Qualitative and absolute quantification kit for detecting hepatitis B virus cccDNA
A hepatitis B virus, absolute quantitative technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, complex components, poor specificity, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost and cumbersome steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0062] Qualitative and absolute quantitative detection cccDNA kits using closed circular DNA safety DNase include (reagents not specified in this kit are commercially available):
[0063] HBV DNA extraction reagents: cell lysate, Tris saturated phenol (PH: 7.6), phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol=25:24:1, absolute ethanol, 75% ethanol, TE buffer.
[0064] Plasmid-Safe TM ATP-Dependent DNase:
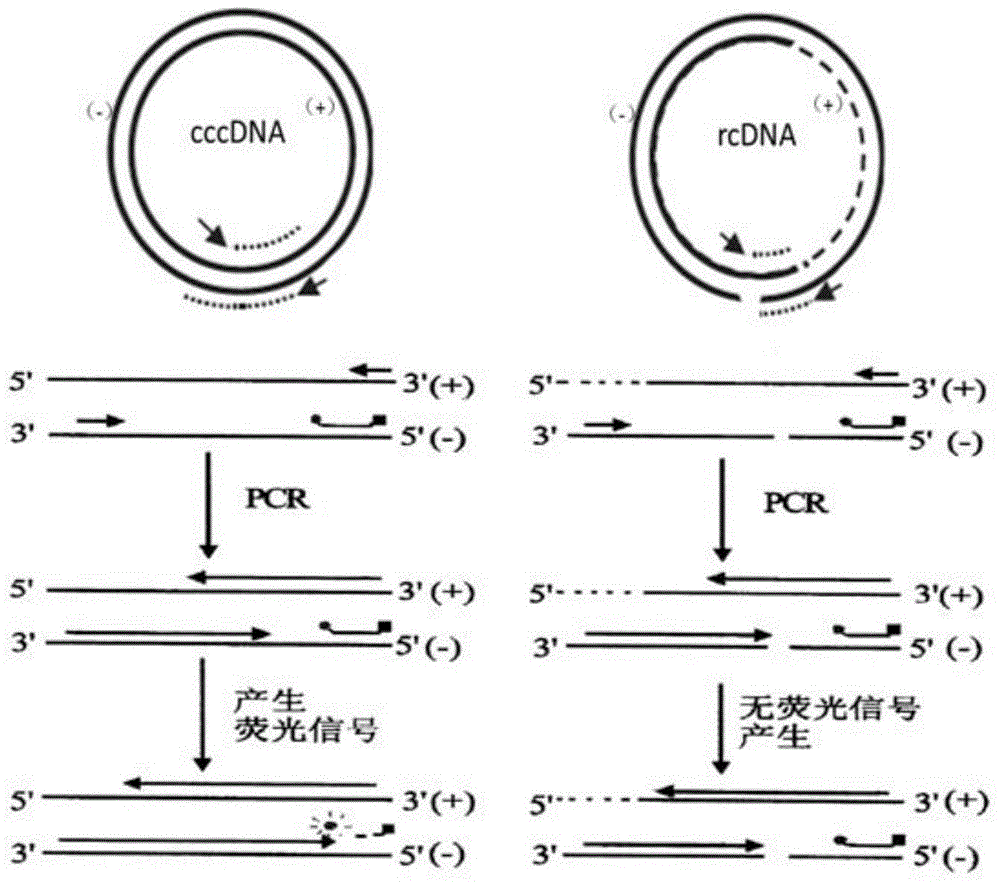
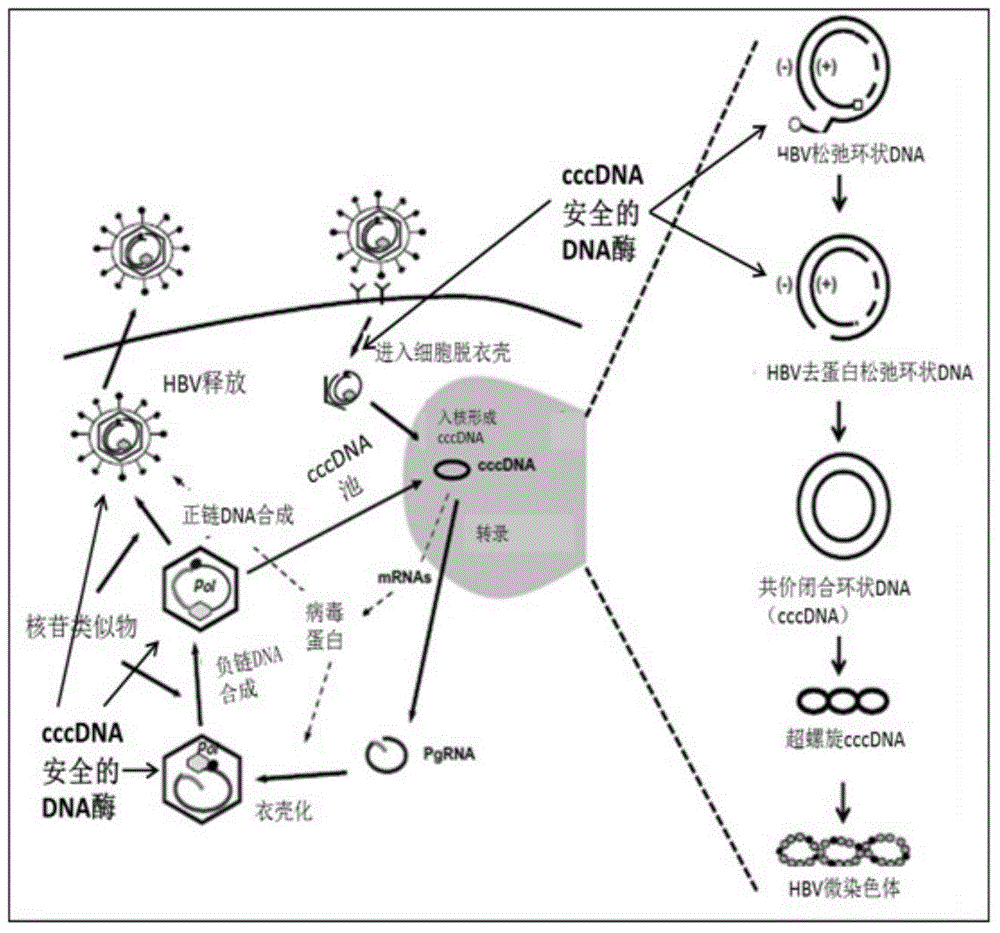
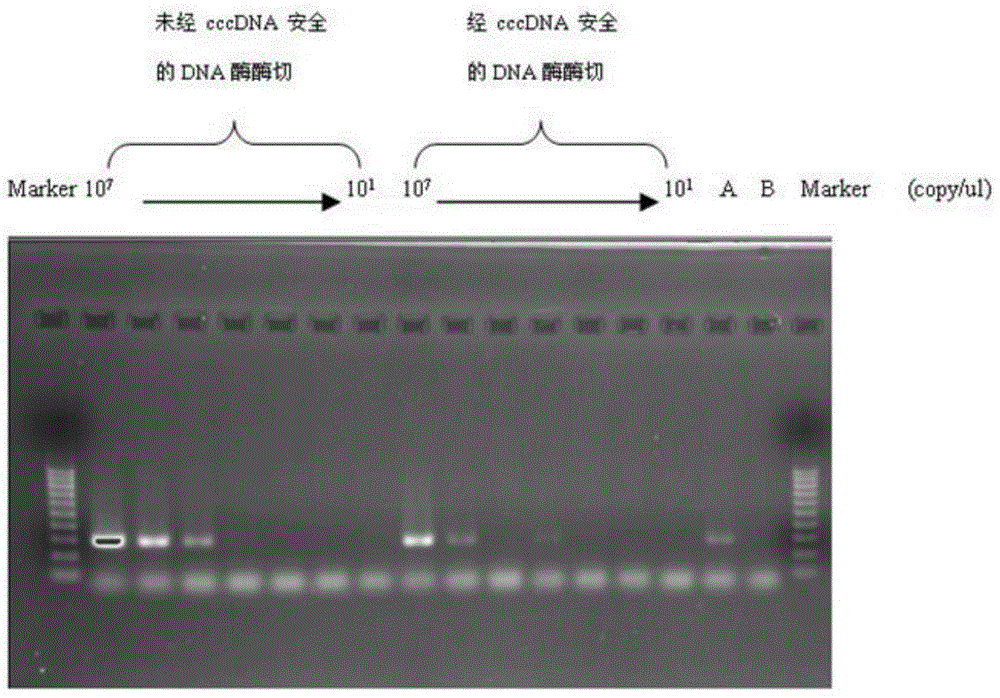
[0065]Effectively degrades rcDNA and ssDNA containing gaps, has no effect on cccDNA, can reduce non-specific amplification caused by rcDNA, reduce the background content of rcDNA, and improve the specificity of the reaction, see figure 2 .
[0066] Primers, probes:
[0067] All are synthesized by biological companies, the design is as follows figure 1 , HBV cccDNA is a fully closed circular DNA, while HBV rcDNA is an incompletely closed circular DNA. The primer probe designed for the negative strand gap of HBV rcDNA uses rcDNA as a template theory. The sequence is as follows:
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com