Biomarkers for down syndrome prenatal diagnosis
A biomarker, region-based technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can address issues such as increased risk of fetuses with Down syndrome
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0187] Example 1 - Discovery of DNA Methylation Biomarkers
[0188] Maternal plasma DNA from peripheral blood of pregnant women contains maternal DNA (mainly derived from white blood cells) and fetal DNA (derived from placental cells). Fetal DNA constitutes approximately 10% of all cell-free DNA in maternal plasma. Fetal and maternal DNA can be distinguished based on DNA methylation differences in specific genomic regions between fetal and maternal DNA. Differences in DNA methylation are also present in placental DNA of normal and diseased fetuses. In some genomic regions, DNA methylation was higher in diseased samples compared to normal samples, but in other regions DNA methylation was lower in diseased samples.
[0189] Reduced representational bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) was used to quantify genome-wide DNA methylation profiles in normal and trisomy 21 placenta samples. Two restriction enzymes (TaqαI and MspI, both from New England Biolabs) were used to digest genomic DN...
Embodiment 2
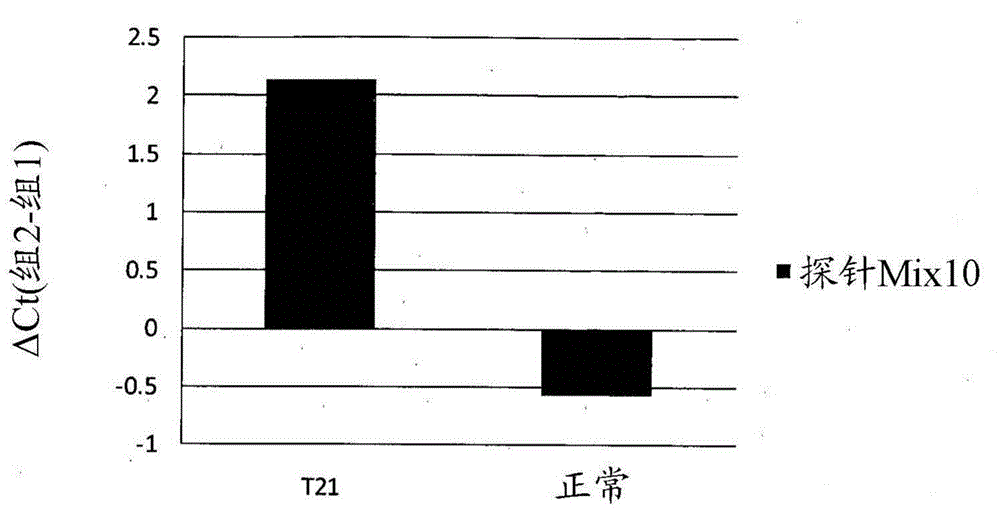
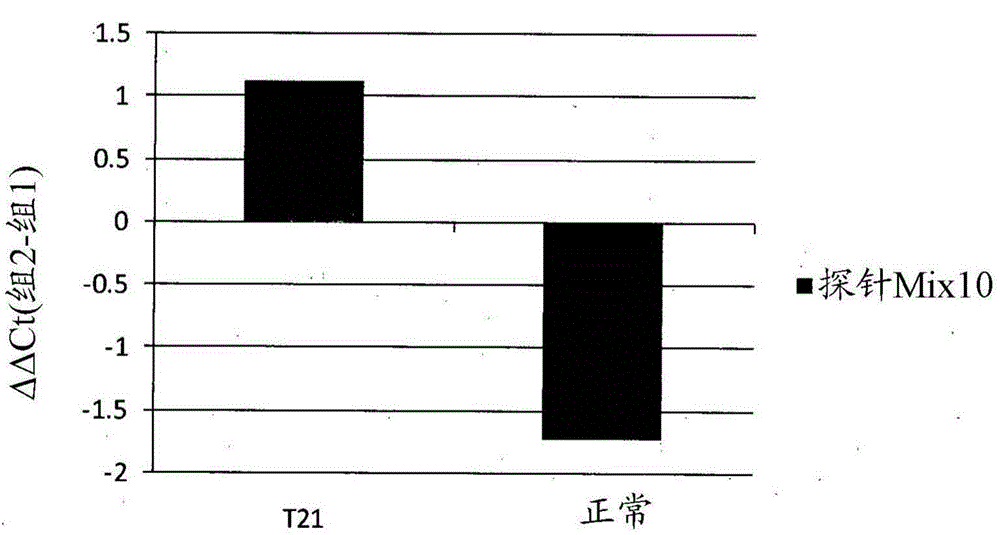
[0192] Example 2 - T21 fetal detection using methylation biomarkers
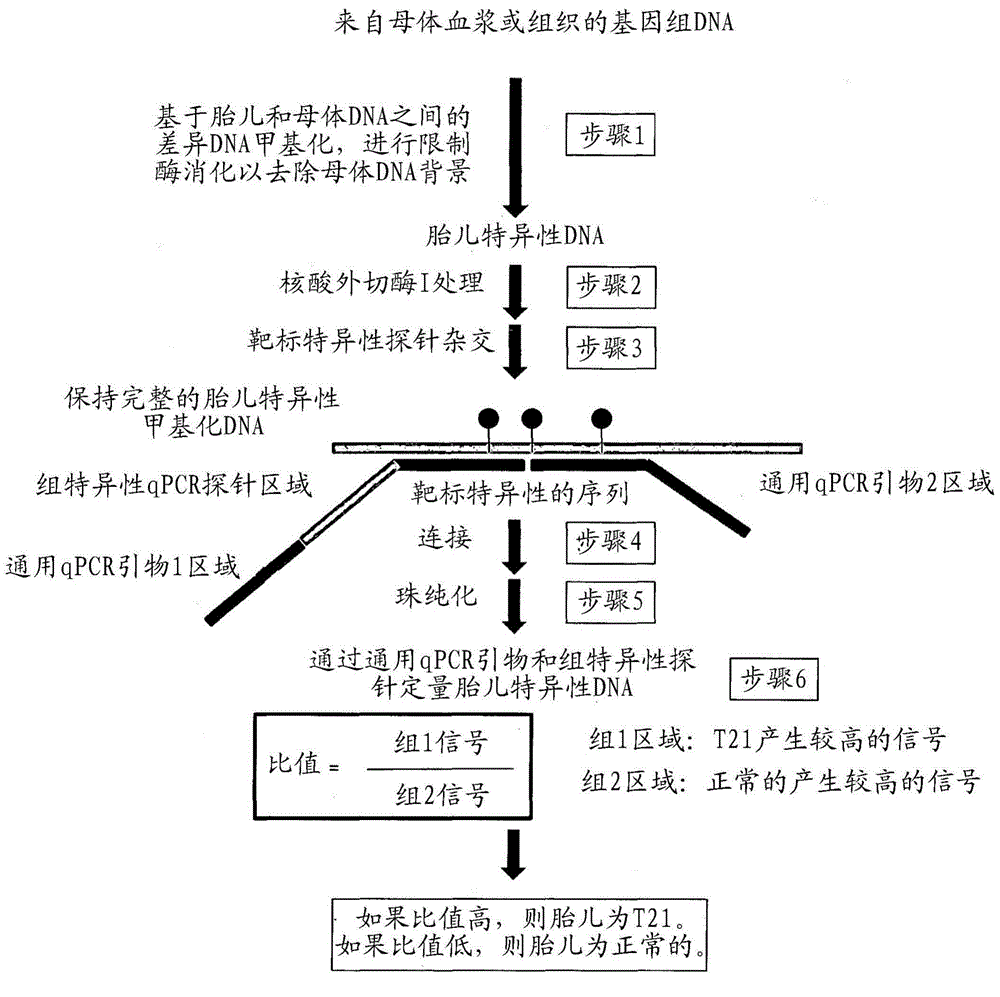
[0193] figure 1 A schematic is shown describing the following steps. Step 1: Removal of unmethylated DNA of selected biomarkers by methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes. In the case of experiments with fetal / maternal DNA mixtures, this step removes the maternal DNA background since the biomarker regions are mostly unmethylated. Methylation-sensitive 25 ng of genomic DNA in a 15 μL system containing 1x Buffer 4, 1x BSA, 9 units of BstUI, 10 units of HpaII, and 10 units of HhaI (New England Biolabs, USA) Restriction enzyme digestion. A mock digestion without restriction enzyme was set up as a control. Samples were incubated at 37°C for 2 hrs, then at 60°C for 2 hrs.
[0194] Step 2: Exonuclease I treatment is used to remove the 3' overhang of the digested DNA. 10 units of exonuclease I (New England Biolabs, USA) were added to the enzyme-digested samples and incubated at 37°C for 1 hr, then heat inact...
Embodiment 3
[0199] Example 3 - T21 fetal detection using methylation biomarkers.
[0200] 10 mL of peripheral blood from each individual was collected into EDTA tubes. Blood samples were centrifuged at 1,790 g for 10 min at 4°C. The supernatant was transferred to a new microcentrifuge tube and centrifuged at 16,100 g for 10 min at 4°C. The upper layer of cell-free plasma was then collected and stored at -80°C. DNA was extracted from 1.6 mL plasma from pregnant women using the QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit (QIAGEN GmbH, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions. DNA samples washed with 75 μL of DNase- and RNase-free water (Sigma) were stored at -80°C.
[0201] Step 1: Removal of unmethylated DNA for selected biomarkers by methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes. In the case of experiments with fetal / maternal DNA mixtures, this step removes the maternal DNA background since the biomarker regions are mostly unmethylated. Half of the genomic DNA extracted from maternal plasma w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com