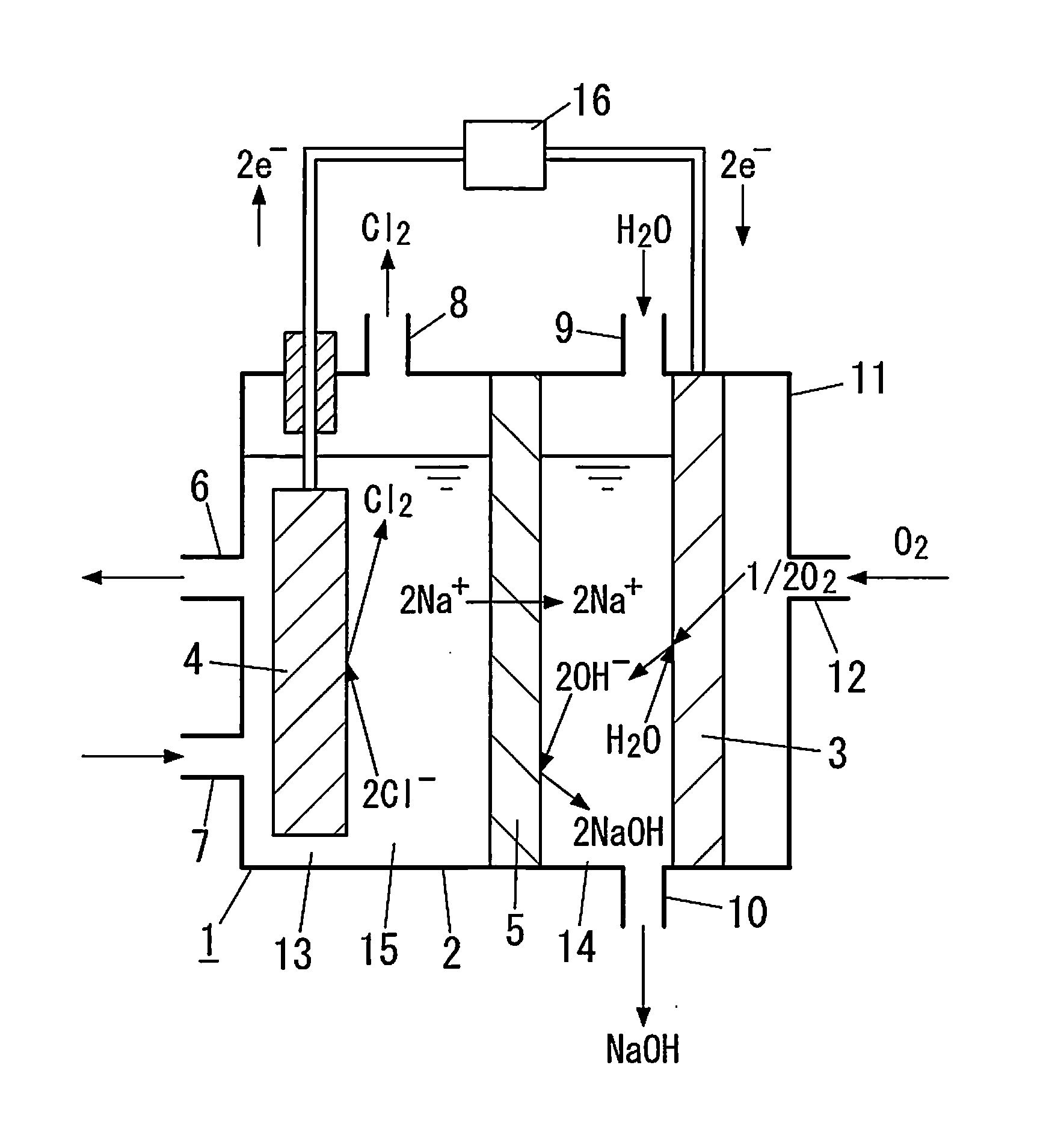
Carbon-based material, electrode catalyst, oxygen reduction electrode catalyst, gas diffusion electrode, aqueous solution electrolysis device, and method of preparing carbon-based material
a carbon-based material and catalyst technology, applied in the field of carbon-based materials, can solve the problems of rare and expensive platinum, unstable cost of platinum, and low cost, and achieve the effect of promoting oxygen reduction reaction and excellent catalyst performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0134]In a reactor, 3 g of graphite (Wako 40 mm), 138 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, and 3.47 g of potassium nitrate were mixed to prepare a mixture liquid. Potassium permanganate was further added slowly thereto, with the reactor being in an ice bath. Subsequently, thus-obtained mixture liquid was stirred at 40° C. for 30 min, and then 240 mL of ion-exchanged water was added thereto, followed by stirring and heating at 90° C. for 1 hour. Thereafter, into the reactor, 600 mL of ion-exchanged water and 18 mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide solution were added to finish the reaction. Then, the resultant mixture liquid was washed with hydrochloric acid and water, followed by removing ions therefrom by dialysis. Furthermore, ultrasonic was applied to the resulting mixture liquid to make graphene oxide separated.
[0135]Thus-obtained graphene oxide was dried. Then, into 200 mg of the dried graphene oxide, an aqueous solution of 0.1 M iron chloride (III) and an ethanol solution of 0.15 M pentae...
examples 2 and 3
[0137]In Examples 2, the amount of an aqueous solution of 0.1 M iron chloride (III) was adjusted so that a percentage of Fe atoms to graphene was 17 mass %. In Examples 3, the amount of an aqueous solution of 0.1 M iron chloride (III) was adjusted so that a percentage of Fe atoms to graphene was 30 mass %. Except for these, the carbon-based materials according to Examples 2 and 3 were prepared in the same manner and under the same conditions as those of Example 1.
referential example 1
[0140]In Referential Example 1, the heating time was two hours in the step of heating the sample which contains graphene oxide, iron chloride (III), and pentaethylenehexamine. Except for this, the carbon-based material according to Referential Example 1 was prepared in the same manner and under the same conditions as those of Example 2.
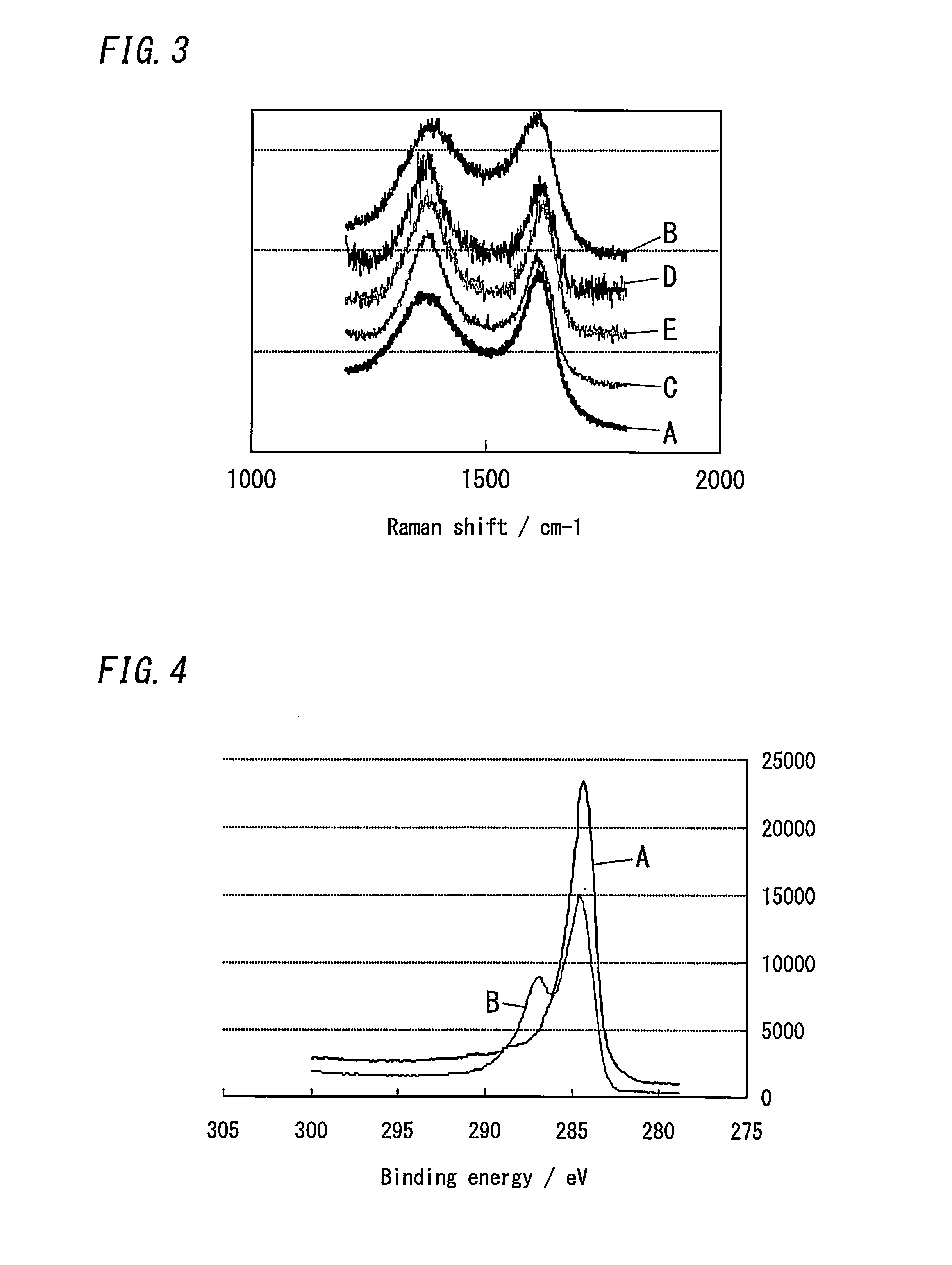
[0141][Raman Spectroscopy]
[0142]Graphite (Wako 40 mm), graphene oxide made of this graphite in the aforementioned manner, and the carbon-based materials obtained in Example 2, Comparative Examples 1 and 2 were analyzed by Raman spectroscopy. FIG. 3 shows thus-obtained Raman spectra. “A”, “B”, “C”, “D”, and “E” in FIG. 3 indicate the Raman spectra of the graphite, the graphene oxide, and the carbon-based materials obtained in Example 2 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2, respectively.
[0143]As shown in FIG. 3, the results confirm that each of the Raman spectra has a G-band peak (the right peak) derived from C(sp2)-C(sp2) bond and a D-band peak (the left p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com