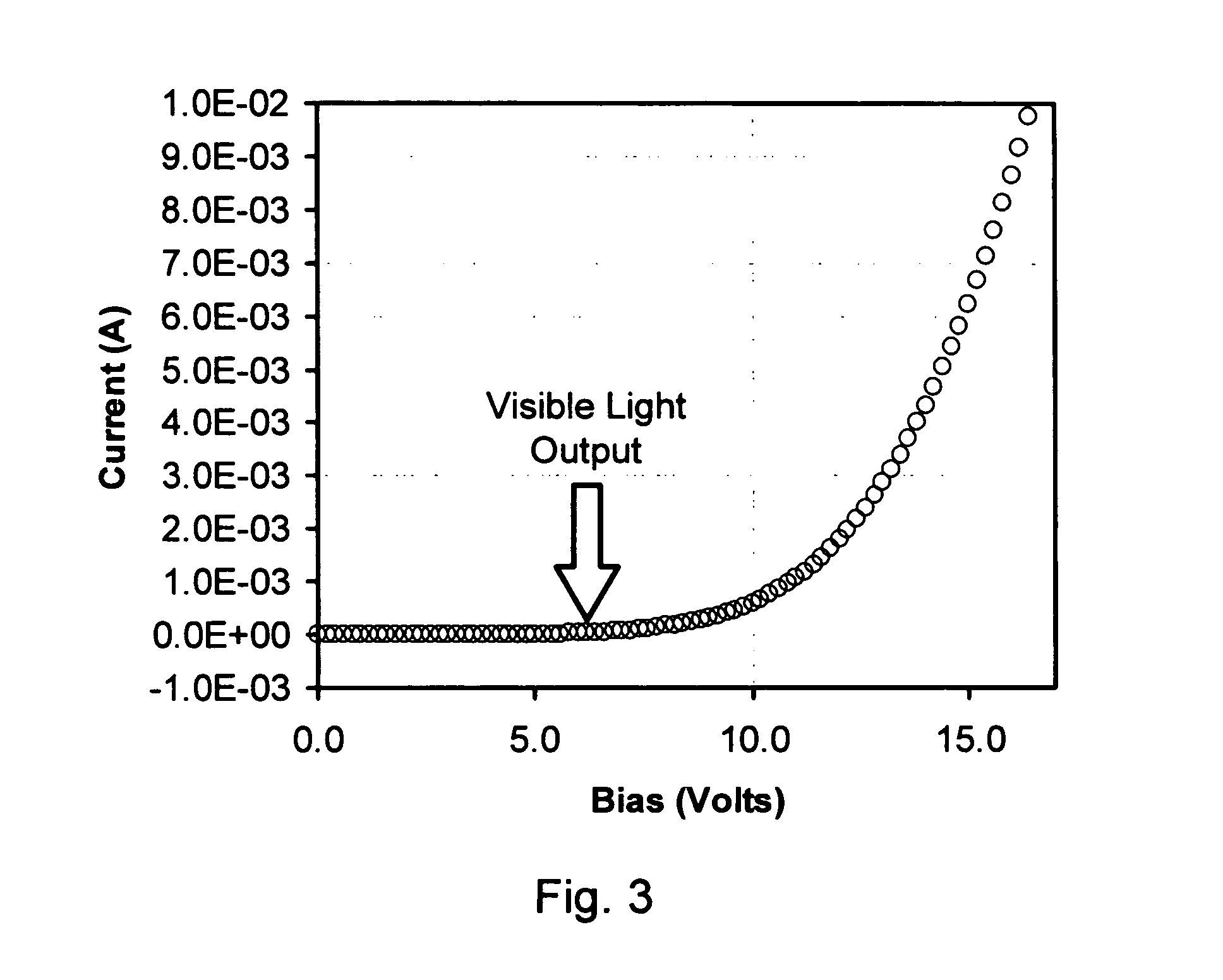
Use of pi-conjugated organoboron polymers in thin-film organic polymer electronic devices
InactiveUS20070215864A1Improve propertiesImproved propertyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhotoluminescenceOrganic field-effect transistor
Pi-conjugated organoboron polymers for use in thin-film organic polymer electronic devices. The polymers contain aromatic and or unsaturated repeat units and boron atoms. The vacant p-orbital of the boron atoms conjugate with the pi-conjugated orbital system of the aromatic or unsaturated monomer units extending the pi-conjugation length of the polymer across the boron atoms. The pi-conjugated organoboron polymers are electron-deficient and, therefore, exhibit n-type semiconducting properties, photoluminescence, and electroluminescence. The invention provides thin-film organic polymer electronic devices, such as organic photovoltaic cells (OPVs), organic diodes, organic photodiodes, organic thin-film transistors (TFTs), organic field-effect transistors (OFETs), printable or flexible electronics, such as radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags, electronic papers, and printed circuit elements, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), polymer light-emitting diodes (PLEDs), and energy storage devices employing the pi-conjugated organoboron polymers. In OLED and PLED applications these materials are used as the electron transport layer (ETL) to improve device efficiency. The polymers which exhibit photo- and electroluminescence are also useful as light-emitting material in PLEDs.
Owner:TDA RES
Organic electroluminescent element
ActiveUS20190207112A1Reduce power consumptionImprove quantum efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnthraceneAryl
With a light-emission-layer material comprising: a novel polycyclic aromatic compound (1) or a multimer thereof in which a plurality of aromatic rings are linked by a boron atom and a nitrogen atom; and a specific anthracene-based compound (3) that achieves optimum light-emission characteristics in combination with said polycyclic aromatic compound or a multimer thereof, it is possible to provide an organic EL element having optimum light-emission characteristics.Ring A to ring C are an aryl ring or the like, Y1 represents B, X1 and X2 represent N—R, R of the N—R is an aryl or the like, and Ar3 and Ar4 are a hydrogen atom, a phenyl, a group represented by formula (4), or the like.
Owner:KWANSEI GAKUIN EDUCATIONAL FOUND +1
Electrolytic solution for non-aqueous energy storage device and lithium ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20150099193A1High voltageGenerates less gasOrganic electrolyte cellsPositive electrodesCarboxylic acidBoron atom
A lithium ion secondary battery that operates at a high voltage, has a high cycle life, and generates less gas, and an electrolytic solution for such a lithium ion secondary battery. An electrolytic solution for a non-aqueous energy storage device, comprising: a non-aqueous solvent; a lithium salt (A) having no boron atom; a predetermined lithium salt (B) containing a boron atom; and a compound (C) in which at least one of hydrogen atoms in an acid selected from the group consisting of proton acids having a phosphorus atom and / or a boron atom, sulfonic acids, and carboxylic acids is replaced with a substituent represented by formula (3):wherein R3, R4, and R5 each independently represent an organic group which has 1 to 10 carbon atoms and which may have a substituent.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Ferromagnetic tunnel junction element, magnetic recording device and magnetic memory device
A ferromagnetic tunnel junction element is a magnetoresistance effect element wherein an electric resistance varies in accordance with a magnetic field applied. The ferromagnetic tunnel junction element includes a pinned layer wherein at least a part of a magnetization direction is held, and an insulation layer formed on the pinned layer, creating an energy barrier that electrons can flow through by a tunnel effect. A first free layer made of a first ferromagnetic material containing boron atoms, is formed on the insulation layer. In the first free layer, a direction of the magnetization switches under an influence of an external magnetic field. A second free layer made of a first ferromagnetic material containing boron atoms, is formed on the first free layer. The direction of magnetization of the second free layer switches under the influence of the external magnetic field, exchanging and coupling with the first free layer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Isotopically-enriched boron-containing compounds, and methods of making and using same
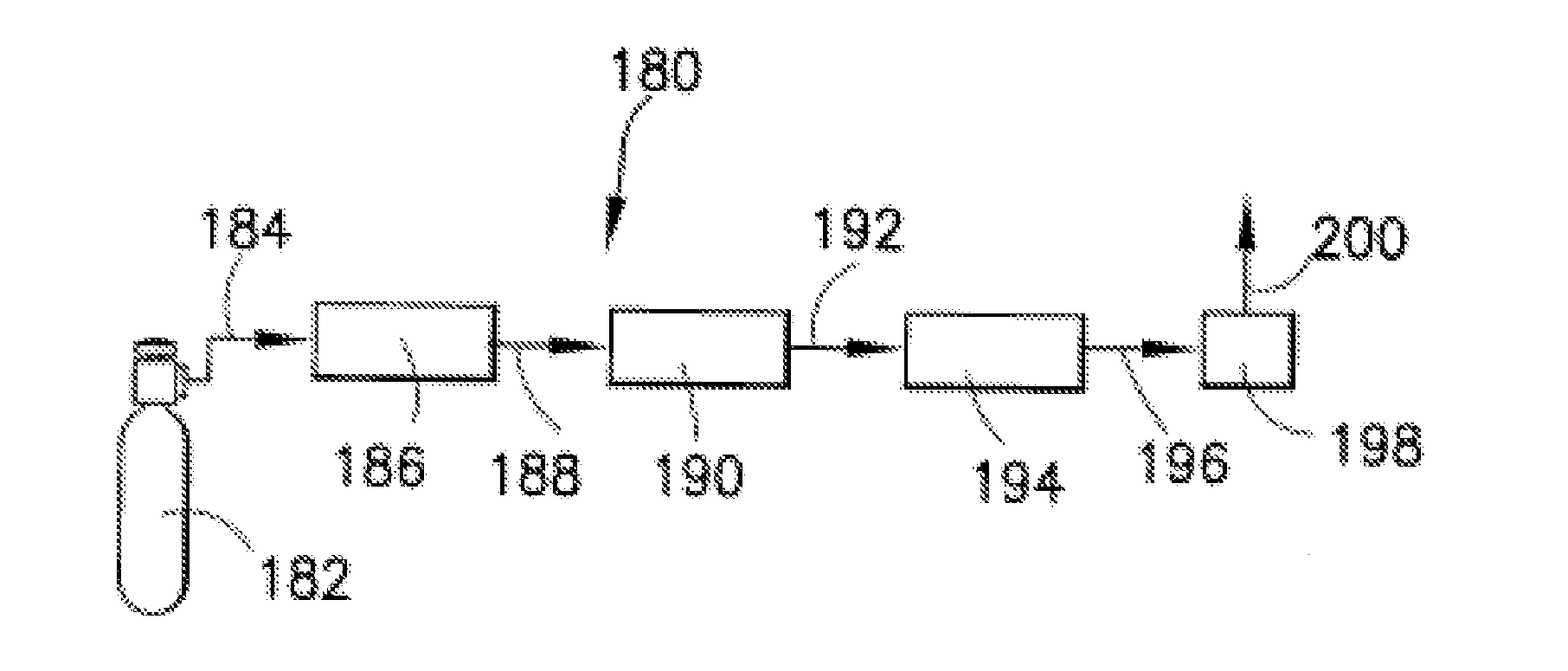
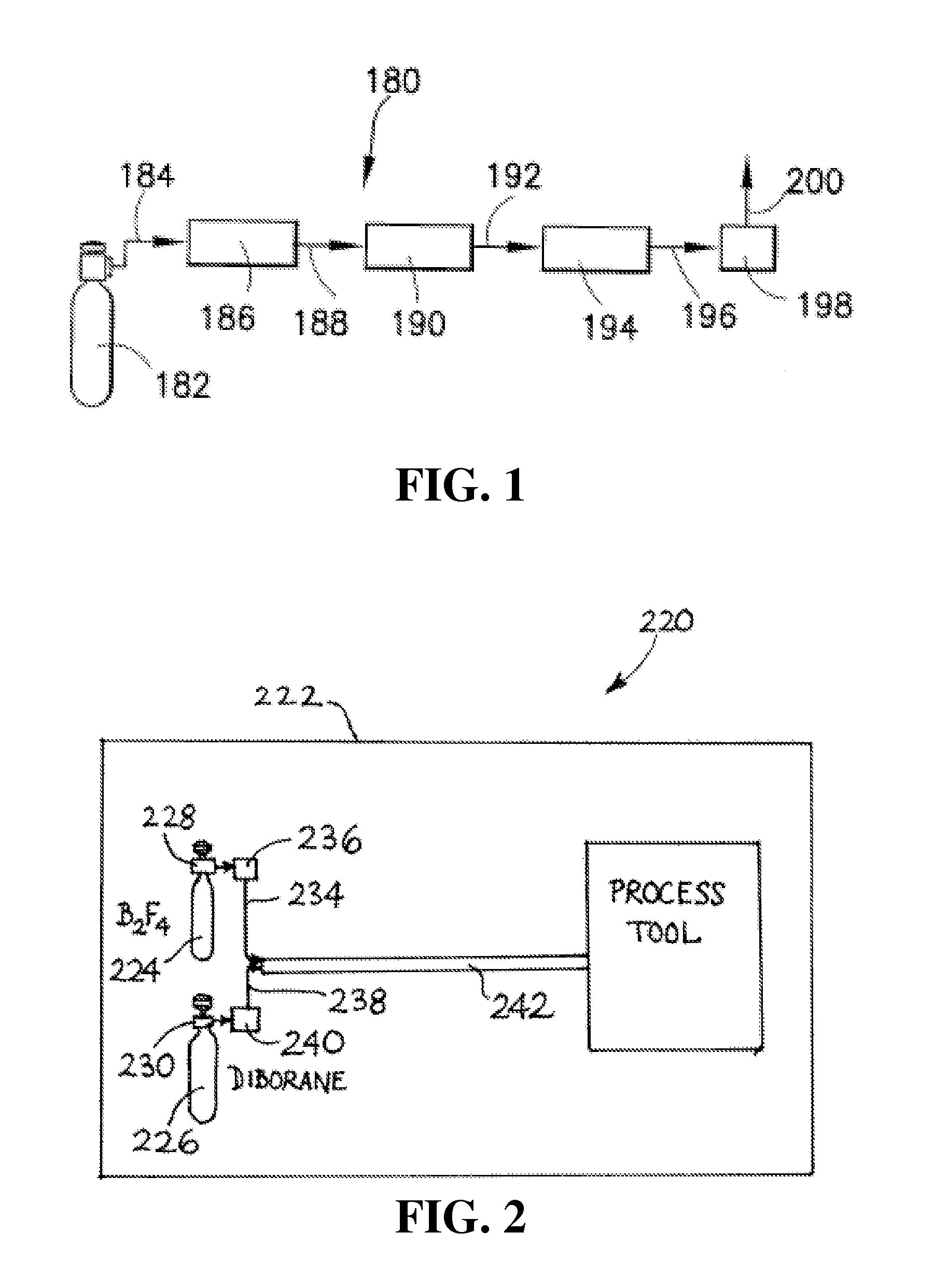
ActiveUS20110159671A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSynthesis methodsChemical compound
An isotopically-enriched, boron-containing compound comprising two or more boron atoms and at least one fluorine atom, wherein at least one of the boron atoms contains a desired isotope of boron in a concentration or ratio greater than a natural abundance concentration or ratio thereof. The compound may have a chemical formula of B2F4. Synthesis methods for such compounds, and ion implantation methods using such compounds, are described, as well as storage and dispensing vessels in which the isotopically-enriched, boron-containing compound is advantageously contained for subsequent dispensing use.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Method for fabricating metal-oxide semiconductor transistors
ActiveUS7473606B2Facilitated DiffusionEliminate needTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMolecular clusterBoron atom
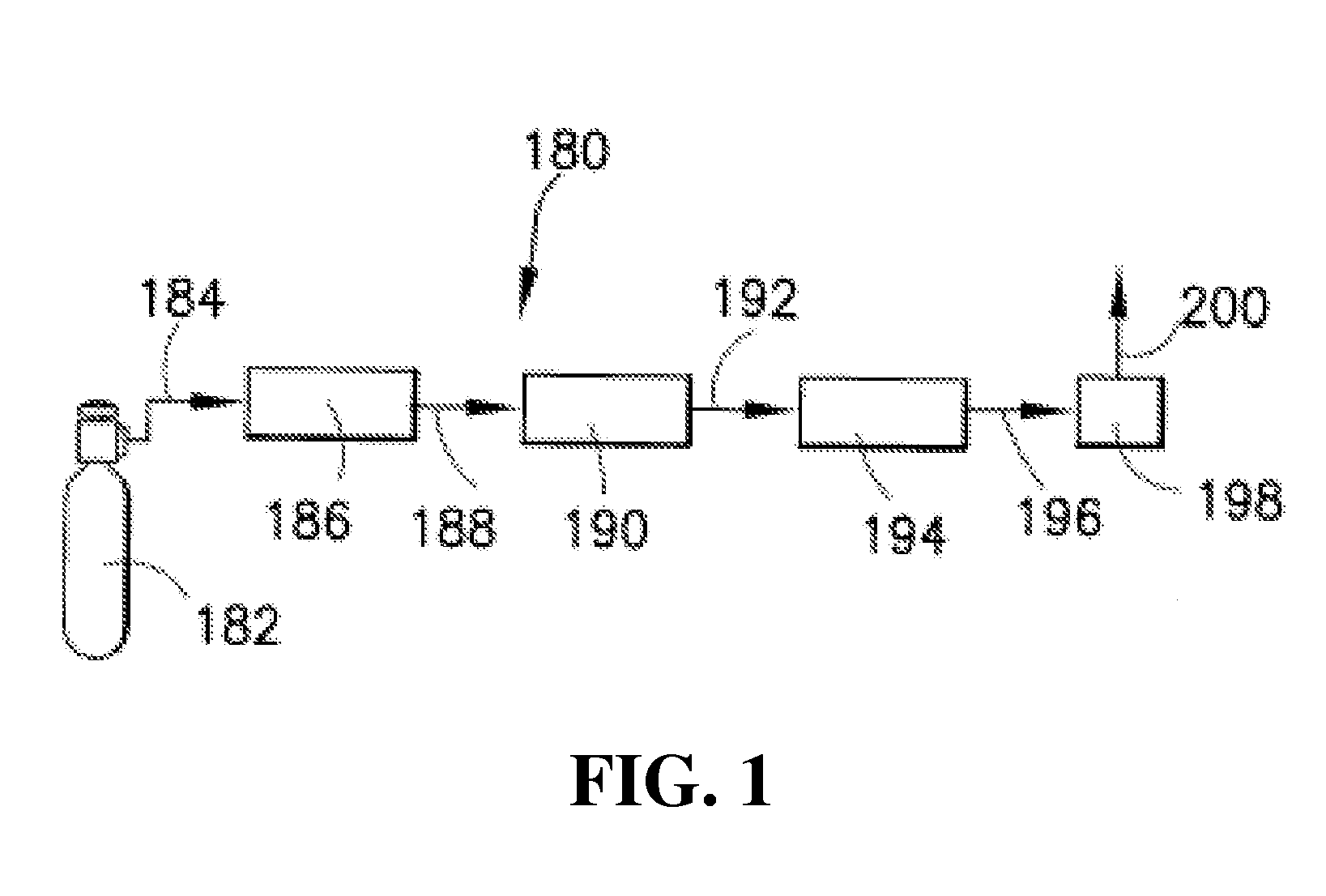
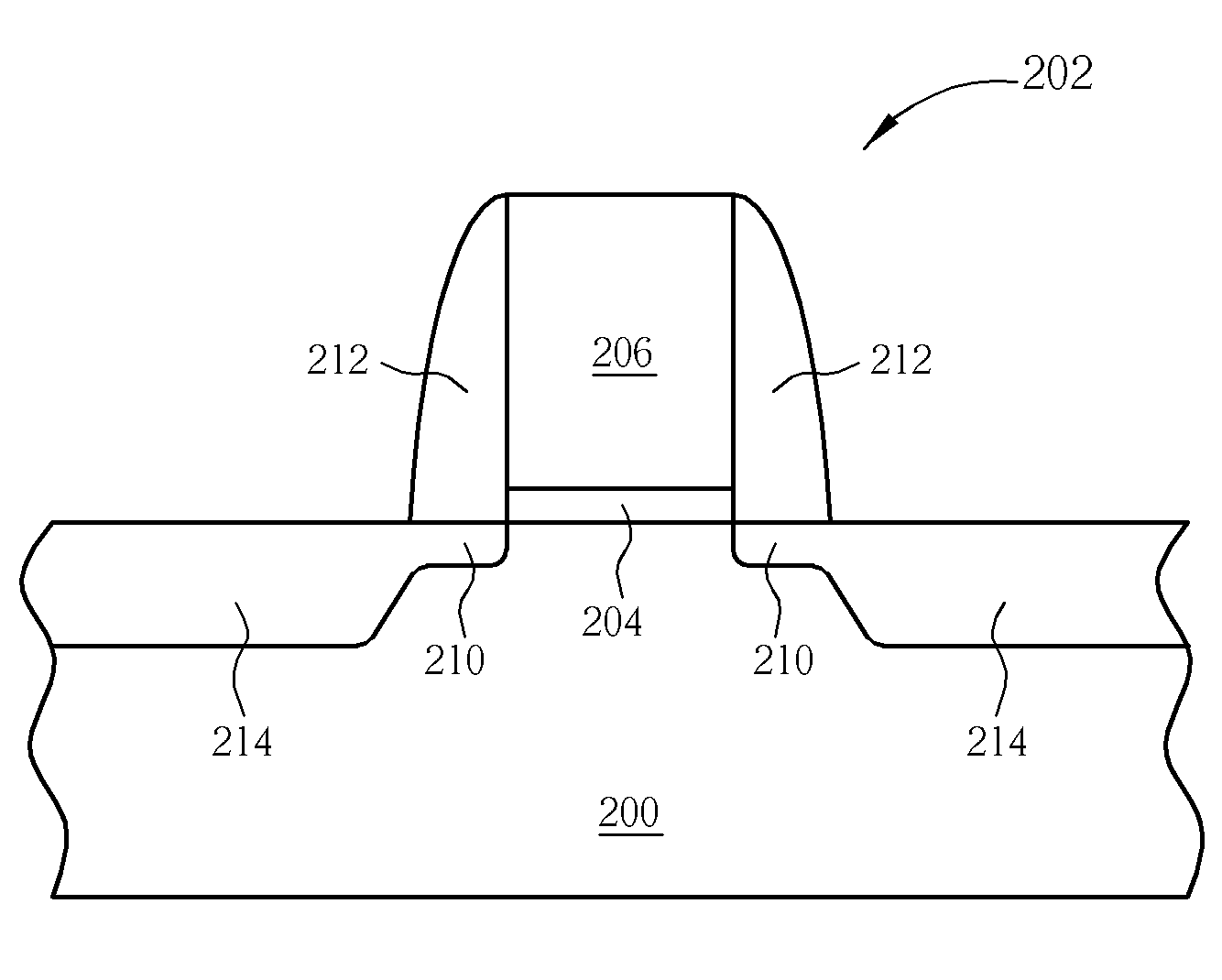
A method for fabricating a metal-oxide semiconductor transistor is disclosed. First, a semiconductor substrate having a gate structure thereon is provided, and a spacer is formed around the gate structure. An ion implantation process is performed to implant a molecular cluster containing boron into the semiconductor substrate surrounding the spacer for forming a source / drain region. The weight ratio of each boron atom within the molecular cluster is preferably less than 10%. Thereafter, a millisecond annealing process is performed to activate the molecular cluster within the source / drain region.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Organic light-emitting device taking exciplex as main body material
ActiveCN110492005AImprove stabilityReduce concentrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSimple Organic CompoundsLight excitation
The invention relates to an organic light-emitting device taking an exciplex as a main body material, in particular to an organic light-emitting device containing the main body material and a fluorescent material, wherein the main body material comprises a first organic compound and a second organic compound, a mixture or an interface formed by the first organic compound and the second organic compound generates the exciplex under the condition of optical excitation or electric field excitation, and the emission spectrum of the formed exciplex and the absorption spectrum of the fluorescent doped material are effectively overlapped to form the effective energy transfer; the first organic compound and the second organic compound have the different carrier transport characteristics, wherein the fluorescent material is an organic compound containing the boron atoms. The organic light-emitting device prepared by the method has the characteristics of high efficiency and long service life.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
Large-grain p-doped polysilicon films for use in thin film transistors
ActiveUS20060051911A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHydrogenIn situ doping
A method is disclosed to form a large-grain, lightly p-doped polysilicon film suitable for use as a channel region in thin film transistors. The film is preferably deposited lightly in situ doped with boron atoms by an LPCVD method at temperatures sufficiently low that the film is amorphous as deposited. After deposition, such a film contains an advantageous balance of boron, which promotes crystallization, and hydrogen, which retards crystallization. The film is then preferably crystallized by a low-temperature anneal at, for example, about 560 degrees for about twelve hours. Alternatively, crystallization may occur during an oxidation step performed, for example at about 825 degrees for about sixty seconds. The oxidation step forms a gate oxide for a thin film transistor device, for example a tunneling oxide for a SONOS memory thin film transistor device.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Isotopically-enriched boron-containing compounds, and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS20120108044A1Improving beam currentIncrease currentElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingSynthesis methodsChemical compound
An isotopically-enriched, boron-containing compound comprising two or more boron atoms and at least one fluorine atom, wherein at least one of the boron atoms contains a desired isotope of boron in a concentration or ratio greater than a natural abundance concentration or ratio thereof. The compound may have a chemical formula of B2F4. Synthesis methods for such compounds, and ion implantation methods using such compounds, are described, as well as storage and dispensing vessels in which the isotopically-enriched, boron-containing compound is advantageously contained for subsequent dispensing use.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Catalyst for oxidative dehydrogenation of light alkane to prepare olefin, optimization method and application thereof
ActiveCN106694017AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbonsAlkaneHexagonal boron nitride
Belonging to the technical field of industrial catalysis, the invention discloses a catalyst for oxidative dehydrogenation of light alkane to prepare olefin, an optimization method and application thereof. The catalyst for oxidative dehydrogenation of light alkane to prepare olefin is a solid non-metal catalyst, is composed of nitrogen atoms and boron atoms, is sp<2> or sp<3> hybridized hexagonal boron nitride, cubic boron nitride and rhombohedral, and presents a boron nitride crystal structure. By means of surface functionalization (preferably hydroxylation), the catalyst surface structure can be optimized. The catalyst can be used for oxidative dehydrogenation reaction of single component and multicomponent light alkane to prepare olefin, the alkane conversion rate and olefin selectivity are high, and the content of generated CO2 is smaller than 5%. Compared with the prior art, the catalyst provided by the invention has no need of loading other metal / metal oxide and other active components, the process is simple, and can significantly improve olefin yield, and the catalyst has good long-term stability, and very low CO2 emission, thus having good industrial development and application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for boron doping of crystalline silicon solar battery
InactiveCN102437238ALow costFast coating speedFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSilicon oxideOptoelectronics
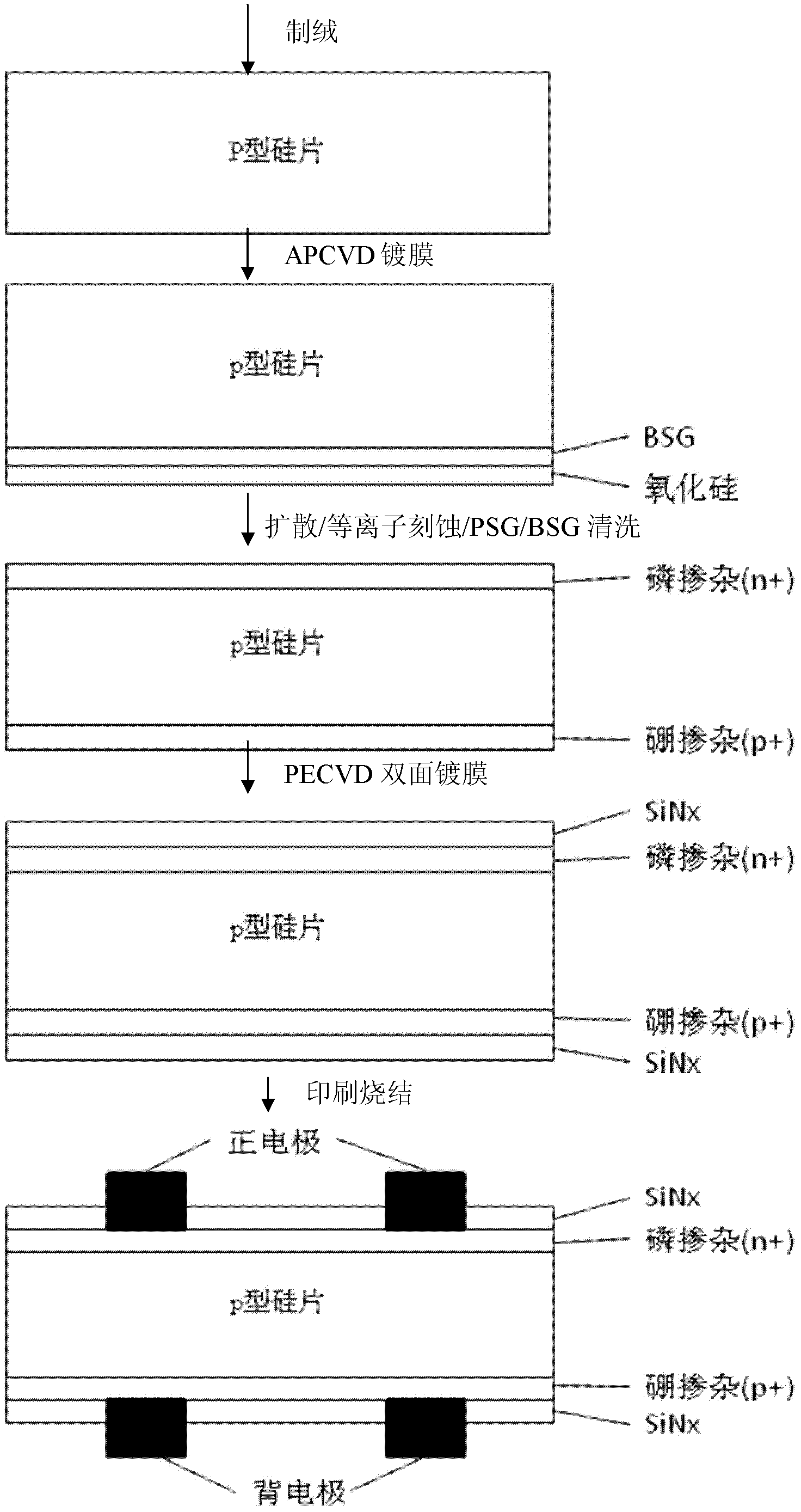
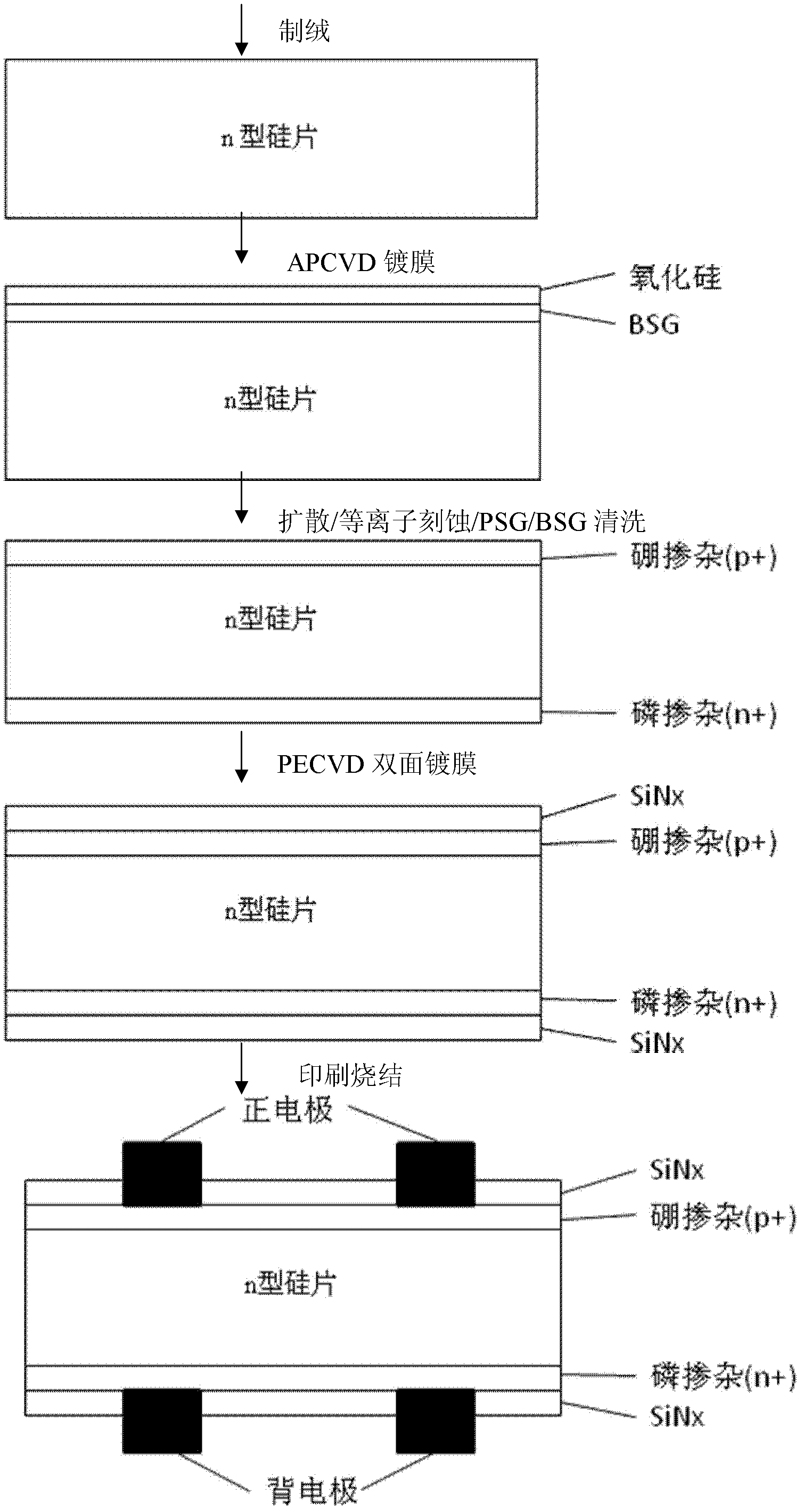
The invention discloses a method for boron doping of a crystalline silicon solar battery, which comprises the following steps that: a first layer of film-boron doped silicon oxide film is deposited on the surface of a silicon chip after the wool making, a second layer of film-silicon oxide film is deposited on the first layer of the film to be used as a barrier layer, then the silicon chip is processed at high temperature, so boron atoms can be diffused into a silicon basic body to form a boron doped layer. Due to the adoption of the method, a boron transmission electrode (p+) can be prepared on an n-type silicon chip, or a boron back surface (p+) is formed on a p-type silicon chip. Through the barrier layer, single-faced boron doping can be realized, and a boron source is free from being sucked into a diffusion furnace tube, so the corrosion of the furnace tube can be reduced, and the service life can be prolonged; and if a phosphorus source is introduced during the high-temperature annealing process, the boron doping and phosphorus doping can be respectively realized on two sides of the silicon chip.
Owner:JA SOLAR TECH YANGZHOU +1
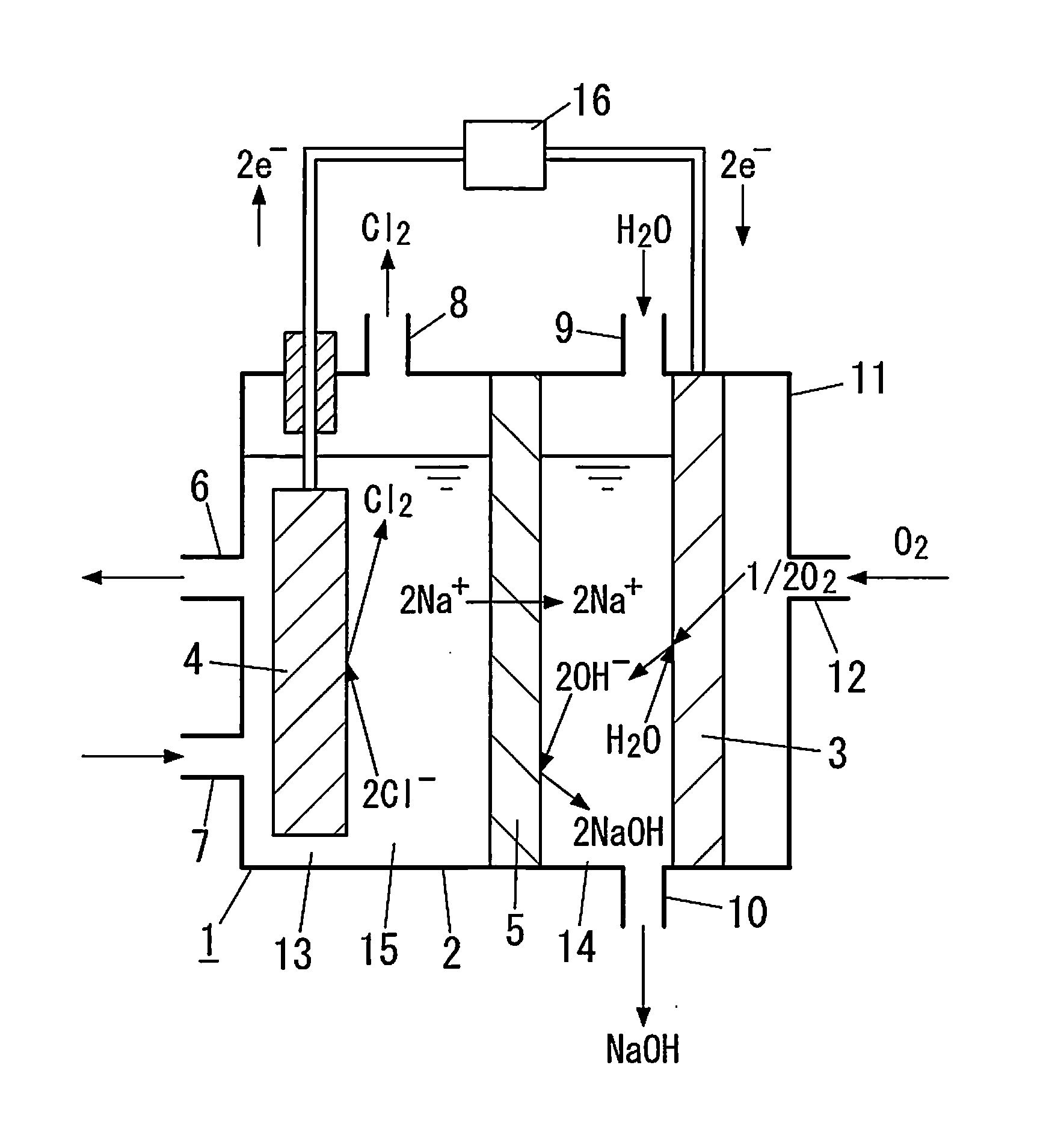
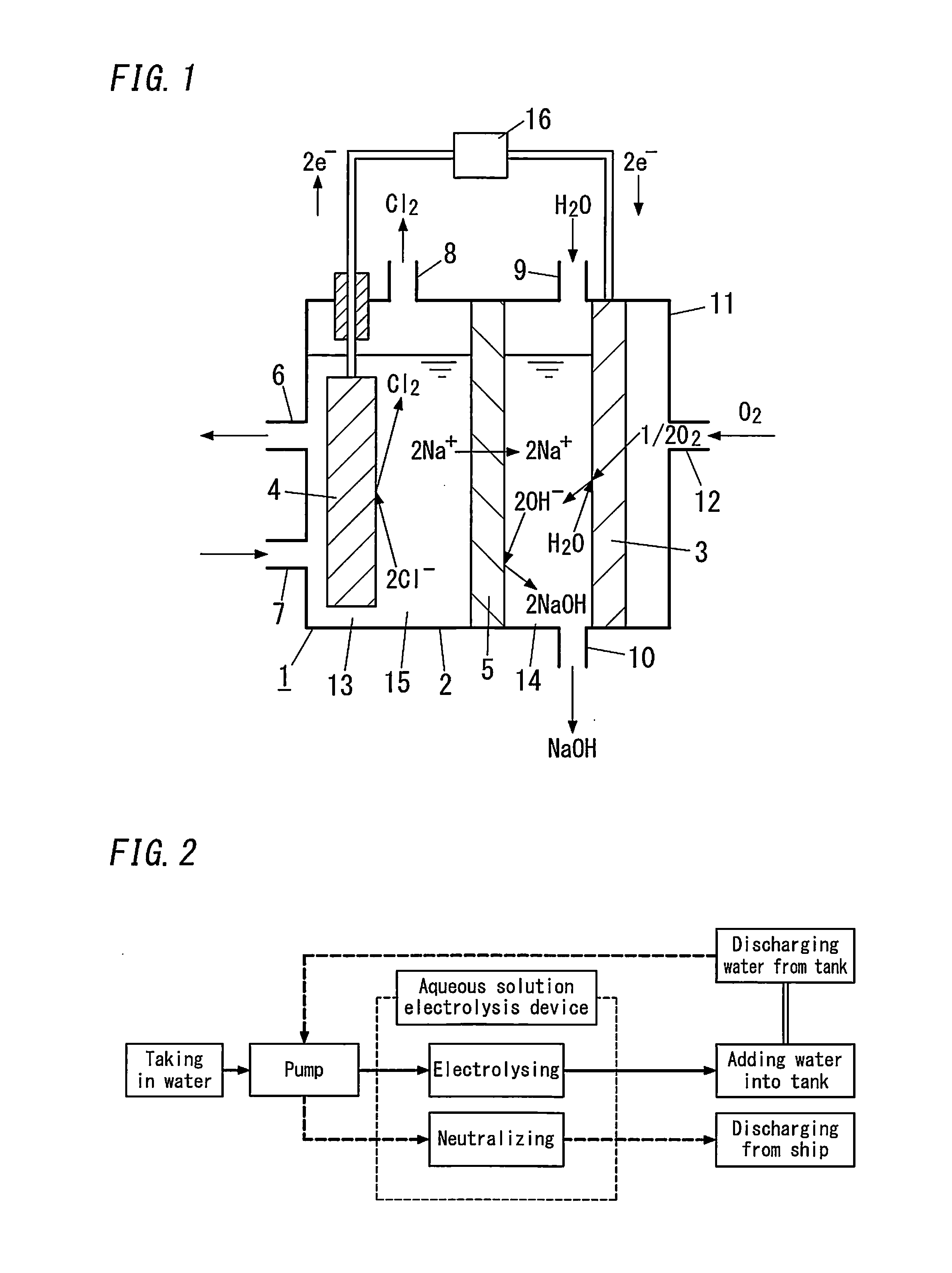
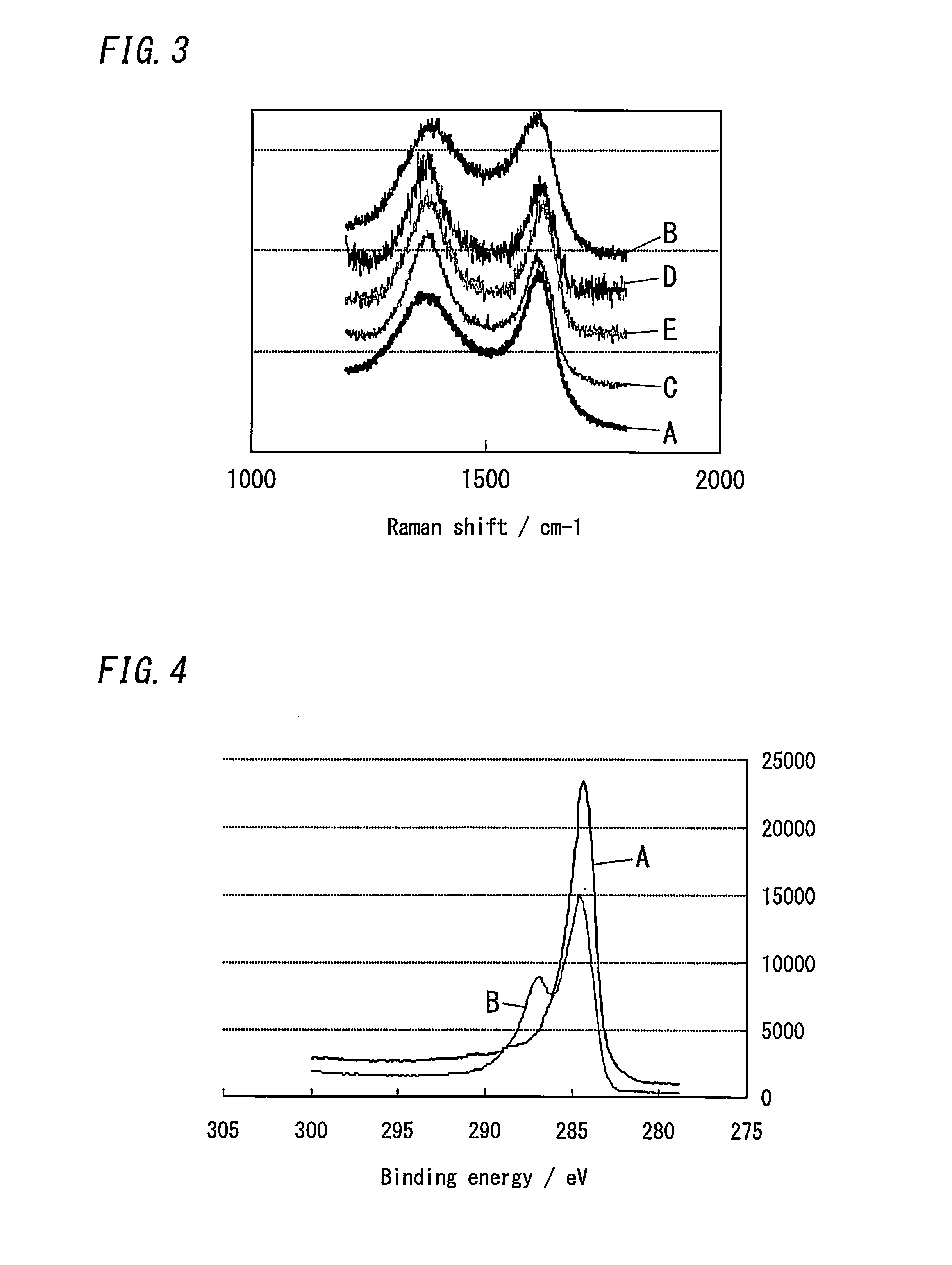
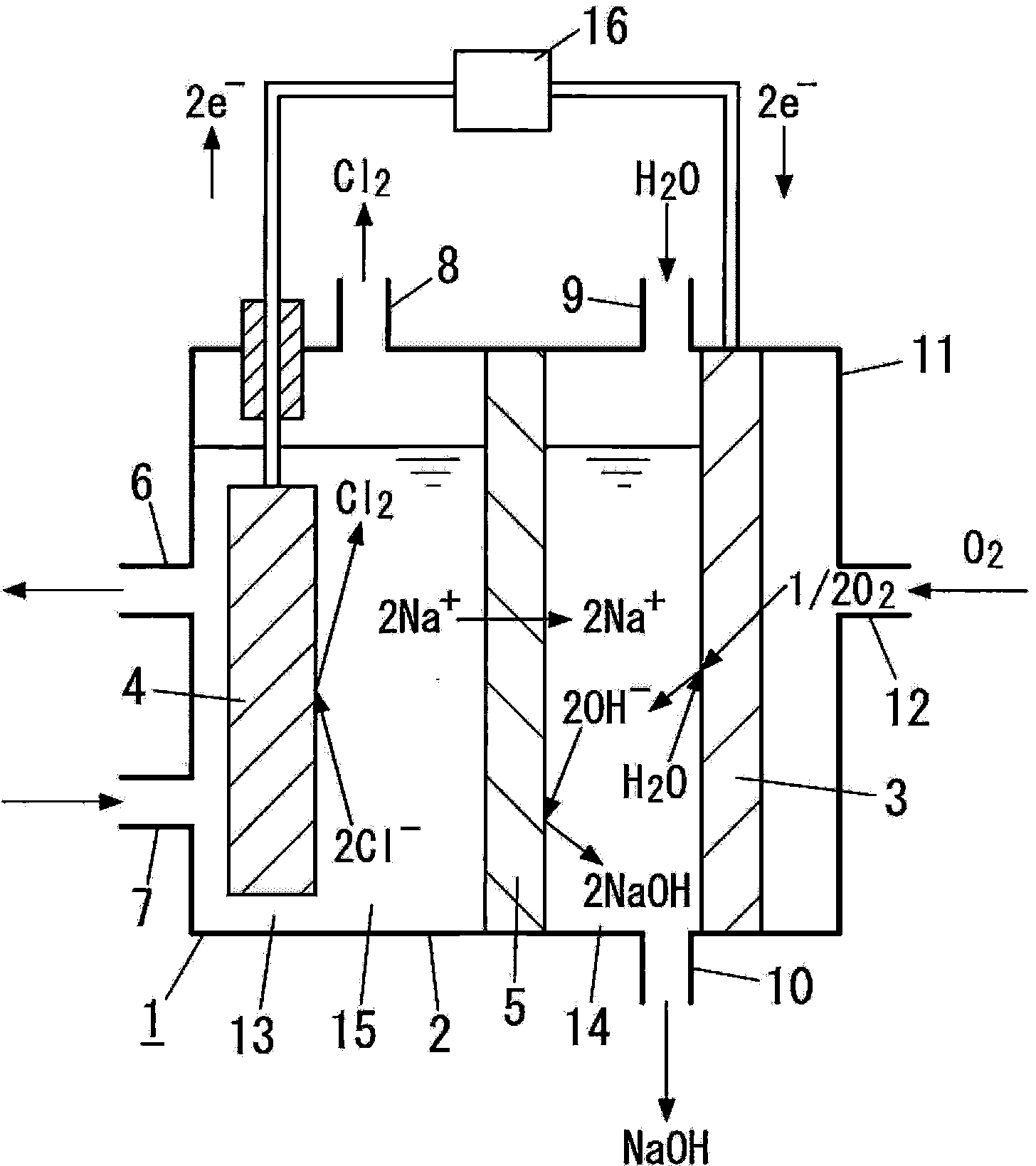
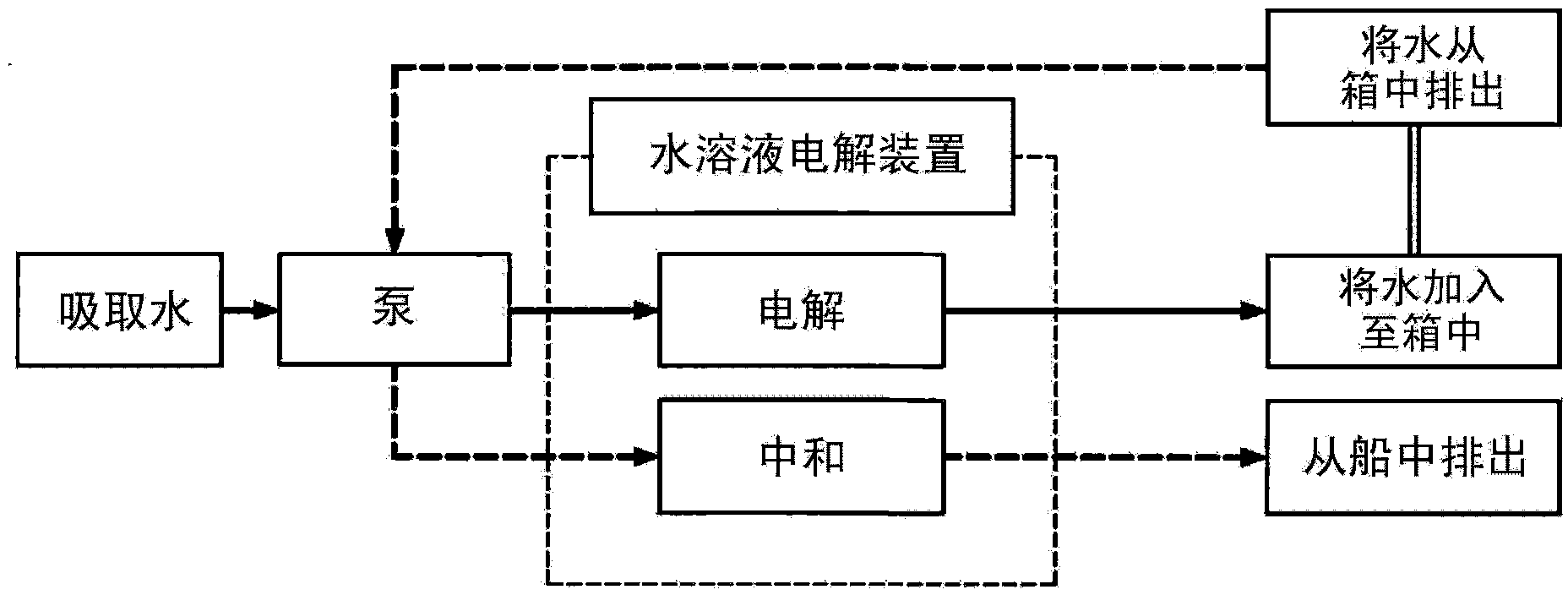
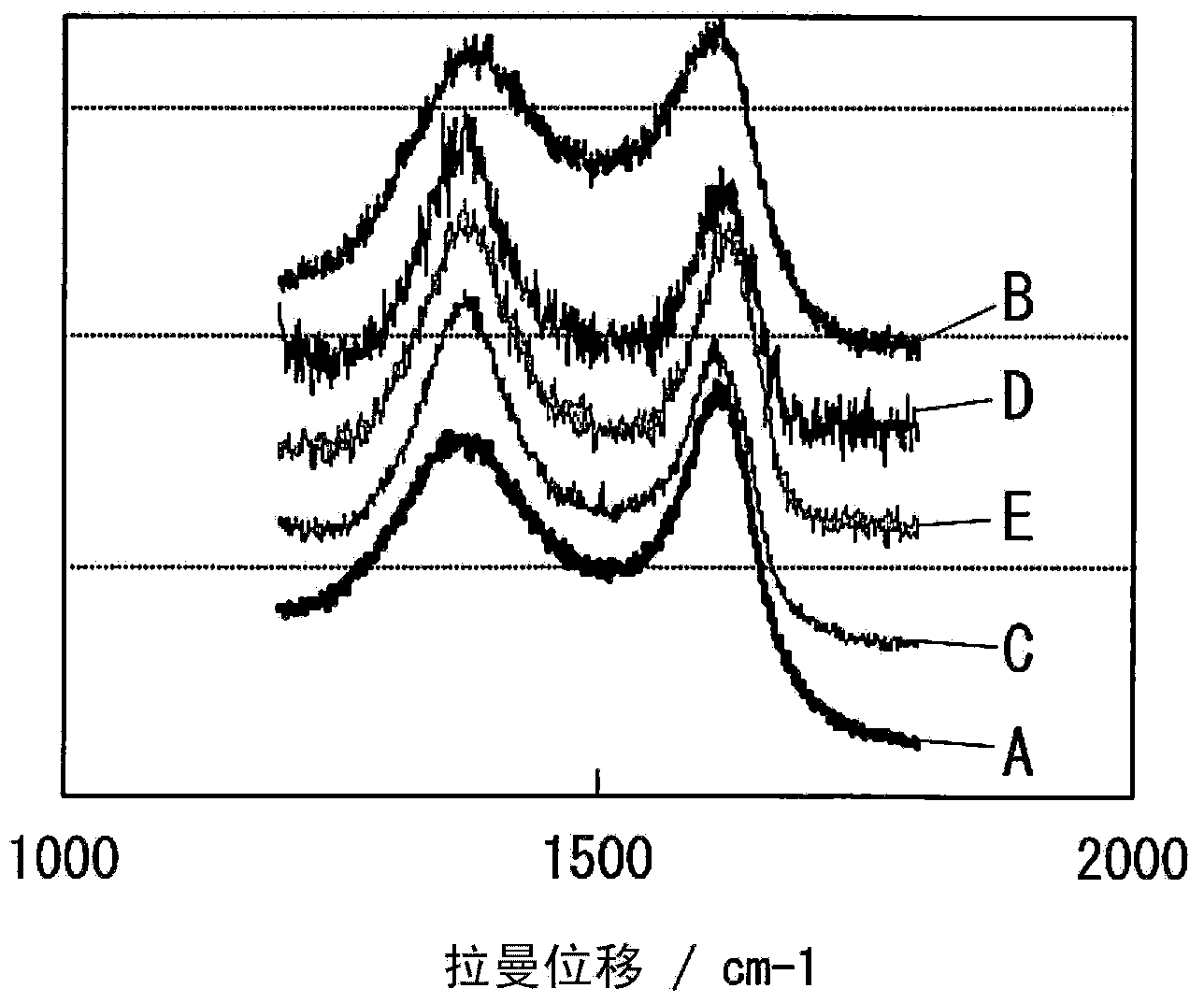
Carbon-based material, electrode catalyst, oxygen reduction electrode catalyst, gas diffusion electrode, aqueous solution electrolysis device, and method of preparing carbon-based material
InactiveUS20140353144A1Improve performanceReduced responseMaterial nanotechnologyCellsElectrolysisX-ray
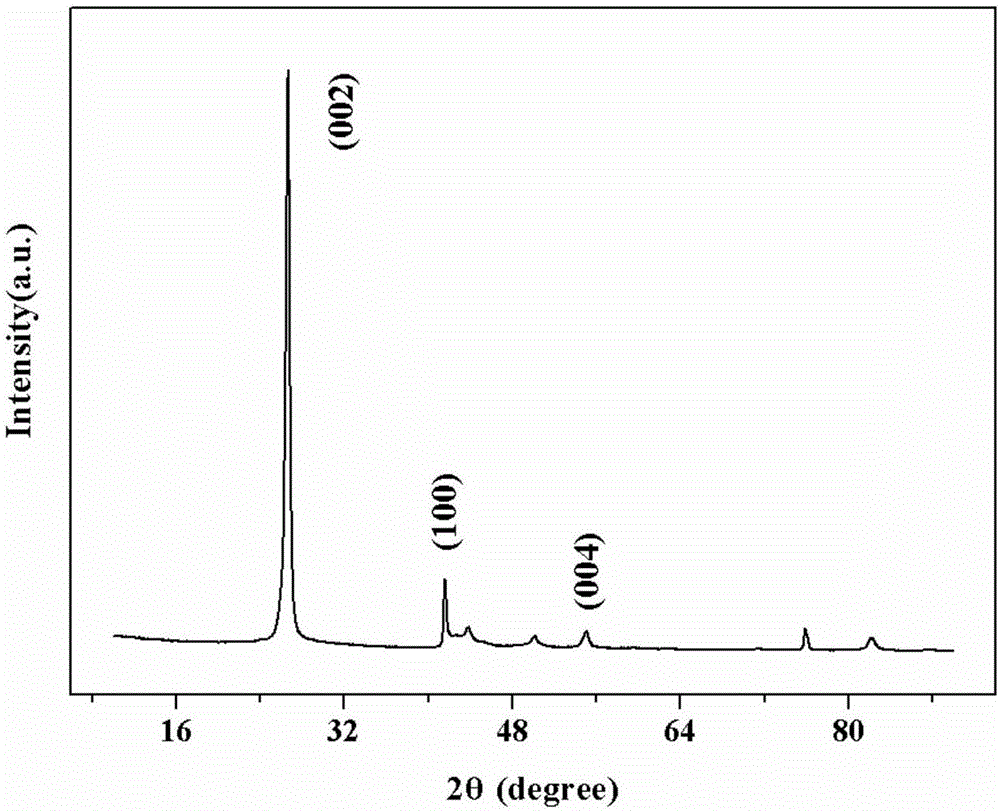
A carbon-based material in accordance with the present invention includes graphene doped with metal atoms and at least one type of non-metal atoms selected from a group consisting of nitrogen atoms, boron atoms, sulfur atoms, and phosphorus atoms. A diffraction pattern obtained by X-ray diffraction measurement of the carbon-based material by use of CuKα radiation showing that a proportion of the highest of intensities of peaks derived from an inactive metal compound and a metal crystal to an intensity of a (002) peak is 0.1 or less.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
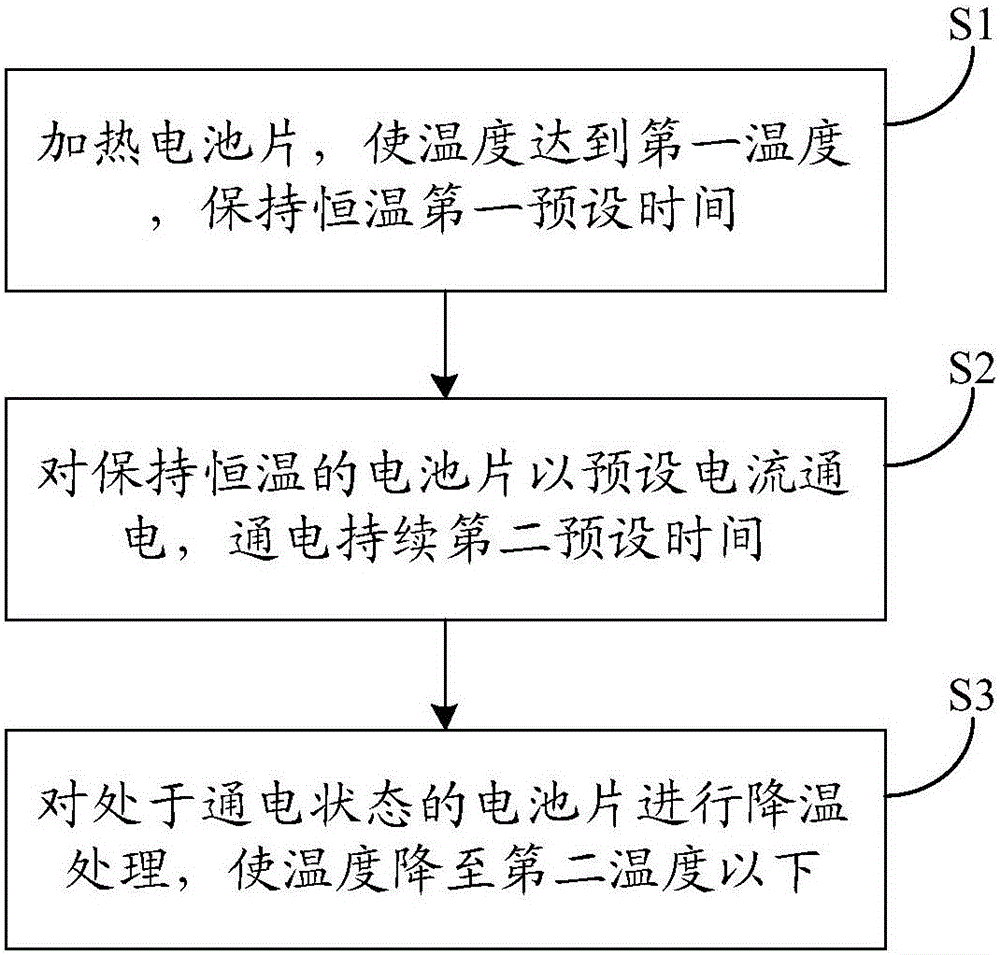
Method for improving light degradation of boron-doped crystalline silicon solar cell
InactiveCN105789382AImprove light-induced attenuationMethods of Improving Light-Induced AttenuationFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHydrogen atomOxygen
The invention discloses a method for improving light degradation of a boron-doped crystalline silicon solar cell. The method comprises the following steps: heating a solar cell to enable the temperature to reach a first temperature and keeping constant temperature for a first preset time; electrifying the solar cell at constant temperature with preset current; electrifying for a second preset time; cooling the solar cell under electrifying state and reducing the temperature to be below the second temperature; after heating and performing constant temperature treatment on the solar cell, electrifying, combining boron atom and oxygen atom in the solar cell into a B-O pair, and combining with hydrogen atom in the surface film and forming into an H-B-O pair; generating the H-B-O pair to enable the B-O pair to deactivate. After the treatment according to the method provided by the invention, the B-O pair complex in the solar cell is reduced, so that the light degradation amplitude is reduced and the light degradation phenomenon of the boron-doped crystalline silicon solar cell can be effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINKO SOLAR CO LTD +1
Isotopically-enriched boron-containing compounds, and methods of making and using same
An isotopically-enriched, boron-containing compound comprising two or more boron atoms and at least one fluorine atom, wherein at least one of the boron atoms contains a desired isotope of boron in a concentration or ratio greater than a natural abundance concentration or ratio thereof. The compound may have a chemical formula of B2F4. Synthesis methods for such compounds, and ion implantation methods using such compounds, are described, as well as storage and dispensing vessels in which the isotopically-enriched, boron-containing compound is advantageously contained for subsequent dispensing use.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
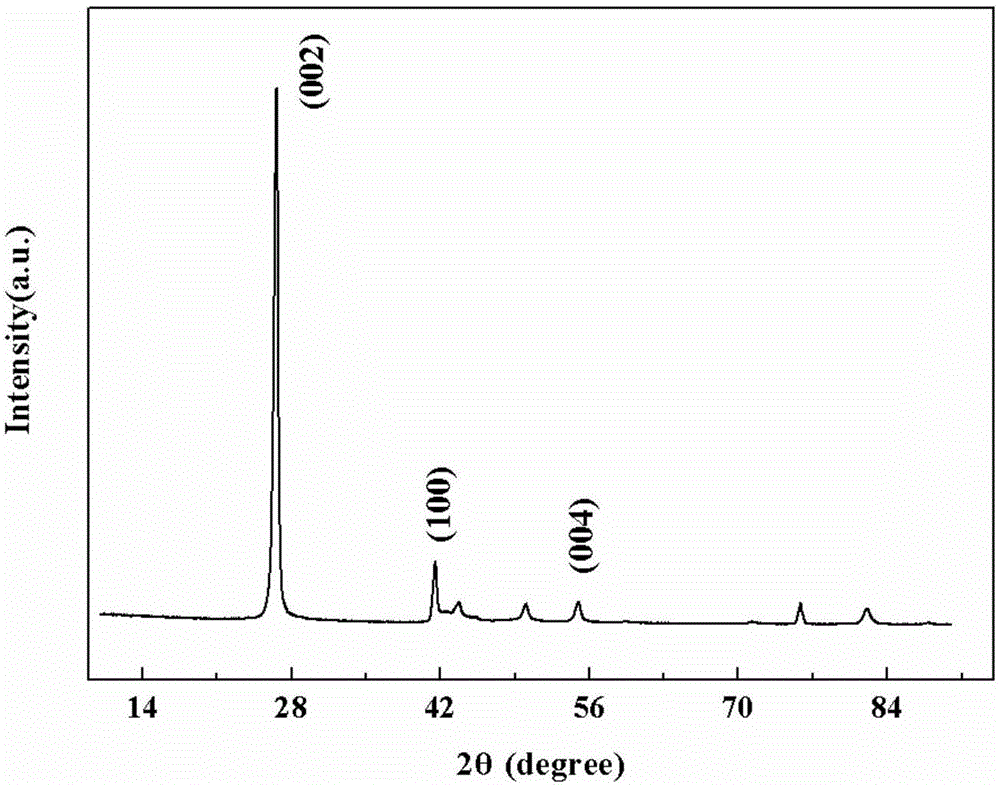
Preparation method of hexagonal phase boron nitride film
ActiveCN103031516AEasy to implementGood insulation propertiesVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGas phaseRoom temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of a hexagonal phase boron nitride film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by a physical vapor deposition method, providing boron atoms by a solid boron source, and forming the hexagonal phase boron nitride film on a substrate, wherein the deposition speed of physical vapor deposition is 0.01 nm / min-20 nm / min, and in the film forming process, the substrate temperature is controlled at 20-1600 DEG C; and the temperature is reduced to room temperature at a speed of 10-400 DEG C / min. when the hexagonal phase boron nitride film is prepared by the preparation method, the solid boron source is used, so that the safety is high, and the preparation method is simple, and easy to implement; the prepared hexagonal phase boron nitride film consists of 1-200 hexagonal phase boron nitride unit layers; and the two-dimensional hexagonal phase boron nitride film prepared by the preparation method has excellent insulating property and flatness and can be used for improving performance of a graphene optoelectronic device.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
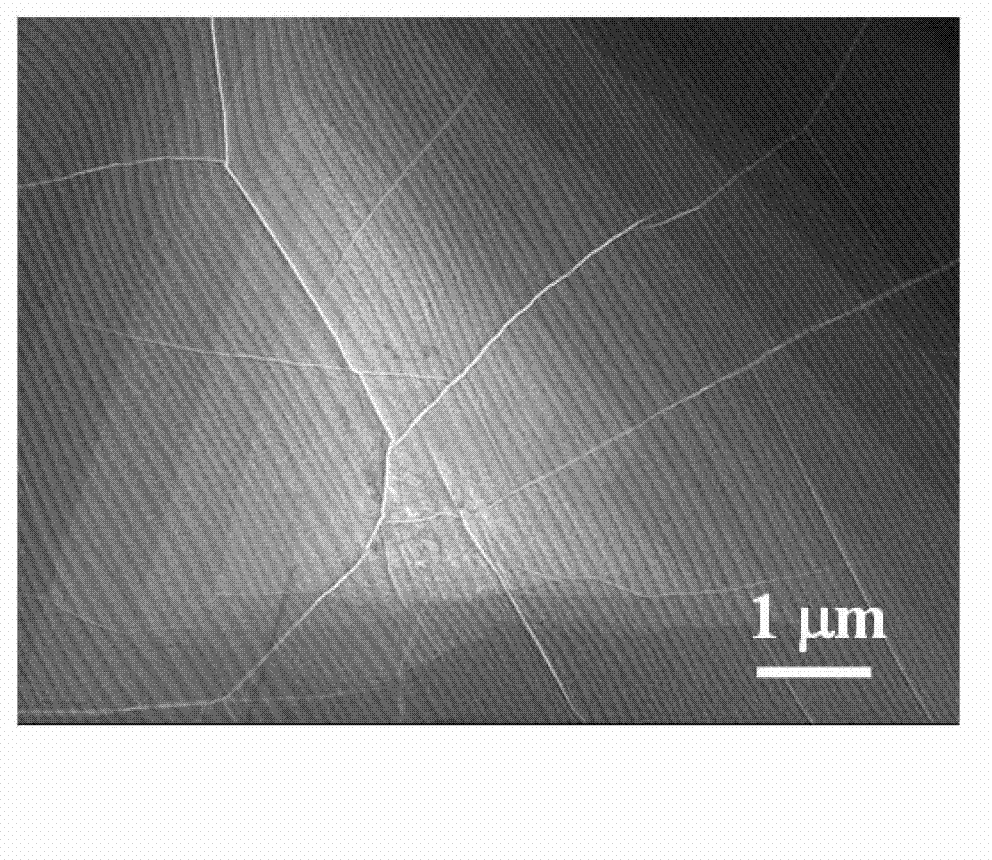
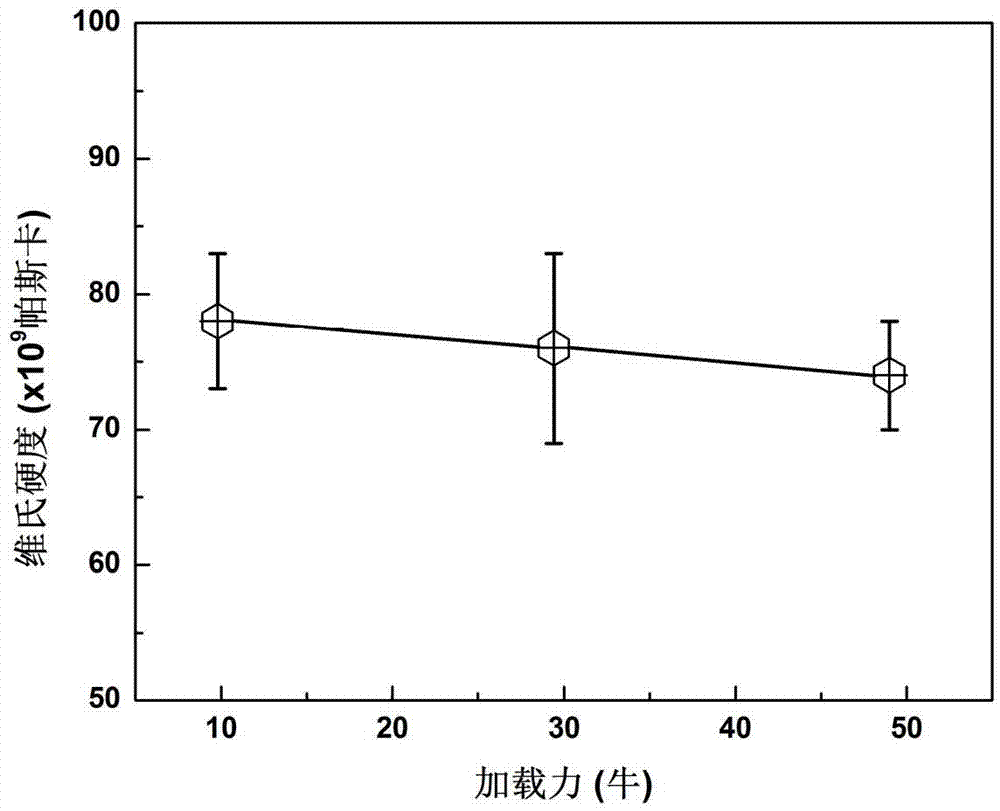
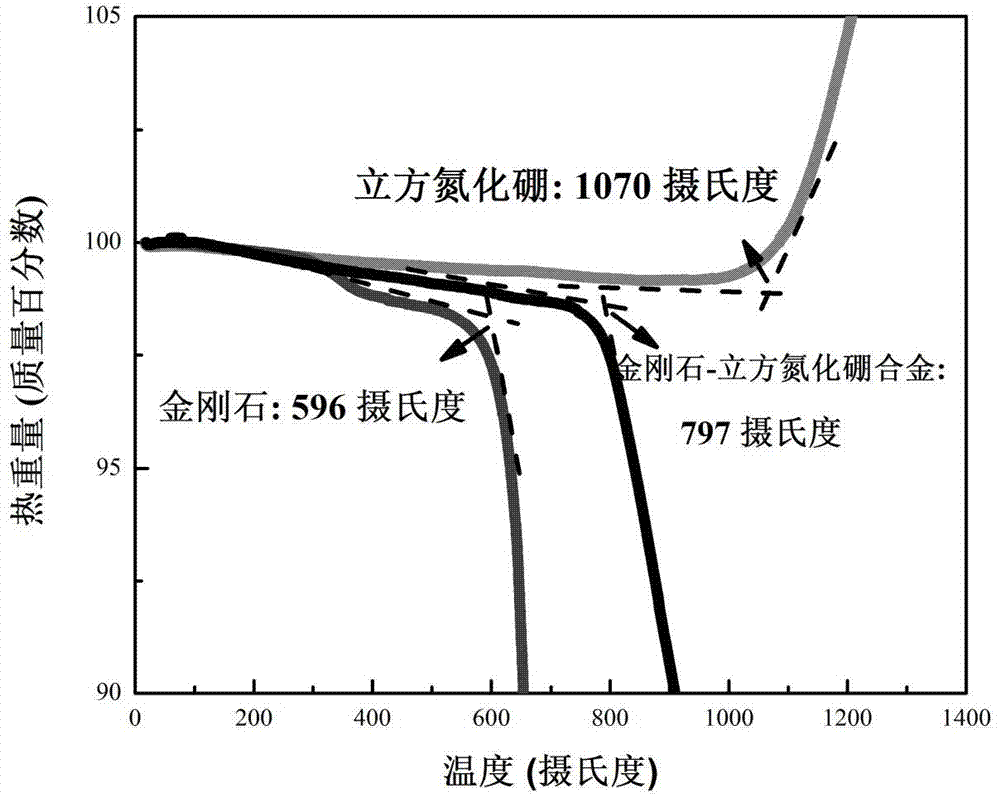
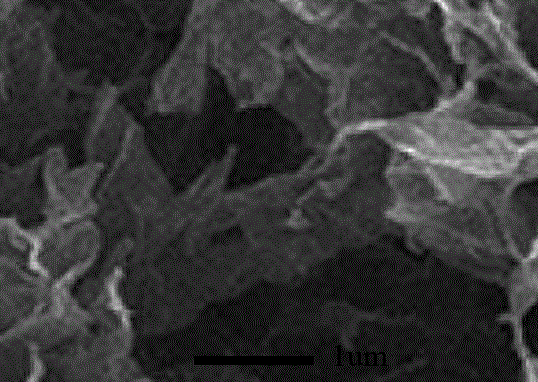
Diamond-cubic boron nitride type universal superhard cutter material, cutter and preparation method of material
InactiveCN104759240AHigh hardnessImprove thermal stabilityUltra-high pressure processesSuperhard materialAlloy
The invention discloses a diamond-cubic boron nitride type universal superhard cutter material, a cutter and a preparation method of the material. The material is characterized in that diamond and cubic boron nitride are used as raw materials, the pre-treatment and the forming are performed on the raw materials to obtain a blank; the blank assembled with a sintering unit is arranged in a high temperature and high pressure device, wherein the intensity of pressure is 7-25GPa, the temperature is 1000-2700 DEG C, the sintering solution strengthening lasts for 10s-30min, the sizes of obtained crystal grains are uniform, and interfaces of the crystal grains are tight and closed; the compact-structure diamond-cubic boron nitride type universal superhard cutter material which is high in atomic density, is in a three-dimensional network shape and has strong covalent bonds can be formed by boron atoms, carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms at the crystal interfaces between the diamond and the cubic boron nitride. The universal superhard material is processed into a cylinder with the same height; two ends of the cylinder are polished and finished and then are processed to be in triangular cylinder shapes with the side lengths and the thicknesses of 2-3mm, the processed cylinder and a steel alloy base body are welded under the vacuum degree being 1*10<-3>Pa at the temperature being 800 DEG C, and then the laser processing is performed, so that the superhard alloy cutter in which the radius of the circular arc of the knife point is 0.4-0.8mm is obtained.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method for boron-nitrogen-co-doped three-dimensional structured positive electrode material of lithium-sulfur battery
InactiveCN105609733AImprove conductivityImprove cycle lifeCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsDoped grapheneBoron atom
The invention provides a preparation method for a boron-nitrogen-co-doped three-dimensional structured positive electrode material of a lithium-sulfur battery. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1), adding graphite oxide into water for performing ultrasonic processing to form a graphene oxide suspension liquid; (2), adding ammonium hydroxide to the graphene oxide suspension liquid, and then adding sodium borohydride to the graphene oxide suspension liquid to obtain three-dimensional boron-nitrogen-co-doped graphene; (3), adding the three-dimensional boron-nitrogen-co-doped graphene obtained in the step (2) and ketjen black into N-methyl pyrrolidone for performing an ultrasonic reaction to form a suspension liquid; (4), adding sulfur to the N-methyl pyrrolidone for performing an ultrasonic reaction until the elemental sulfur is fully dissolved to form a suspension liquid; and (5), mixing the two kinds of suspension liquid obtained in the step (4) and the step (3), and then adding distilled water to obtain the three-dimensional structured positive electrode material of the lithium-sulfur battery. Due to sulfur adsorption by the synergistic effects of boron atoms and nitrogen atoms in the boron-nitrogen-co-doped graphene, the shuttle effect is lowered, so that the cycling life of the lithium-sulfur battery is prolonged.
Owner:钟玲珑
Carbon-based material, electrode catalyst, oxygen reduction electrode catalyst, gas diffusion electrode, aqueous solution electrolytic device, and production method for carbon-based material
ActiveCN103974900AImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologyActive material electrodesRocking curveElectrolysis
Provided is a carbon-based material having high catalytic activity. This carbon-based material comprises a graphene doped with a metal atom and at least one type of non-metallic atom selected from a nitrogen atom, a boron atom, a sulfur atom, and a phosphorous atom. The ratio, for the carbon-based material, between the maximum peak intensity derived from an inactive metal compound and a metal crystal, and the (002) surface peak intensity in a rocking curve obtained by x-ray diffraction measurement using a CuKalpha ray is no more than 0.1.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Semi-conductor type single-walled carbon nano tube and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a semiconductor-typed single-walled carbon nano tube and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the carbon nano tube technical field. The carbon atoms on the tube wall of the single-walled carbon nano tube are replaced by doping atoms which comprise nitrogen atoms, boron atoms, oxygen atoms or sulfur atoms. The preparation method thereof comprises: at the reaction temperature, in an inert environment and under the catalysis of a catalyst which is positioned on substrate, the reaction gas is deposited on the substrate by chemical vapor deposition, so as to obtain the carbon nano tube; the reaction gas comprises carbon source and doped source which come from the same substance or different substances; after the chemical vapor deposition, a semiconductor-typed single-walled carbon nano tube is prepared. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of simple equipment, easy operation, low raw material cost and strong product repeatability, and can obtain single-walled carbon nano tubes which are all semiconductor-typed.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101956178AImprove electrochemical performanceImprove conductivityChemical vapor deposition coatingBoron atomElectrochemistry
The invention provides a boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond film. The boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond film is prepared by using the following steps of: preparing a boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond film on a monocrystalline silicon substrate by adopting a CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) method and annealing the film in vacuum at 800-1200 DEG C for 30-60 min to obtain the boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond film. By using the vacuum annealing method, the invention ensure that boron atoms aggregated on a grain boundary of the nanocrystalline diamond film are dispersed into nanocrystalline diamond grains and the amount of trans-polyacetylene on the grain boundary is greatly reduced, thereby effectively improving the p-type conductive performance and the electrochemical performance of the boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond film. The invention has very important scientific meaning and engineering values to the application of the boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond film in nano-electronic devices and the electrochemical field, such as water treatment, heavy metal detection, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Amido-organoborate initiator systems
InactiveUS20070079931A1Facilitate their formulationImprove relationshipSilicon organic compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsCounterionNitrogen
In one embodiment, the invention is a system for initiating free radical polymerization comprising: a) in one part, one or more amido-borate compounds containing one or more anionic amido-borate moieties comprising an organoborate wherein the boron atom is bonded to a nitrogen atom of ammonia or an organic compound containing one or more nitrogen atoms, such as a hydrocarbyl amine, a hydrocarbyl polyamine, or an aromatic heterocycle containing one or more nitrogen atoms and optionally containing one or more heteroatoms or heteroatom containing functional moieties, and one or more cationic counter ions and b) in a second part, a liberating compound which reacts with the nitrogen atom(s) bound to the boron atom(s) upon contact with the amido-borate to form an organoborane radical. In another embodiment, the invention is a two part polymerizable composition comprising in one part, one or more amido-borate compounds and in the second part, a liberating compound which reacts with the nitrogen atoms bound to the boron atom upon contact with the amido-borate to form an organoborane radical and one or more compounds capable of free radical polymerization. The first part may further comprise one or more compounds capable of free radical polymerization. This facilitates formulating compositions that have commercially desirable volumetric ratios of the two parts.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Preparation method of boron-doping carbon nitride as well as product and application thereof
ActiveCN109569691AEvenly dopedImprove photocatalytic performanceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsChemical reactionBoron doped carbon
The invention relates to a preparation method of boron-doping carbon nitride as well as a product and application thereof. By virtue of a hydrothermal reaction way of melamine and boric acid, on one hand, boron atoms have chemical reaction with melamine, so that the boron and carbon-nitrogen elements are mixed in an atomic level; on the other hand, the hydrothermal reaction is performed for the melamine in an acid environment, so that a supermolecule-like structure is formed, and the separation of a carbon nitride lamina structure in the subsequent roasting process can be facilitated; and a precursor synthesized in the reaction is roasted to prepare boron-doped carbon nitride which is uniform in doping and has a thinner lamina structure. The boron-doping carbon nitride prepared by adoptingthe preparation method of the invention is uniform in element doping, thinner in lamina, better in optical catalysis, simple in preparation operation, low in difficulty and suitable for enlarged production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com