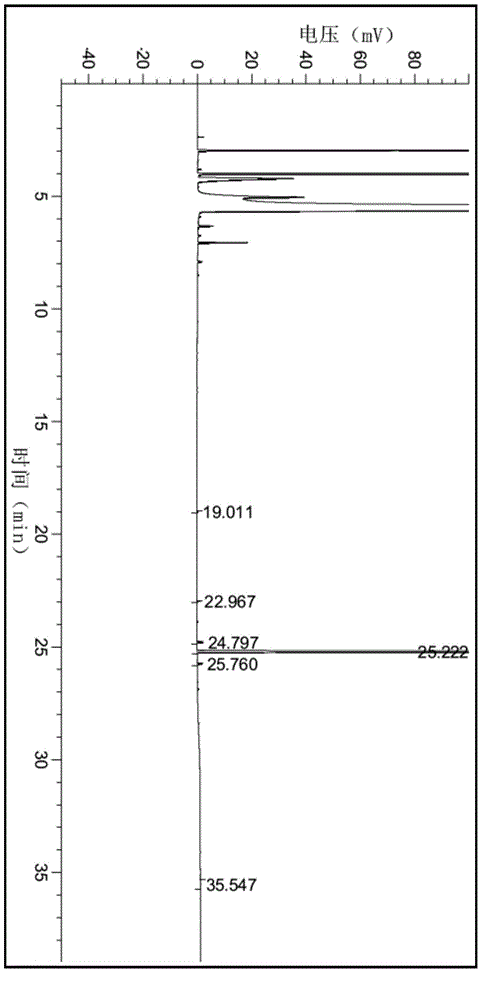
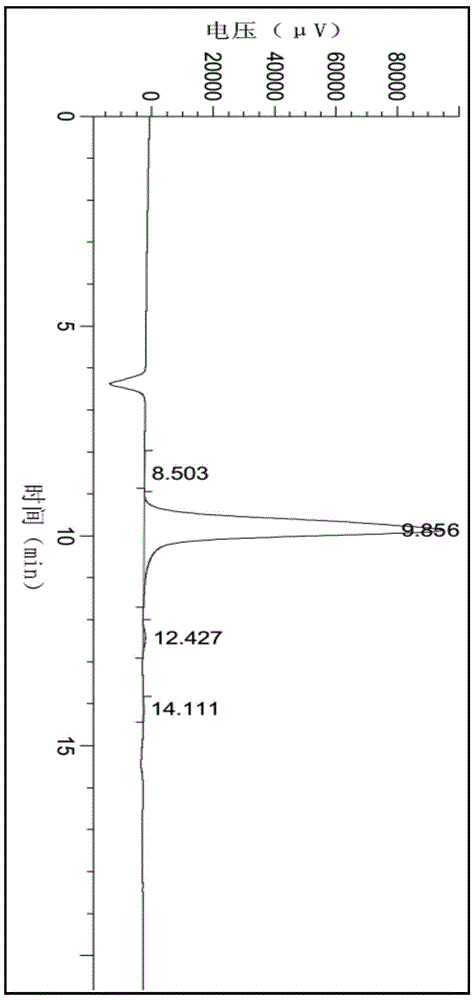
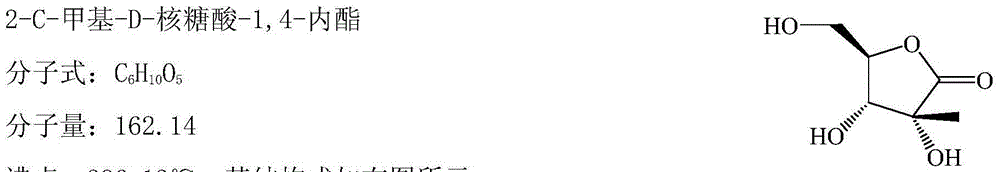
Method for preparing 2-C-methyl-D-ribotide-1,4-lactone
A technology of 2-C-ribose acid, which is applied in the field of preparing 2-C-methyl-D-ribose-1,4-lactone and lactone compounds, which can solve the problem of low yield, high cost and risk factor Advanced problems, to achieve the effect of high yield, short reaction time and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) The materials for the first step reaction are shown in the table below. At room temperature, add D-glucose, dibenzylamine, acetic acid, and ethanol to the one-mouth bottle, and heat to 70°C.
[0028] raw material name Specification MW (g / mol) Feeding amount mol% (eq) D-glucose 99% 180.16 60g 1.0 Dibenzylamine industry. 197.12 75g 1.0 acetic acid CP. -- 18ml -- ethanol industry -- 420ml 7(v / m)
[0029] After reacting for 3 hours, a white solid was formed, followed by TLC until the raw material disappeared, and cooled to room temperature. The precipitated solid was filtered, and the filter cake was washed with 200 ml of absolute ethanol, sucked dry, and dried. 112 g of white solid 1-deoxy-1-(N,N-amino)-D-fructose was obtained, HPLC≥98%, yield 90%.
[0030] (2) The materials for the second step reaction are shown in the table below. At room temperature, add 80g of 1-deoxy-1-(N,N-amino)-D-fructose, calcium o...
Embodiment 2
[0034] (1) The materials for the first step reaction are shown in the table below. At room temperature, add D-glucose, dibenzylamine, acetic acid, and ethanol into the one-mouth bottle, and heat to 75°C.
[0035] raw material name Specification MW (g / mol) Feeding amount mol% (eq) D-glucose 99% 180.16 60g 1.0 Dibenzylamine industry. 197.12 82.5g 1.1 acetic acid CP. -- 18ml -- ethanol industry -- 420ml 7(v / m)
[0036] After reacting for 4 hours, a white solid was formed, followed by thin-layer chromatography until the raw material disappeared, and cooled to room temperature. The precipitated solid was filtered, and the filter cake was washed with 200 ml of absolute ethanol, sucked dry, and dried. 118 g of white solid 1-deoxy-1-(N,N-amino)-D-fructose was obtained, HPLC≥98.3%, yield 91%.
[0037] (2) The materials for the second step reaction are shown in the table below. At room temperature, add 80g of 1-deoxy-1-(N,N-...
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) The materials for the first step reaction are shown in the table below. At room temperature, add D-glucose, dibenzylamine, acetic acid, and ethanol to the one-mouth bottle, and heat to 80°C.
[0043] raw material name Specification MW (g / mol) Feeding amount mol% (eq) D-glucose 99% 180.16 60g 1.0 Dibenzylamine industry. 197.12 90g 1.2 acetic acid CP. -- 18ml -- ethanol industry -- 420ml 7(v / m)
[0044] After reacting for 5 hours, a white solid was formed, followed by TLC until the raw material disappeared, and cooled to room temperature. The precipitated solid was filtered, and the filter cake was washed with 200 ml of absolute ethanol, sucked dry, and dried. 111 g of white solid 1-deoxy-1-(N,N-amino)-D-fructose was obtained, HPLC≥97.8%, yield 89.5%.
[0045] (2) The materials for the second step reaction are shown in the table below. At room temperature, add 80g of 1-deoxy-1-(N,N-amino)-D-fructose, calci...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com