Artificial cervical intervertebral disc with ultrahigh activity type chamfering U-shaped structure
A cervical intervertebral disc and mobility technology, applied in the direction of spinal implants, etc., can solve the problems of increasing surgical difficulties and patient pain, easily causing heterotopic ossification, and causing inflammation, so as to meet long-life anti-fatigue performance and prevent wear and tear Granules, activity-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
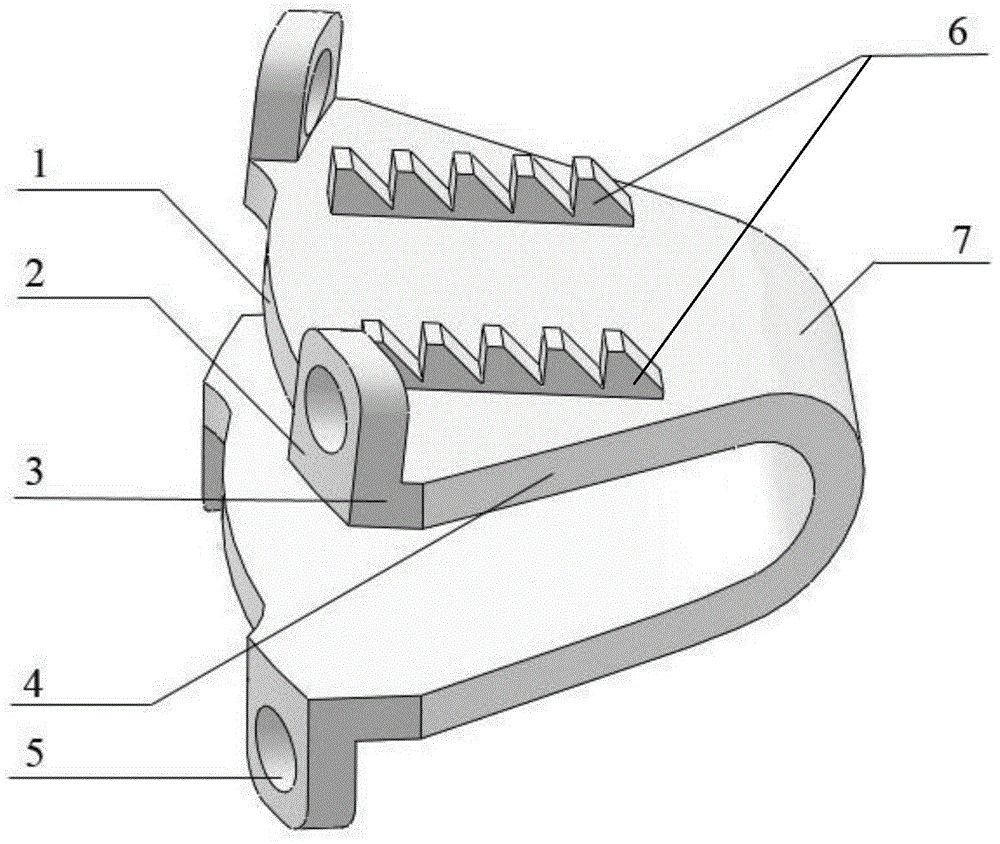
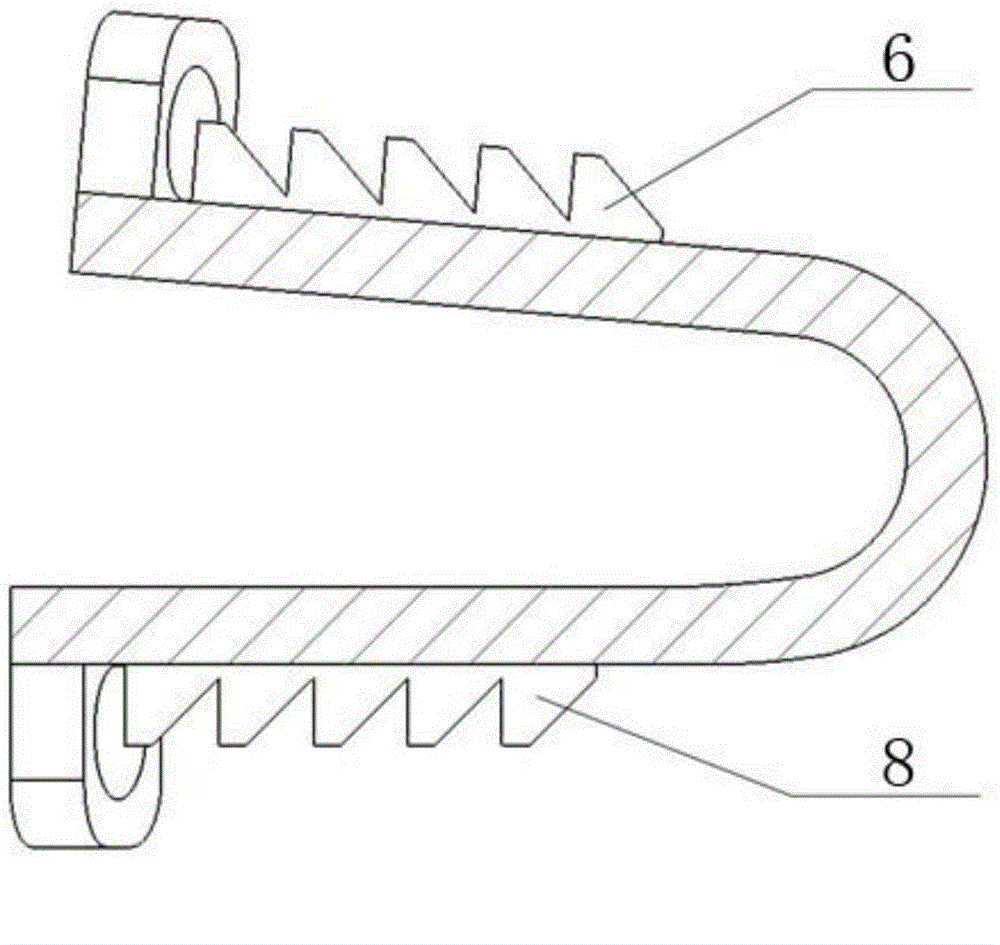
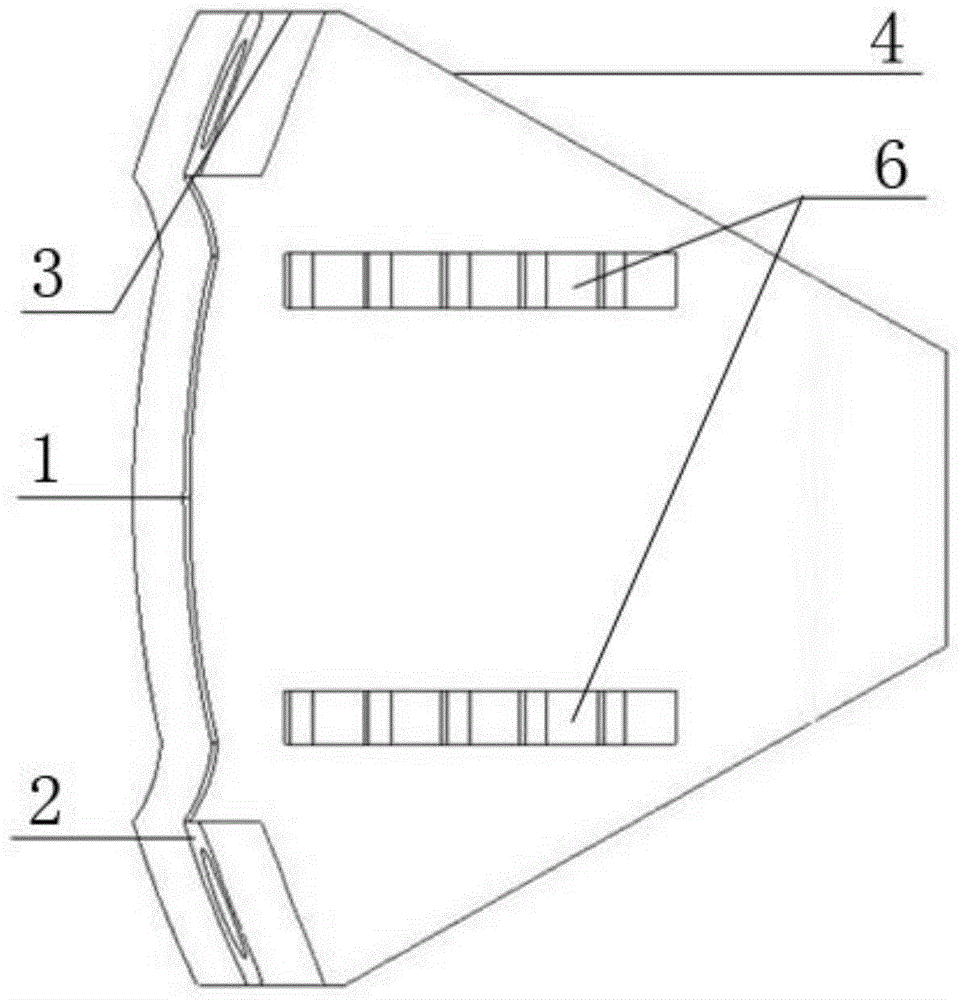
[0033] Embodiment 1: Before implanting the artificial cervical intervertebral disc body (7) of the present invention with an ultra-high mobility cut-angle Ω-shaped structure, the patient's cervical spine is first subjected to discectomy and the upper and lower vertebral bodies are polished, and then According to the sagittal and transverse diameters of the patient's cervical vertebral body, an artificial cervical intervertebral disc with the following specifications was selected: the length of the lower end plate was 16 mm, the front end width of the end plate was 17.8 mm, the distance between the front edge of the cut corner and the end surface of the bolt hole was 2 mm, and the cut angle was 25°, the front half of the side (4) adopts a straight line transition, and the physiological curvature of the upper and lower end plates is 5°; the wall thickness of the elastic structure (7) is 1.2 mm, and the overall height of the rear end is 6 mm. The distance between the front edge (1...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: Before the implantation of the artificial cervical intervertebral disc body (7) of the present invention with an ultra-high mobility angle-cut Ω-shaped structure, the patient's cervical spine is first subjected to discectomy and the upper and lower vertebral bodies are polished, and then According to the sagittal diameter and transverse diameter of the patient's cervical vertebrae, select the artificial cervical intervertebral disc body (7) of the following specifications: the length of the lower end plate is 16 mm, the front end width of the end plate is 17.8 mm, and the distance between the front edge of the cut corner and the end face of the bolt hole is 1 mm , the cutting angle is 15o, the front half of the side (4) adopts a straight transition, and the physiological curvature of the upper and lower end plates is 3o; the wall thickness of the artificial cervical disc body (7) is 1mm, and the overall height of the rear end is 6mm. The distance between th...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: Before implanting the artificial cervical intervertebral disc body (7) of the present invention with a cut-angle Ω-shaped structure with ultra-high mobility, the patient's cervical spine is first subjected to discectomy and the upper and lower vertebral bodies are polished, and then According to the sagittal and transverse diameters of the patient's cervical vertebrae, select the artificial cervical intervertebral disc body (7) of the following specifications: the length of the lower end plate is 18 mm, the front end width of the end plate is 19.8 mm, and the distance between the front edge of the chamfer and the end surface of the bolt hole is 1.5 mm. mm, the cut angle is 30o, the front half of the side (4) adopts a straight transition, and the physiological curvature of the upper and lower end plates is 5o; The distance between the front edge (1) of the cervical intervertebral disc body (7) and the end face of the bolt hole (2) is 1mm; the front end of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com