Method for expressing human lysozyme-antibacterial peptide Parasin I fusion protein by virtue of pichia pastoris
A technology of human lysozyme and Pichia pastoris, applied in the field of biotechnology and genetic engineering, to achieve strong antibacterial activity and increase the effect of expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
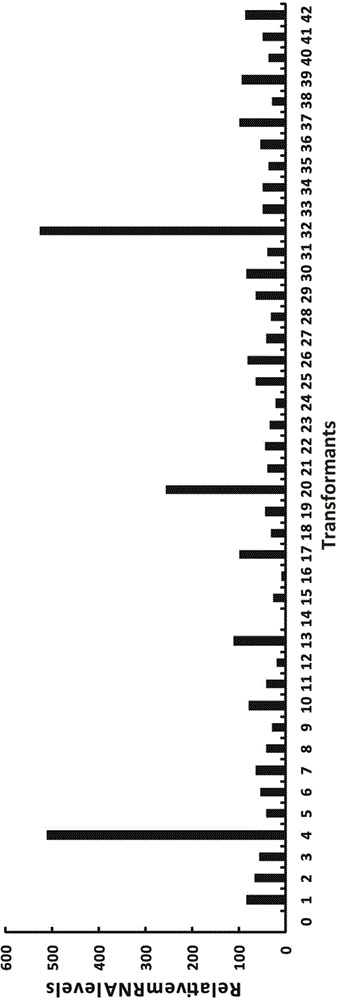
Embodiment
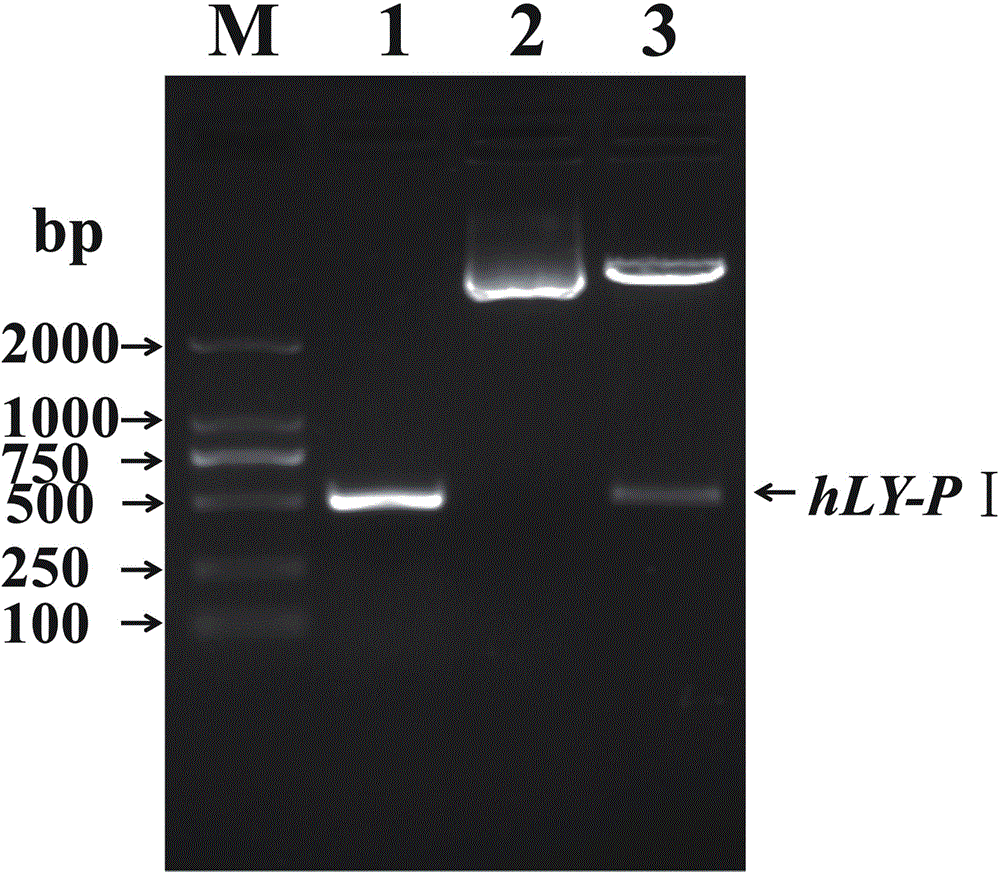
[0036] The molecular biology experimental techniques used in the examples include PCR amplification, plasmid extraction, plasmid transformation, DNA fragment ligation, enzyme digestion, gel electrophoresis, etc., unless otherwise specified, generally operate in accordance with conventional methods. For details, please refer to "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Third Edition) (Sambrook J, Russell DW, Janssen K, Argentine J. Huang Peitang et al. translation, 2002, Beijing: Science Press), or according to the conditions suggested by the manufacturer.
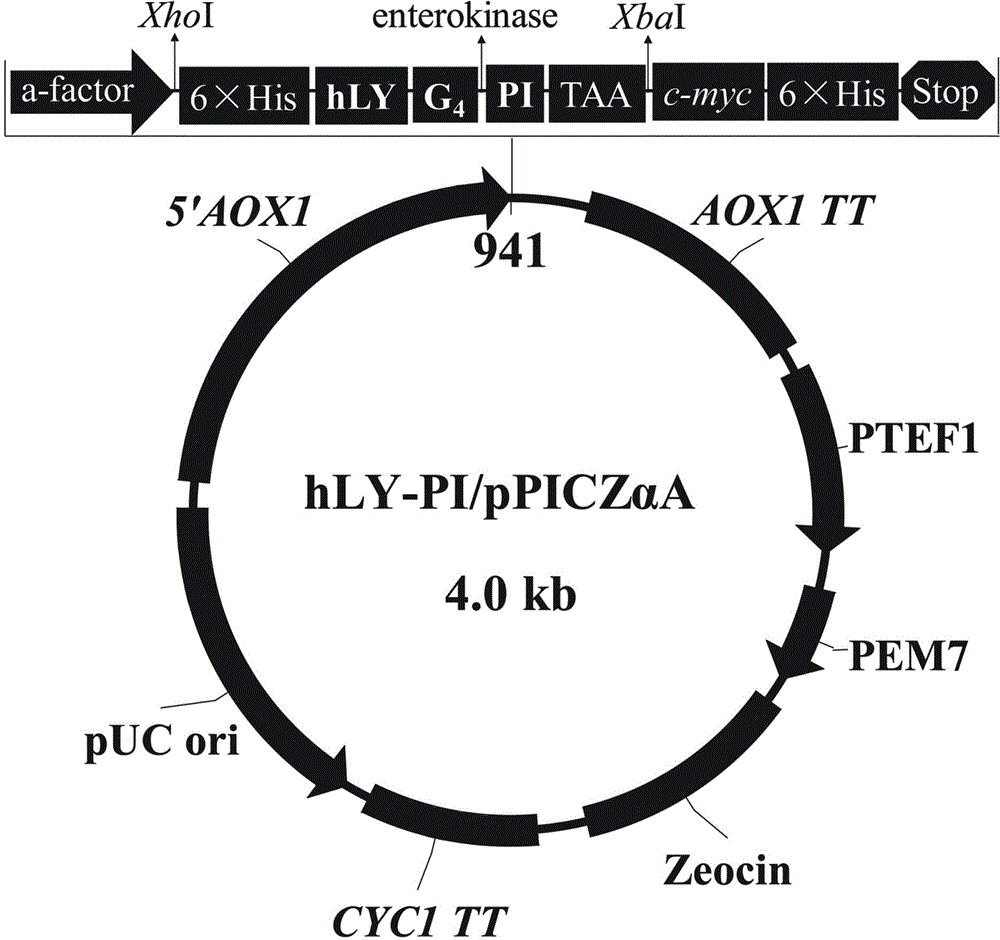
[0037] Pichia pastoris ( Pichia pastoris) X-33 was purchased from Invitrogen. The pPICZαA expression vector was purchased from Invitrogen. The pPICZαA expression vector (Invitrogen Company) was preserved in our laboratory.
[0038] 1. Obtaining the amino acid sequence of human lysozyme (SEQ ID NO:1):
[0039] The human lysozyme protein sequence (GenBank Accession No. AAC63078.1) was searched from the NCBI website.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com