Methods of controlling fungal pathogens using polyene fungicides
A fungicide, nystatin technology, applied in the field of treatment and/or prevention of sudden death syndrome, which can solve the problem of ineffectiveness of fungicides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Example 1: In the agar diffusion test, the bacteriostatic zone of different concentrations of natamycin against the North American soybean sudden death syndrome pathogen was evaluated.
[0088] The PDA plate containing the two-week-old SDS pathogen was submerged in sterile distilled water and scraped off with an L-rod to release the spores. The spore solution was injected into a 50 mL conical tube through about 4 layers of gauze. Spores were quantified using a hemocytometer and then diluted to 1 x 105 Spores / mL. (Tile 1×10 on the plate 4 spores). To prepare a lawn plate of Sudden Death Syndrome of North American Soybean Death Syndrome, 100 μL of the spore suspension was spread on a commercially available PDA plate. Use a straw-plunger to punch holes in the lawn plate of SDS.
[0089] Natamycin stock solutions were diluted with sterile distilled water to concentrations of 500 ppm, 250 ppm, 100 ppm, 50 ppm, 25 ppm, 12.5 ppm, 6.25 ppm, 3.13 ppm, 1.56 ppm, 0.78 ppm and ...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Example 2: In planta (in planta) test was used to evaluate the control of natamycin on soybean sudden death syndrome.
[0092] Sorghum was prepared for inoculation. 1 to 2 liters of sorghum seeds were placed in a production bag, autoclaved, and then inoculated with 30-45 mL of SDA spore suspension. Place the bag in a fume hood at room temperature, then shake and mix every few days for 3 weeks until complete. Milo inoculum was evaluated by counting the number of spores per gram of seed using a hemocytometer. Milo grows to 4.57×10 5 Spores / g.
[0093] Enumeration of spores of the pathogen Sudden Death Syndrome of North American Soybean before soil inoculation. First, 25 mL of sterile water containing 0.1% Tween 80 was added to a sterile 50 mL conical tube. Weigh the weight of the tube. Then several grains of inoculated milo from production bags were added under aseptic conditions. Weigh the tube again to get the exact mass of inoculated spores added to the tube. T...
Embodiment 3
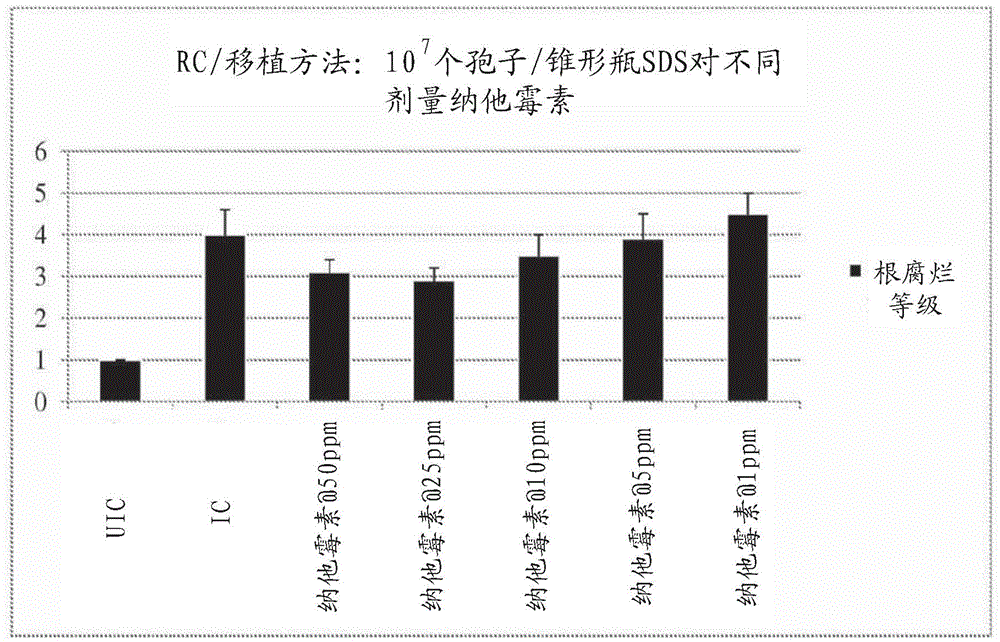
[0099] Example 3: An experiment of using a lower concentration of natamycin on seedlings as a watering treatment for controlling SDS in plants.
[0100] Using a similar protocol as described in Example 2, two lower concentrations of natamycin (50 ppm, 25 ppm, 10 ppm, 5 ppm and 1 ppm) were evaluated for the treatment of SDS. Two trials were performed.
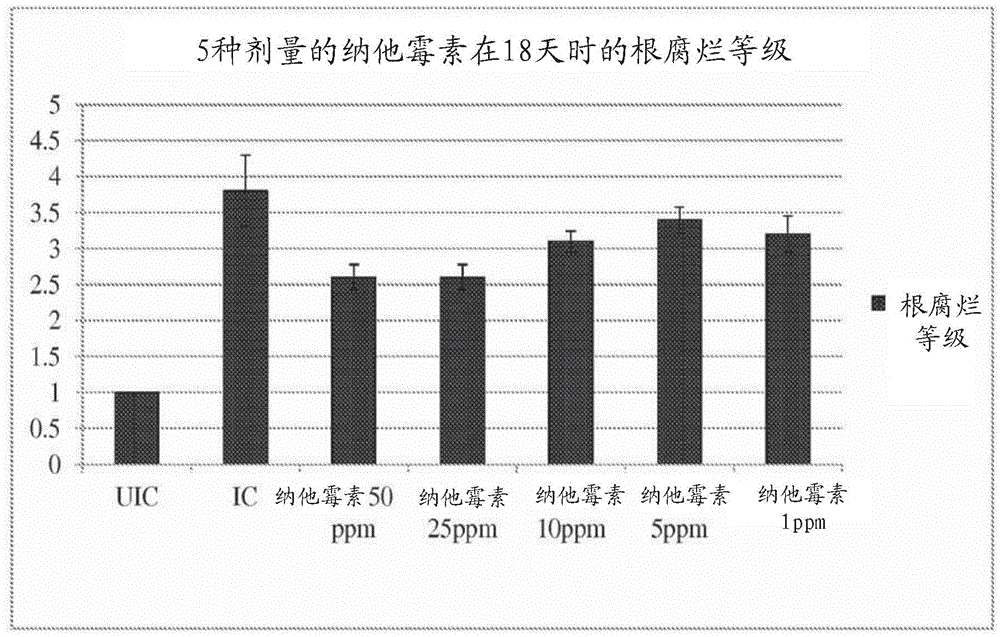
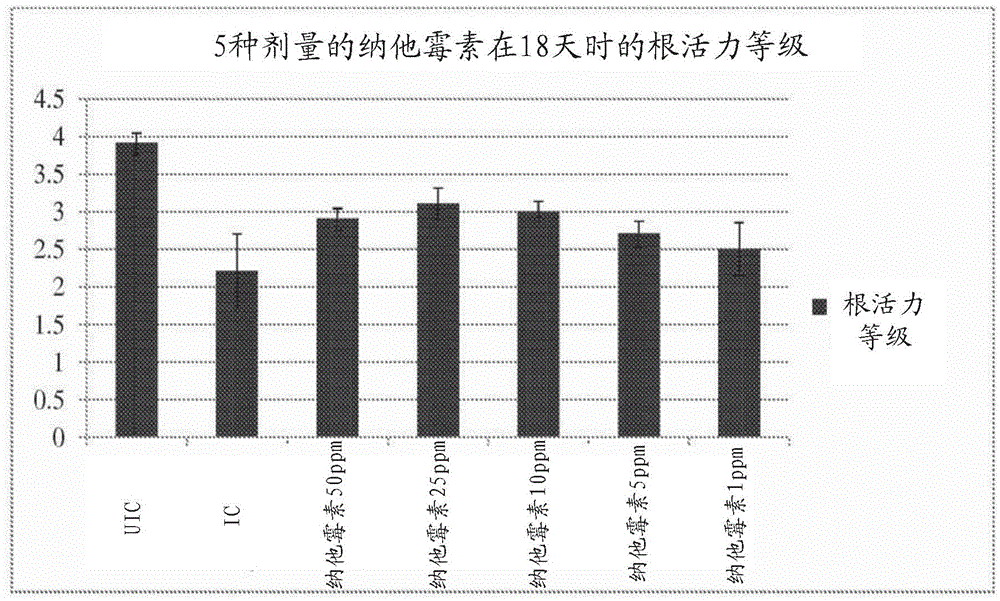
[0101] The natamycin solution was used as a watering treatment in an amount of 50 mL per container. Soybean seedlings were transplanted into SDS-infected soil at a ratio of 1 × 10 SDS spores 7 Spore / container. On the second day after transplantation, natamycin solution was applied to the container. Eighteen days later the soybean roots were washed.
[0102] figure 1 and figure 2 shows the results of the first experiment, image 3 and Figure 4 The results of the second experiment are shown. In particular, the data show that plants treated with natamycin at 50 ppm, 25 ppm and 10 ppm per container had significantly lowe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com