Device and method for rotatably controlling optical tweezers by femtosecond laser
A femtosecond laser and optical tweezers technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of limited particle capture and directional movement, limited application range, thermal damage, etc., and achieve stable rotation manipulation, high precision and stability captured effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
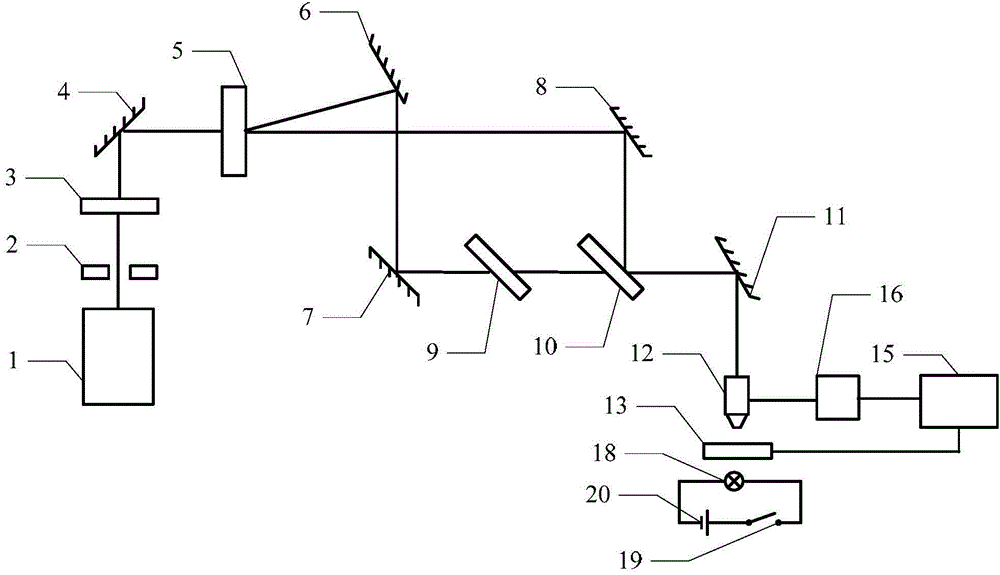
[0016] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 Describe this specific embodiment, a femtosecond laser rotation control optical tweezers device described in this specific embodiment includes a femtosecond pulse laser 1, an aperture 2, an attenuation plate 3, a first 800nm total reflection plane mirror 4, a vortex grating 5. The second 800nm total reflection plane mirror 6, the third 800nm total reflection plane mirror 7, the fourth 800nm total reflection plane mirror 8, the beam splitter 10, the fifth 800nm total reflection plane mirror 11, the microscope 12 and the stage 13,
[0017] The pulsed laser light emitted by the femtosecond pulsed laser 1 enters the attenuation plate 3 through the diaphragm 2, and the attenuation plate 3 attenuates the light intensity of the pulsed laser light and then injects the pulsed laser light into the first 800nm total reflection plane mirror 4, and the first 800nm total reflection The flat mirror 4 totally reflects t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0026] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the device for controlling optical tweezers by femtosecond laser rotation described in Embodiment 1 is that the femtosecond pulse laser 1 is a titanium-doped sapphire femtosecond laser, and the emitted pulse The laser repetition rate is greater than 70 MHz and the pulse width is 120 femtoseconds.
[0027] In this embodiment, a femtosecond laser is used as the light source of the optical tweezers device. Since the femtosecond laser has high time and space resolution characteristics, it provides a guarantee for improving the capturing power of the optical tweezers. Combining femtosecond laser technology with time-resolved spectroscopy technology, it can also conduct research on ultrafast biological processes in organisms and two-photon fluorescence dynamics. The high time and space resolution characteristics of femtosecond laser can also realize non-invasive local modification of cells.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0028] Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and the device for controlling optical tweezers by femtosecond laser rotation described in Embodiment 1 is that the stage 13 is a three-dimensional micro-displacement platform.
[0029] The stage 13 described in this embodiment is controlled with high precision by a three-dimensional linear excitation source, and the control accuracy is 50 nm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com