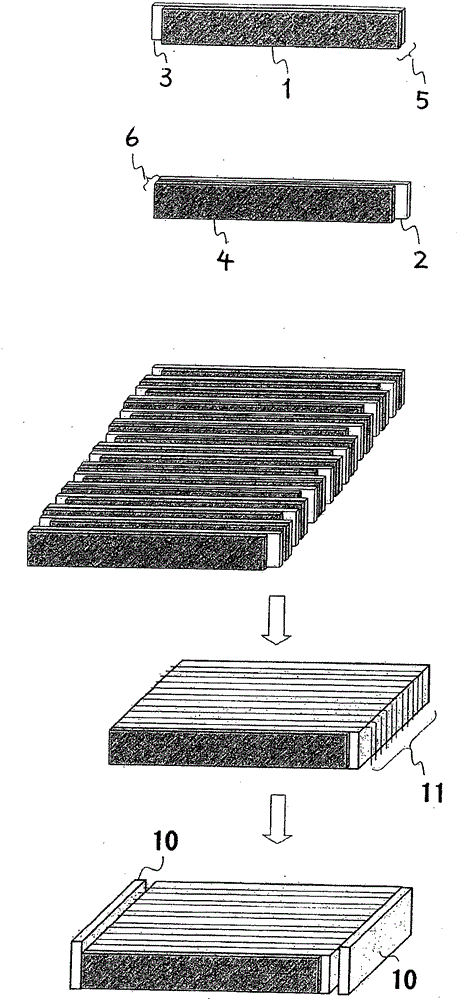
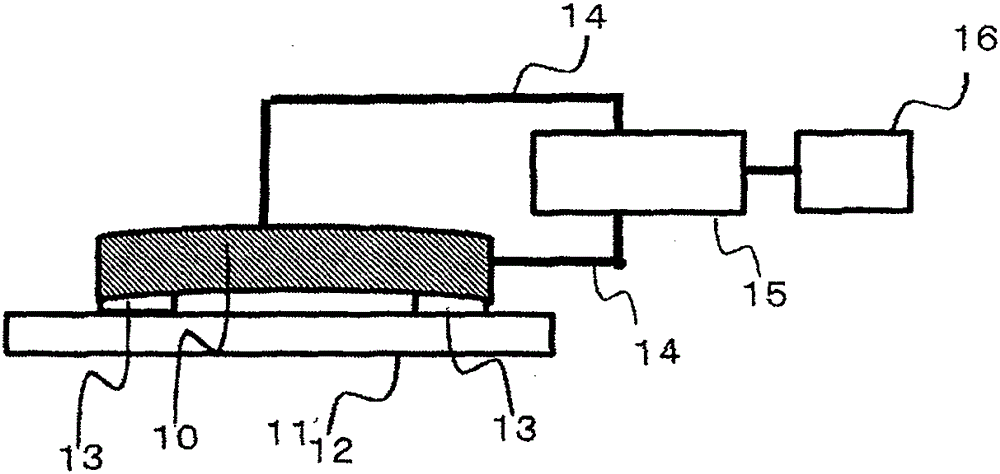
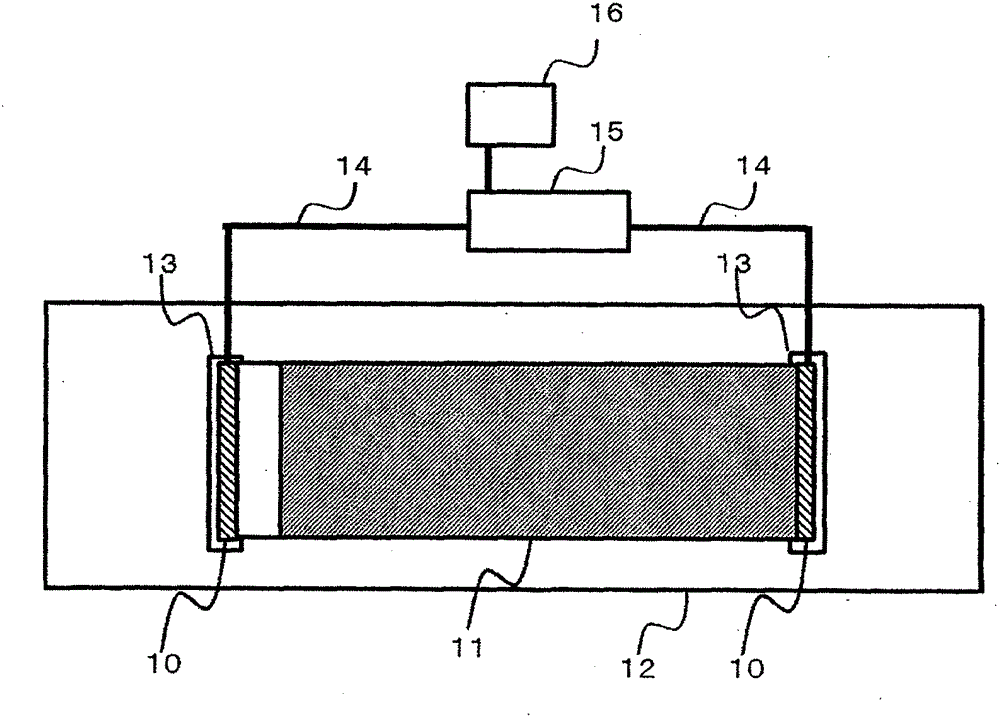
Piezoelectric vibrating body
A technology of piezoelectric vibration and piezoelectric layer, which is applied in piezoelectric-electric polymer transducers, circuits, piezoelectric/electrostrictive transducers, etc. Hard vibrating plate resonance and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0163] Hereinafter, the present invention will be further specifically described through examples, but the present invention is not limited thereto. The physical properties of each layer and the piezoelectric speaker were evaluated by the following methods.
[0164] (1) Physical properties of each layer
[0165] The end portions of the laminate were notched very equally, and the layers were peeled off to evaluate the physical properties of the layers.
[0166] (1-1) Main orientation direction
[0167] Using an ellipsometer (type M-220; JASCO), the obtained film was subjected to a transmitted light measurement in which the incident angle of 550 nm monochromatic light was changed, and the sample stage fixed with the film was set at a distance relative to the optical axis. The in-plane rotation with the optical axis perpendicular is performed, and the direction in which the refractive index in the in-plane direction is the highest is obtained, and this direction is defined as t...
Synthetic example 1
[0176] Synthesis Example 1: Synthesis of poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA)
[0177] Nitrogen replacement was carried out in the vertical stirring tank (40L) equipped with all-area wings equipped with vacuum piping, nitrogen piping, catalyst addition piping, L-lactide solution addition piping, and ethanol initiator addition piping. After that, load 30Kg of L-lactide, 0.90kg of stearyl alcohol (0.030 mol / kg), 6.14g of stannous octoate (5.05×10-4 mol / 1kg), and raise the temperature to 150°C under a nitrogen pressure of 106.4kPa . Stirring was started when the contents were dissolved, and the internal temperature was further raised to 190°C. Since the reaction started when the internal temperature exceeded 180° C., the reaction was continued for 1 hour while maintaining the internal temperature at 185° C. to 190° C. while cooling. Furthermore, after stirring and reacting for 1 hour at 106.4 kPa of nitrogen pressure and 200 degreeC - 210 degreeC of internal temperature, stirring was stop...
Synthetic example 2
[0180] Synthesis example 2: Synthesis of poly D-lactic acid (PDLA)
[0181] In addition, except that D-lactide was used instead of L-lactide, in the same manner as in Synthesis Example 1, a glass transition temperature (Tg) of 55°C, a melting point (Tm) of 175°C, a weight average molecular weight of 120,000, and a molecular weight of D-lactic acid (PDLA) with a variance of 1.8 and a lactide content of 0.005% by mass.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com