Genome restriction map splicing method and system
A splicing system and genome technology, which is applied in the field of genomic restriction map splicing methods and systems, can solve the problems of loss of accuracy, difficulty in directly recovering the genome, Bayesian model a priori, and high computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
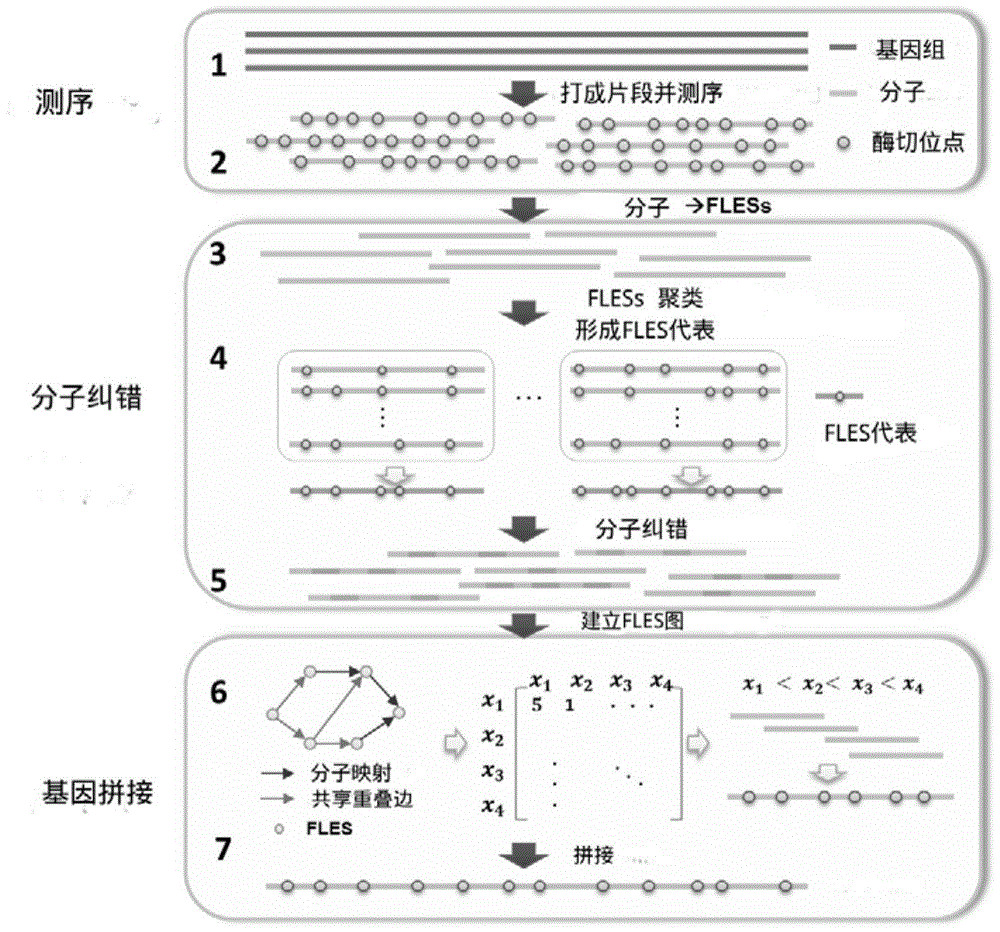
[0070] The enzyme-cut map stitching algorithm nanoARCS is mainly composed of two parts: molecular error correction and molecular splicing. The algorithm flow chart is shown in figure 2 . The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, wherein the "molecules" appearing in the present invention all represent "gene sequence molecules".
[0071] Step 1: The main steps of molecular error correction are divided into data preprocessing, clustering and error correction;
[0072] Step 11: data preprocessing;
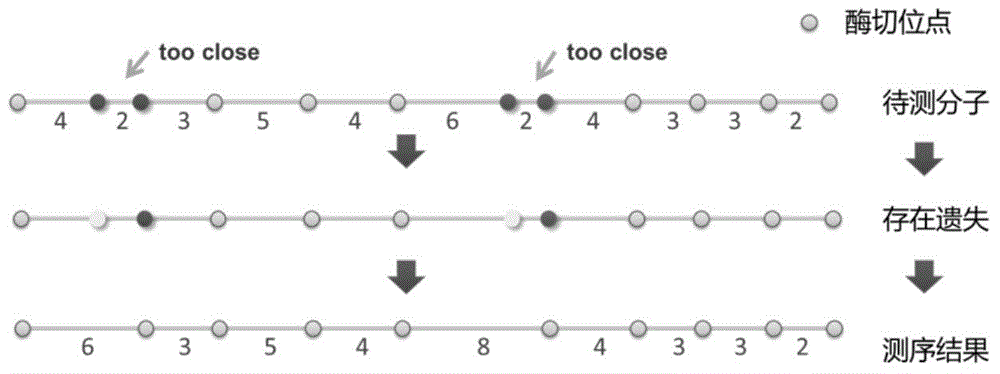
[0073] The main features of enzyme digestion map data are: 1) Irys system such as figure 1 The resolution of the restriction map generated as shown is about the order of Kbp. That is, if two restriction sites are close together, there is a high chance that one of the sites will be missed. Such as image 3 As shown in , only one fluorescent signal is recognized in the enzyme digestion map for the sites that are relatively ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com