A method for screening electricity-producing functional bacteria capable of degrading chlorophenol, mixed bacteria obtained by screening and application
A technology of mixing bacteria and electrical functions, applied in the directions of bacteria, chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of water body and aquatic organism pollution, affecting the ecological environment safety of water bodies, and achieve significant economic and environmental significance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
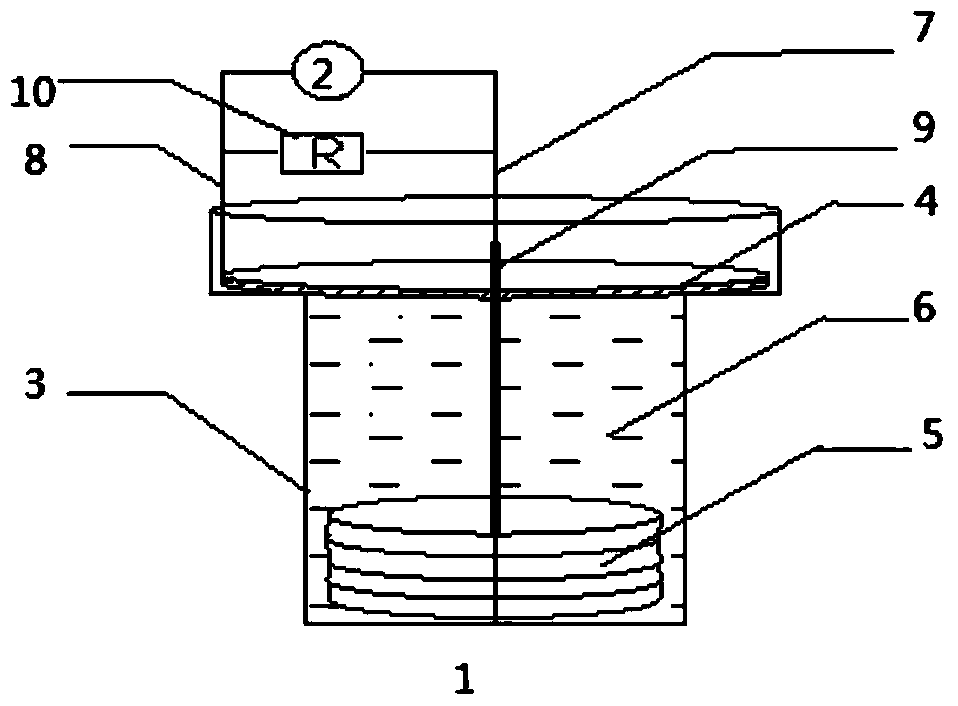
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Using marine hydrothermal deposits as the bacterial source, start a single-chamber air cathode microbial fuel cell containing toxic chlorophenols with a concentration of 50mg / L, with a constant external resistance of 510 ohms between the cathode and anode, and monitor the voltage output of the system. When the output voltage is stable After running, the output voltage will be stable within 2-3 cycles, increase the concentration of chlorophenol in the anolyte to 120mg / L, further screen the electricity-producing bacteria that are resistant to high concentrations of chlorophenol and can degrade chlorophenol, and have the ability to degrade chlorophenol Electrobacteria form biofilms on anode graphite felt.
Embodiment 2
[0030] The removal effect of COD in the waste water treatment process of embodiment two
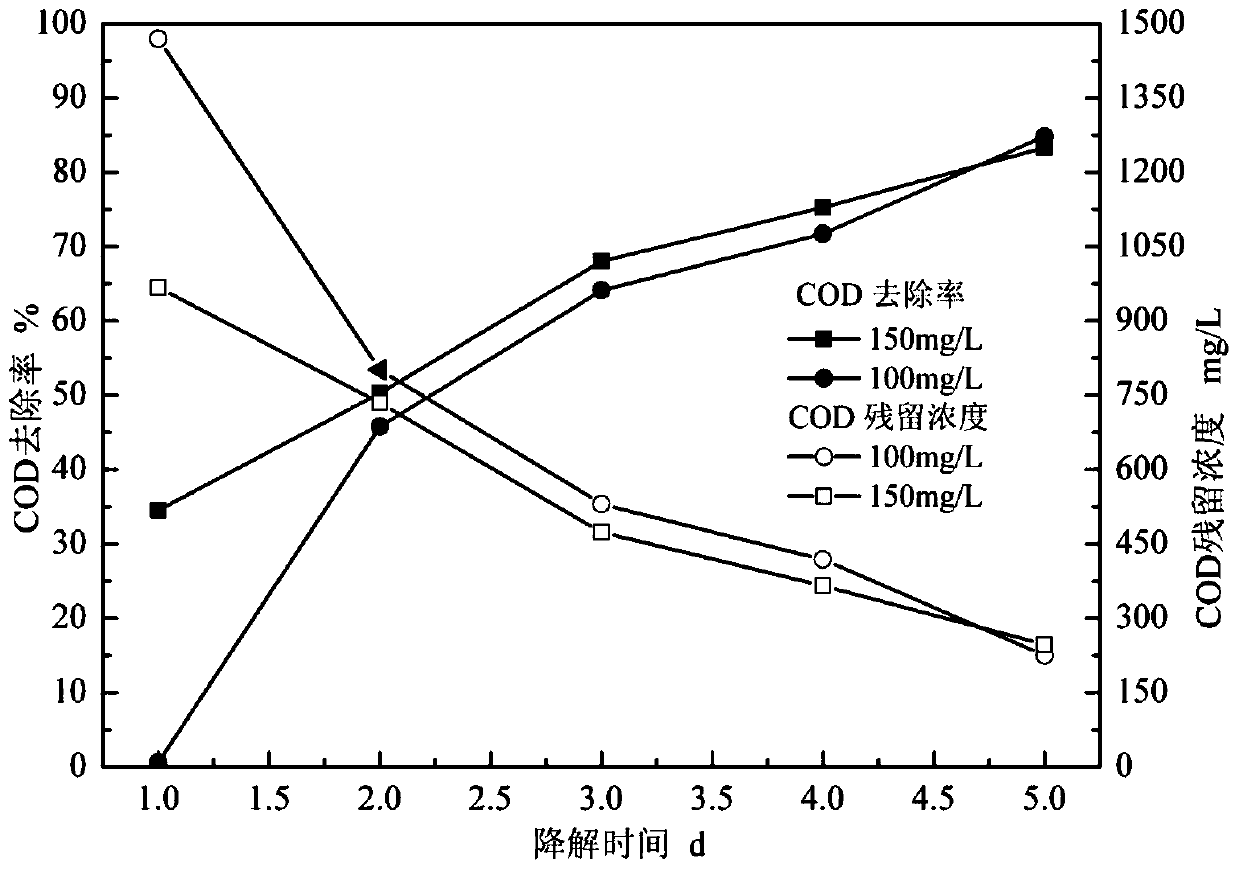
[0031] Chemical oxygen demand (COD), as one of the comprehensive indicators of the degree of water pollution, is an indicator that needs to be monitored in the process of wastewater treatment. Start the microbial fuel cell system, run the system of Example 1 at room temperature and investigate the operation of the system. For the COD degradation of the system, see figure 2 .
[0032] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that when the initial concentration of TCP is 100mg / L, the COD removal rate reaches 82.34% after 5 days of treatment; when the initial concentration of TCP is 150mg / L, after the same treatment for 5 days, the COD removal rate reaches 83.85%. The COD removal effects of the two were similar, indicating that within the investigation range of the initial TCP concentration, the increase of the initial TCP concentration had little effect on the COD removal effect.
Embodiment 3
[0033] The removal effect of chlorophenol in the waste water treatment process of embodiment three
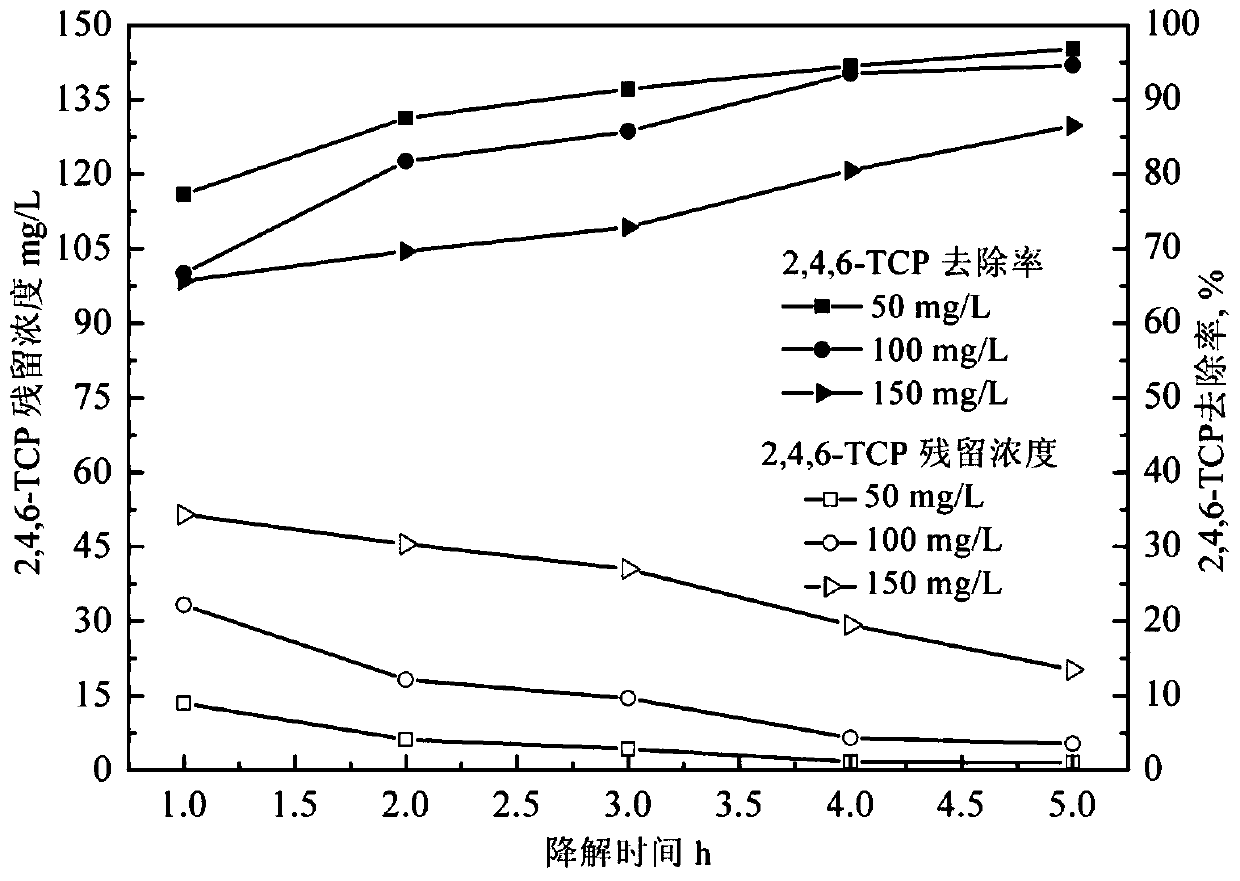
[0034] For the chlorophenol-containing wastewater treatment system, the first thing to investigate is the removal effect of toxic chlorophenols in the chlorophenol-containing wastewater. This embodiment adopts the method of embodiment one, examines respectively the removal rate of the chlorophenol in different reaction concentration batches, see image 3 . Depend on image 3It can be seen that when the initial TCP concentration increases, the residual TCP concentration in the solution also increases, and the removal rate of TCP decreases. When the initial concentration is 50mg / L, the removal rate of TCP can reach 97.45%. When the initial concentration increased to 150mg / L, the removal rate of TCP decreased to 87.32%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com