A method for rapidly determining the survival status of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis in milk and milk products by using blu-v PMA technology
A BLU-V, mycobacteria technology, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of reduced PMA treatment effect, false positives, short peak brightness time, etc., to achieve the effect of protecting health, rapid development, improving efficiency, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Primer specificity verification
[0031] Genomic DNA of 6 standard strains of Map (P10 and P18), Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, Escherichia coli, and Mycobacterium phlei was extracted, and TaqMan fluorescent quantitative PCR amplification was performed to test the specificity of the method of the present invention. (Mycobacterium paratuberculosis ( M. paratuberculosis ) Standard strains: P18 (United States), P10 (Japan) (both standard strains of bovine paratuberculosis), all provided by Jilin Veterinary Research Institute. Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, Escherichia coli, and Mycobacterium phlei are all preserved by the Technical Center Laboratory of Shanxi Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau. )
[0032] 1. Preparation of DNA
[0033] Take 50 μL of bacterial solution, add it to 400 μL TE, and mix well. The specific steps for extracting the DNA template are as follows:
[0034] (1) Heat in a water bath at 80°C for 20 minutes, then cool to room temper...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Optimization of Optimum Reaction Conditions of MAP Standard Strain Acting on PMA
[0049] 1. Preparation of MAP standard strains (P10 and P18) membrane damage bacteria
[0050] Take 1 mL of P10 and P18 bacterial solutions (take as much bacteria as possible) into 2 mL EP tubes with 50 magnetic beads, seal them with a parafilm, and put them in a nucleic acid extractor (once every 5 s). Fully suspend the bacterial solution; after suspension, inactivate in an 80°C water bath for 20 min.
[0051] 2. PMA treatment of MAP standard strains (P10 and P18)
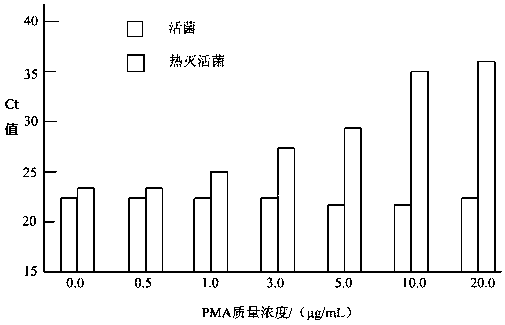
[0052] Dissolve 0.5 mg of PMA in 1 mL of RNase-free water to make a 0.5 mg / mL PMA stock solution and store at -20 °C. Place the inactivated bacterial solution in a centrifuge and centrifuge at 14,500 r for 5 min; after centrifugation, discard the supernatant; then add 500 μL of EB Buffer to the remaining bacterial cells and mix well.
[0053] 3. Optimization of PMA mass concentration
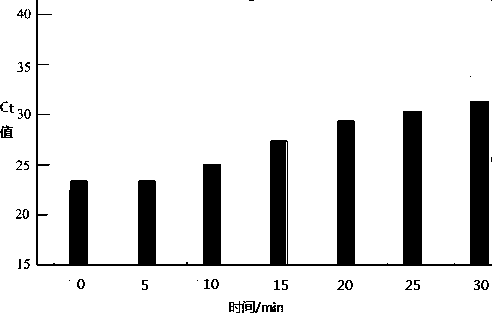
[0054] A certain amount of PMA was ad...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Quantitative detection of live bacteria in milk and milk products under optimal PMA reaction conditions
[0061] 1. Preparation of membrane-damaging bacteria (P10 and P18) in artificially polluted MAP milk samples
[0062] Take 1 mL of P10 and P18 bacterial solutions (take as much bacteria as possible) into 2 mL EP tubes with 50 magnetic beads, seal them with a parafilm, and put them in a nucleic acid extractor (once every 5 s). Fully suspend the bacterial mass to form a bacterial suspension; aseptically take the negative milk samples with no MAP detected by fluorescent PCR, common PCR and electrophoresis, that is, take 1 mL of yogurt and 0.5 g of milk powder in 2 mL of sterilized EP tube; add 500 μL of bacterial suspension to each of the obtained milk samples, mix thoroughly on a vortex shaker; after mixing, place in an 80 °C water bath for 20 min to inactivate. Through this treatment, the cell wall and cell membrane of the bacteria are damaged to varying degrees to a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com